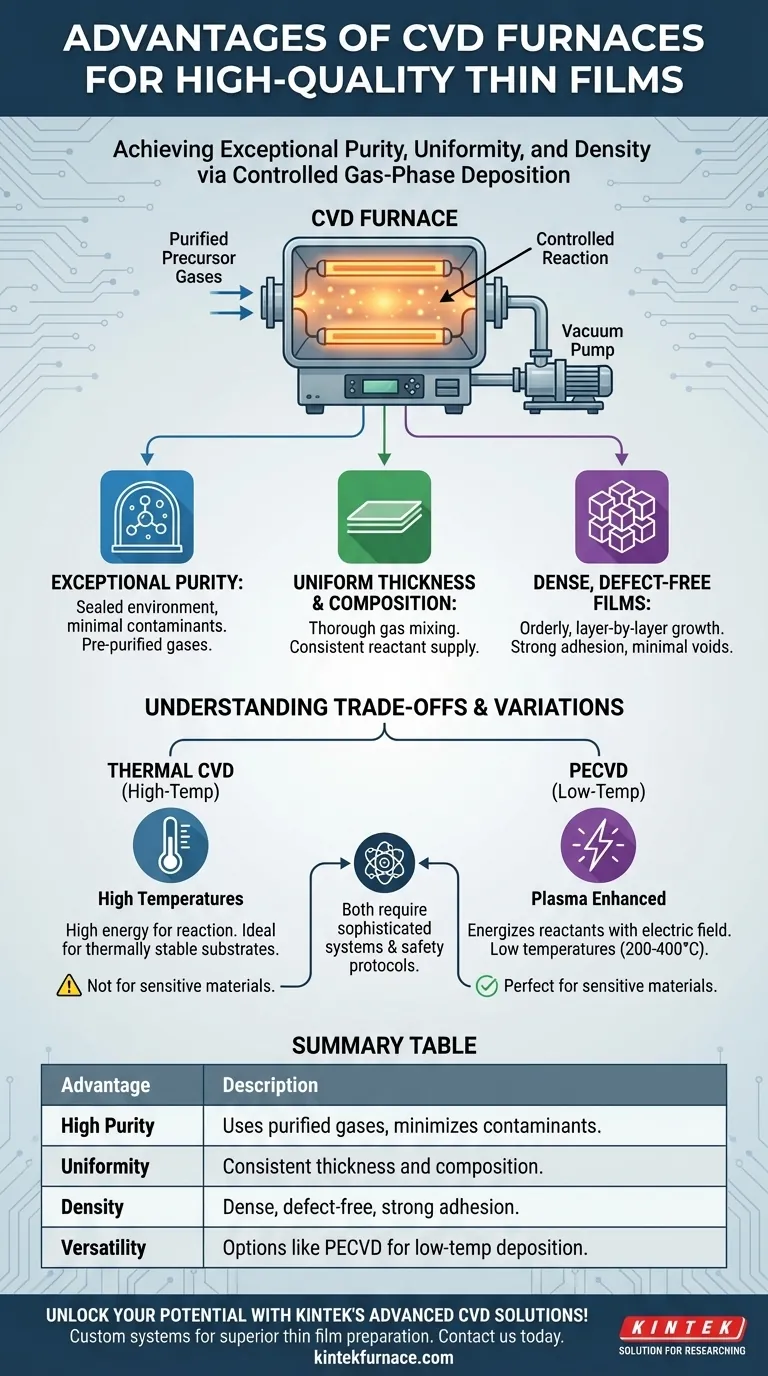
The primary advantage of a CVD furnace is its ability to produce exceptionally high-quality thin films characterized by high purity, uniformity, and density. This is achieved because the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process operates in the gas phase, enabling precise control over reactant mixing and deposition conditions, which minimizes impurities and ensures consistent film structure across a substrate.
The power of a CVD furnace lies not in the heat itself, but in its ability to create a highly controlled gaseous environment. This control over gas purity and reaction conditions is the fundamental reason CVD consistently delivers films with superior material properties for demanding applications like semiconductors.
