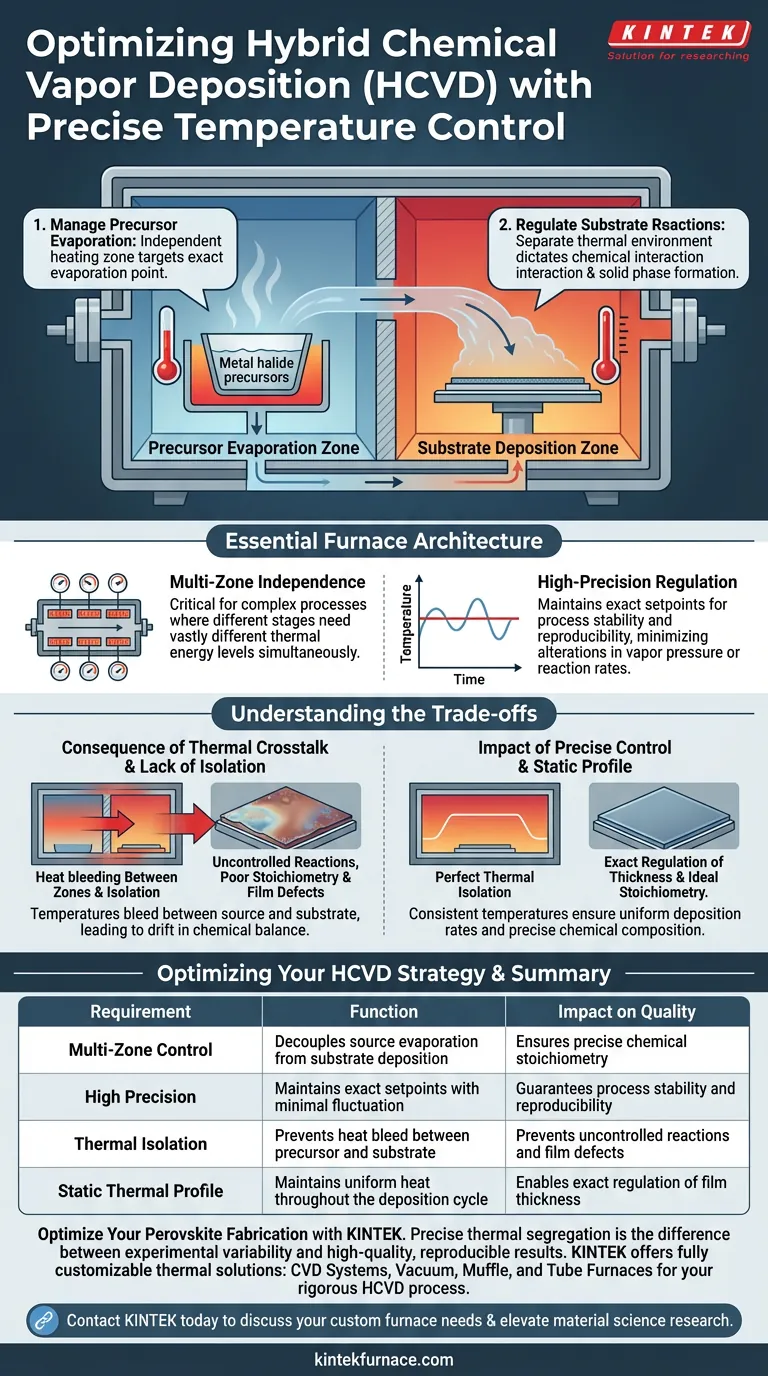
The critical requirement for reaction furnaces in Hybrid Chemical Vapor Deposition (HCVD) is the implementation of multi-zone, independent, and precise temperature control. This thermal architecture allows the system to maintain distinct heating environments within a single process chamber. Specifically, it enables the strict separation of the evaporation temperature required for metal halide precursors from the deposition temperature necessary for the substrate.
Success in HCVD relies on decoupling the thermal management of source materials from the target substrate. By utilizing multi-zone control, you ensure that vapor-phase precursors react only under specific conditions, granting you precise regulation over the film's thickness and chemical composition (stoichiometry).
