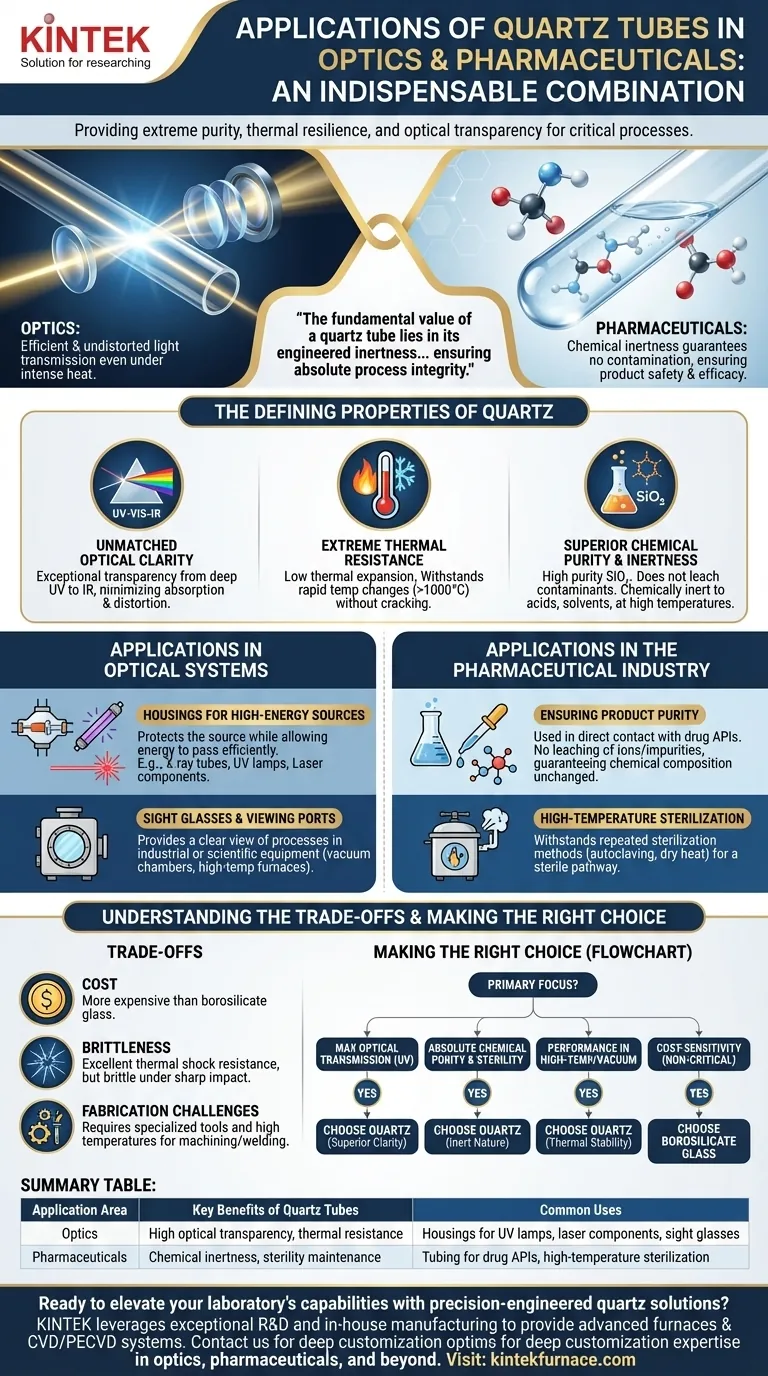
In both optics and pharmaceuticals, quartz tubes are indispensable for one core reason: they provide an unmatched combination of extreme purity, thermal resilience, and optical transparency. In optical systems, this allows for the efficient and undistorted transmission of light, even under intense heat. In pharmaceuticals, its chemical inertness guarantees that the material will not contaminate or react with sensitive drug formulations, ensuring product safety and efficacy.
The fundamental value of a quartz tube lies in its engineered inertness. It is chosen specifically because it does not react chemically, distort optically, or fail under extreme thermal stress, thereby ensuring absolute process integrity in both sterile pharmaceutical environments and precision optical systems.

The Defining Properties of Quartz
To understand its applications, one must first understand the material itself. Quartz is not chosen by accident; its specific physical and chemical properties make it uniquely suited for a range of demanding tasks where lesser materials would fail.
Unmatched Optical Clarity
Quartz, specifically high-purity fused quartz, offers exceptional transparency across a very broad spectrum of light, from deep ultraviolet (UV) to the infrared (IR) range. This is far superior to standard glass.
