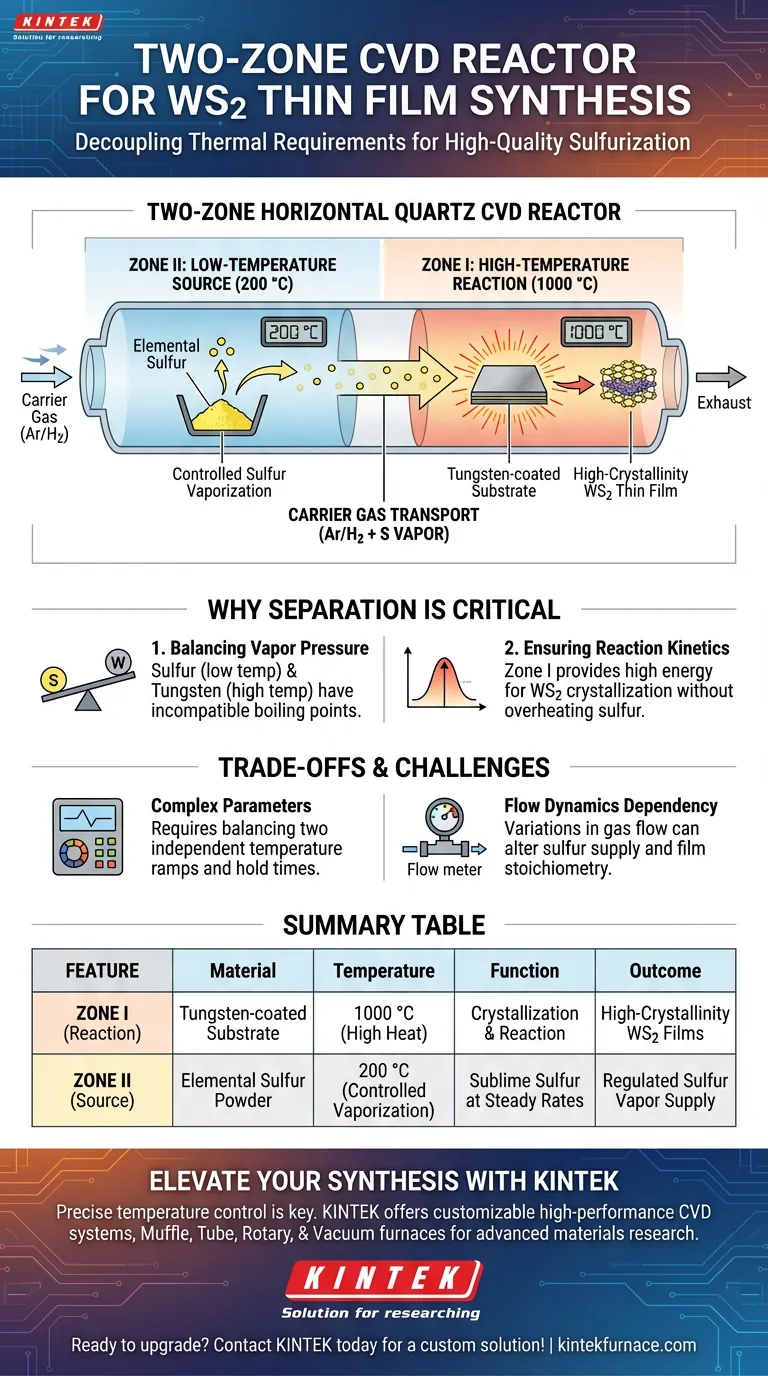
A two-zone horizontal quartz CVD reactor facilitates sulfurization by decoupling the thermal requirements of the precursor and the substrate. This system maintains the sulfur source at a relatively low temperature (200 °C) in Zone II to control vaporization, while simultaneously heating the tungsten-coated substrate to a high temperature (1000 °C) in Zone I. A mixed carrier gas of argon and hydrogen transports the sulfur vapor from the cool zone to the hot zone, allowing the sulfur to react with the metal tungsten layer to form high-crystallinity tungsten disulfide (WS$_2$) thin films.
The core advantage of this reactor design is the independent temperature control of distinct zones, which allows you to maintain a steady supply of sulfur vapor without subjecting the source material to the extreme heat required for the crystallization of the tungsten substrate.
The Mechanics of the Two-Zone System
To understand how this reactor achieves high-quality sulfurization, we must look at how it manages the drastic temperature difference required by the materials involved.
Zone I: The High-Temperature Reaction Environment
Zone I is the designated reaction chamber where the actual film formation occurs.