Essential Furnace Architecture
Multi-Zone Independence
The reaction furnace must not operate as a single thermal block. It requires multiple heating zones that can be controlled individually.
This independence is the fundamental feature that allows the system to support complex chemical processes where different stages require vastly different thermal energy levels simultaneously.
High-Precision Regulation
General heating capabilities are insufficient for HCVD; the process demands precise thermal management.
Fluctuations in temperature can alter vapor pressure or reaction rates. Therefore, the furnace must maintain exact setpoints to ensure the process remains stable and reproducible.
Controlling the Deposition Process
Managing Precursor Evaporation
Metal halide precursors must be heated to a specific point to transition effectively into the vapor phase.
An independent heating zone allows you to target this exact evaporation temperature without influencing the rest of the chamber. This ensures a consistent supply of vapor without thermally degrading the material before it reaches the substrate.
Regulating Substrate Reactions
The substrate requires a separate, controlled thermal environment to facilitate the correct chemical reactions.
By maintaining a distinct deposition temperature, you dictate how the vapor-phase precursors interact upon contact. This control is vital for guiding the formation of the solid phase on the substrate surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Consequence of Thermal Crosstalk
If a furnace lacks sufficient zone isolation, temperatures may bleed between the source and the substrate.
This lack of separation leads to uncontrolled chemical reactions. Consequently, the stoichiometry—the precise chemical balance of the final material—will likely drift outside of target specifications.
Impact on Film Uniformity
Precise control is not just about chemical composition; it is also the primary variable for physical dimensions.
Inconsistent temperatures lead to variable deposition rates. To achieve exact regulation of thickness in perovskite thin films, the thermal profile must remain static throughout the deposition cycle.
Optimizing Your HCVD Strategy
To achieve high-quality perovskite films, align your equipment capabilities with your specific deposition goals.
- If your primary focus is precise film thickness: Ensure your furnace maintains a stable, independent thermal environment for the substrate to strictly control the rate of deposition.
- If your primary focus is ideal stoichiometry: Prioritize the precision of the precursor zone to ensure the evaporation rate matches the chemical requirements of the reaction.
Precise thermal segregation is the defining factor in transitioning from experimental variability to reproducible, high-quality HCVD fabrication.
Summary Table:
| Requirement | Function | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-Zone Control | Decouples source evaporation from substrate deposition | Ensures precise chemical stoichiometry |
| High Precision | Maintains exact setpoints with minimal fluctuation | Guarantees process stability and reproducibility |
| Thermal Isolation | Prevents heat bleed between precursor and substrate | Prevents uncontrolled reactions and film defects |
| Static Thermal Profile | Maintains uniform heat throughout the deposition cycle | Enables exact regulation of film thickness |
Optimize Your Perovskite Fabrication with KINTEK
Precise thermal segregation is the difference between experimental variability and high-quality, reproducible results. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing.
Whether you require specialized CVD systems, Vacuum, Muffle, or Tube furnaces, our equipment is fully customizable to meet the rigorous multi-zone requirements of your Hybrid Chemical Vapor Deposition (HCVD) process.
Ready to elevate your material science research? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs and ensure your lab is equipped for the next generation of thin-film innovation.
Visual Guide
References
- Maoding Cheng, Qinglong Jiang. Progress and Application of Halide Perovskite Materials for Solar Cells and Light Emitting Devices. DOI: 10.3390/nano14050391
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role do high-purity quartz boats play during the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) of MoS2? Optimize Thin-Film Growth
- In which fields is CVD commonly used? Essential Applications in Electronics, Coatings, and More
- How does the ALD process ensure effective passivation on WS2 surfaces? Achieve Superior Dielectric Integrity
- What is the role of a Horizontal Tube LPCVD in solar cells? Unlock High-Efficiency Bifacial Cell Fabrication
- What are the advantages of CVD furnaces in preparing high-quality thin films? Achieve Superior Thin Films with High Purity and Uniformity
- What is the significance of the cold wall CVD technique in graphene research? Unlock Precision Growth for High-Quality Graphene
- Why is a precision mass flow controller essential for GaN thin films? Achieve High-Purity Semiconductor Growth
- How does CVD compare to other thin film deposition methods? Discover the Best Fit for Your Lab



