This clarity ensures that light passes through the material with minimal absorption, distortion, or interference, which is critical for any precision optical instrument.
Extreme Thermal Resistance
Quartz exhibits a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it can withstand rapid and extreme temperature changes—known as thermal shock—without cracking or warping.
It can be heated to over 1000°C and then rapidly cooled without damage, a property essential for high-energy processes.
Superior Chemical Purity and Inertness
Quartz is essentially pure Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂). This high purity means it does not leach contaminants into substances it contacts.
Furthermore, it is chemically inert to a wide range of acids, solvents, and other chemicals, even at high temperatures. The only common substances that will attack it are hydrofluoric acid and hot phosphoric acid.
Applications in Optical Systems
In optics, the goal is to control and transmit light without the container itself affecting the outcome. Quartz's properties make it ideal for this.
Housings for High-Energy Sources
The combination of thermal resistance and optical clarity makes quartz the perfect material for enclosing high-intensity light sources.
Applications include X-ray tubes, UV lamps for sterilization, and high-power laser system components. The quartz tube protects the source while allowing the energy to pass through efficiently.
Sight Glasses and Viewing Ports
In industrial or scientific equipment like vacuum chambers or high-temperature furnaces, a quartz tube or window acts as a "sight glass."
It provides a clear view of the process inside while maintaining the pressure differential and withstanding the extreme temperatures that would destroy normal glass.
Applications in the Pharmaceutical Industry
In pharmaceuticals, the primary concerns are purity, sterility, and preventing any chemical reaction between a container and its contents.
Ensuring Product Purity
The chemical inertness of quartz is its most valued trait in this field. It is used for tubing, vessels, and sampling instruments that come into direct contact with drug APIs (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients).
Because it does not leach ions or other impurities, it guarantees that the chemical composition and efficacy of the drug remain unchanged.
High-Temperature Sterilization
Pharmaceutical equipment must be repeatedly sterilized. Quartz tubes and components can easily withstand high-temperature sterilization methods like autoclaving or dry heat.
This ensures a completely sterile pathway for processing and packaging sensitive medications without the material degrading over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While quartz is a high-performance material, its selection is a deliberate engineering decision that involves clear trade-offs.
Cost
Fused quartz is significantly more expensive to produce than standard borosilicate glass. Its use is therefore reserved for applications where its unique properties are a strict requirement, not a preference.
Brittleness
Like other ceramics and glasses, quartz is brittle. It has excellent thermal shock resistance but can shatter under sharp mechanical impact. Care must be taken during the installation and handling of quartz components.
Fabrication Challenges
Machining, welding, and forming quartz requires specialized tools and extremely high temperatures. This adds complexity and cost to the manufacturing of custom-designed parts compared to working with metals or polymers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the choice to use quartz is driven by a non-negotiable need for performance.
- If your primary focus is maximum optical transmission, especially in the UV spectrum: Quartz is the superior choice over any standard glass due to its exceptional clarity.
- If your primary focus is maintaining absolute chemical purity and sterility: The inert nature of quartz makes it essential for applications involving sensitive pharmaceutical compounds.
- If your primary focus is performance in high-temperature or vacuum environments: The thermal stability and structural integrity of quartz provide reliability where other materials would fail.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitivity for a non-critical application: A material like borosilicate glass may offer a more economical solution if you can accept its lower performance ceiling.
By understanding these principles, you can confidently determine when quartz is not just an option, but a mission-critical requirement.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Benefits of Quartz Tubes | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Optics | High optical transparency, thermal resistance | Housings for UV lamps, laser components, sight glasses |
| Pharmaceuticals | Chemical inertness, sterility maintenance | Tubing for drug APIs, high-temperature sterilization |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's capabilities with precision-engineered quartz solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization expertise ensures we can meet your unique experimental needs in optics, pharmaceuticals, and beyond. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your process integrity and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What technical requirements affect the external thermal strength of furnace tubes? Optimize for High-Temp Performance
- What is the necessity of using vacuum-sealed quartz tubes? Ensuring Integrity in Ti-Cu Alloy Heat Treatment
- What is a Quartz Tube Furnace and what is its primary function? Essential for Real-Time Material Observation
- What are the key features of a quartz tube furnace? Discover High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- What is a quartz tube furnace and what is its primary use? Essential for Controlled High-Temp Processing



