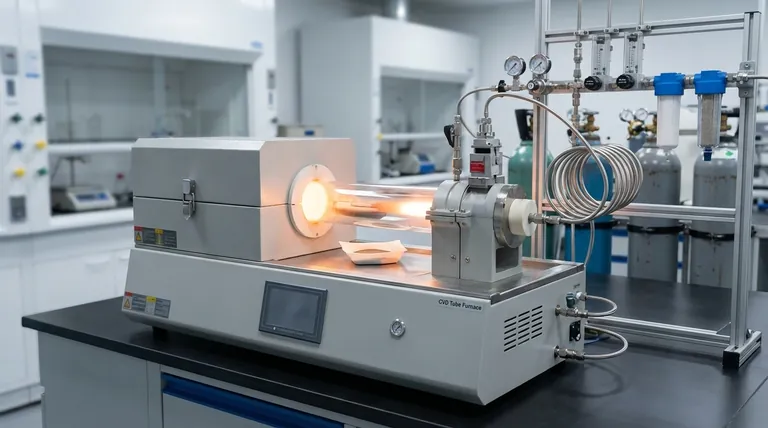

The Foundation of CVD Quality: The Gas-Phase Advantage
The core strength of the CVD process is that the film is built from gaseous precursor molecules. This fundamental principle is what enables its key advantages over other deposition methods.
Achieving Exceptional Purity
The process begins with precursor gases that can be purified to extremely high levels before they ever enter the reaction chamber.
Because the entire reaction occurs in a sealed, controlled gas-phase environment, the risk of introducing solid or liquid contaminants is virtually eliminated. This is a distinct advantage over solution-based techniques.
Ensuring Uniform Thickness and Composition
Within the furnace, the gaseous reactants mix thoroughly, ensuring a consistent concentration of precursor molecules is available across the entire surface of the substrate.
This uniform supply of reactants directly translates into a film with highly consistent thickness and chemical composition, which is critical for fabricating reliable electronic devices.
Creating Dense, Defect-Free Films
The controlled chemical reaction allows atoms to deposit onto the substrate in an orderly, layer-by-layer fashion.
This methodical growth process results in a dense film structure with strong adhesion and minimal voids or pinholes, leading to superior mechanical and electrical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
While powerful, the CVD process is not a single, one-size-fits-all solution. Understanding its limitations and variations is crucial for proper application.
The High-Temperature Requirement
Traditional thermal CVD relies on high temperatures to supply the activation energy needed to break down the precursor gases and initiate the chemical reaction on the substrate.
This high-temperature requirement can make it unsuitable for depositing films on temperature-sensitive materials, such as polymers or semiconductor wafers that already contain delicate, pre-fabricated structures.
The Low-Temperature Solution: PECVD
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is a critical variation that overcomes the temperature limitation. It uses an electric field to generate a plasma within the furnace.
This plasma energizes the reactant gases, providing the necessary energy for deposition without requiring extreme heat. PECVD can produce high-quality films at much lower temperatures, typically between 200°C and 400°C.
Complexity and Precursor Safety
CVD systems involve sophisticated vacuum chambers, high-purity gas delivery systems, and exhaust management. This can increase the complexity and cost compared to some simpler deposition methods.
Furthermore, many precursor gases used in CVD are toxic, flammable, or corrosive, requiring strict safety protocols and handling procedures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice between different CVD methods depends entirely on the specific requirements of your substrate and the desired properties of the final film.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and crystallinity on a thermally stable substrate: Conventional thermal CVD is often the ideal choice due to its high-temperature process.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-quality films on temperature-sensitive materials: Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is the superior option, as it achieves deposition at significantly lower temperatures.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay between temperature, plasma, and gas control empowers you to select the precise deposition technique for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High Purity | Uses purified gases in a sealed environment to minimize contaminants. |
| Uniformity | Ensures consistent thickness and composition across the substrate. |
| Density | Creates dense, defect-free films with strong adhesion and minimal voids. |
| Versatility | Includes options like PECVD for low-temperature deposition on sensitive materials. |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced CVD furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnace options like CVD/PECVD Systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for superior thin film preparation. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your research and production efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations
- Why are CVD tube furnace sintering systems indispensable for 2D material research and production? Unlock Atomic-Scale Precision
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis



