This zone houses the tungsten-coated substrate and is heated to 1000 °C.
This extreme heat provides the necessary activation energy for the chemical reaction between the tungsten and sulfur, ensuring the resulting WS$_2$ thin films achieve high crystallinity.
Zone II: The Low-Temperature Source
Zone II functions as the evaporation chamber for the precursor material.
It contains the elemental sulfur source and is maintained at a much lower temperature of 200 °C.
This temperature is sufficient to sublime or vaporize the sulfur at a controlled rate, preventing the source from being exhausted too quickly, which would happen if it were exposed to the temperatures in Zone I.
The Carrier Gas Transport Mechanism
The link between these two thermal zones is the flow of gas.
The system utilizes a mixed carrier gas composed of argon and hydrogen.
This gas mixture flows over the heated sulfur in Zone II, picking up the vapor and physically transporting it downstream into the high-temperature Zone I to initiate the reaction.
Why Separation is Critical for WS$_2$
The synthesis of WS$_2$ presents a specific chemical engineering challenge: the melting and boiling points of the reactants are incompatible.
Balancing Vapor Pressure
Sulfur has a high vapor pressure and volatilizes easily at low temperatures.
If sulfur were placed directly into a 1000 °C environment, it would flash-evaporate instantly, resulting in poor coverage and wasted material.
Ensuring Reaction Kinetics
Conversely, the tungsten precursor requires high thermal energy to rearrange its atomic structure into a layered sulfide crystal.
By separating the zones, the reactor allows the substrate to remain at the critical 1000 °C point without degrading the control over the sulfur supply.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the two-zone system offers precision, it introduces variables that must be carefully managed to avoid defects.
Complexity of Process Parameters
You are no longer managing a single thermal profile; you must balance two independent heating ramps and hold times.
If Zone II (Sulfur) heats up too fast relative to Zone I (Substrate), sulfur vapor may arrive before the tungsten is hot enough to react, leading to deposition failures.
Dependency on Flow Dynamics
The system relies entirely on the carrier gas to move reactants.
Variations in the argon/hydrogen flow rate can alter the concentration of sulfur reaching the substrate, potentially affecting the stoichiometry of the final film.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring a two-zone CVD reactor for WS$_2$ synthesis, your temperature settings dictate the quality of your output.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Quality: Prioritize the stability of Zone I at 1000 °C, as insufficient heat here will lead to amorphous or poorly structured films.
- If your primary focus is Film Stoichiometry: Focus on the precise thermal control of Zone II (200 °C) and gas flow, as this dictates the exact amount of sulfur available for the reaction.
Success in this process relies on synchronizing the sulfur vaporization rate with the reaction kinetics of the tungsten substrate.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Zone I (Reaction) | Zone II (Source) |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Tungsten-coated substrate | Elemental sulfur powder |
| Temperature | 1000 °C (High heat) | 200 °C (Controlled vaporization) |
| Function | Facilitates crystallization & reaction | Sublimes sulfur at steady rates |
| Carrier Gas | Ar/H2 mixture | Ar/H2 mixture |
| Outcome | High-crystallinity WS2 thin films | Regulated sulfur vapor supply |
Elevate Your Thin Film Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise temperature control is the cornerstone of high-quality WS2 thin films. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance CVD systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum furnaces, specifically designed for advanced materials research.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique sulfurization or deposition requirements. Whether you are optimizing film stoichiometry or crystal quality, our team is ready to provide the precision tools you need.
Ready to upgrade your lab's capabilities? Contact KINTEK today for a custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Thin Films of Tungsten Disulfide Grown by Sulfurization of Sputtered Metal for Ultra-Low Detection of Nitrogen Dioxide Gas. DOI: 10.3390/nano15080594
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the temperature control requirements for HCVD furnaces? Achieve Precise Multi-Zone Thermal Management
- What are the steps of the CVD process? Master the Key Stages for Superior Thin Films
- What is the significance of the vacuum pressure control system in the CVD coating process for powders?
- What role does a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) system play in the synthesis of NCNTs? Precision Material Engineering
- What are the types of CVD processes? Explore Key Methods for Thin Film Deposition
- What biomedical applications do CVD furnaces have? Enhance Implant Safety and Drug Delivery
- How does precursor solution concentration affect (001) oriented TiO2 thin films? Master Precision PAD Synthesis
- What is chemical vapor deposition in a CVD furnace? Build Materials with Atomic Precision



















