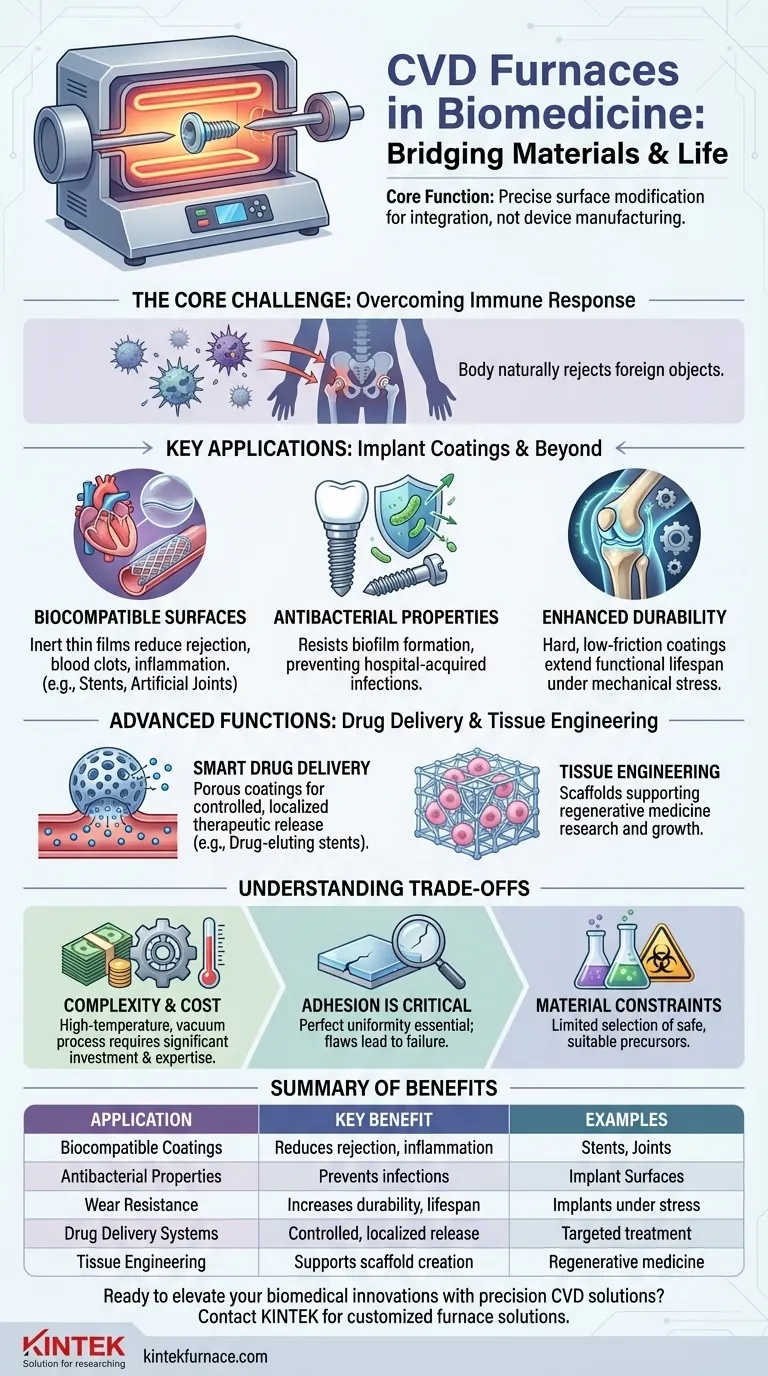
In the biomedical field, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) furnaces are primarily used to create highly specialized, functional coatings on medical implants and to develop advanced biomaterials. These applications include creating biocompatible surfaces for devices like vascular stents and artificial joints, imparting antibacterial properties to prevent infection, and engineering novel systems for targeted drug delivery.
The core function of a CVD furnace in biomedicine is not to manufacture the medical device itself, but to precisely modify its surface at a molecular level. This transforms a potentially reactive foreign object into one that the human body can safely accept and interact with.

The Core Challenge: Integrating Devices with the Body
The human body is an incredibly complex environment, finely tuned to identify and attack foreign materials. This immune response is a primary obstacle to the long-term success of any implanted medical device.
Creating Biocompatible Surfaces
The most critical application of CVD is to deposit a biocompatible thin film onto the surface of an implant. This inert layer acts as a barrier between the device and the body.
This coating dramatically reduces the risk of post-implantation complications, such as inflammation, blood clots, and tissue rejection.
Common examples include coatings for heart valves, vascular stents, dental implants, and artificial joints, enhancing their safety and longevity.
Imparting Antibacterial Properties
Hospital-acquired infections are a major risk for any surgical implant. CVD furnaces can be used to apply coatings that actively resist or kill bacteria.
By modifying the surface of an implant with specific materials, these furnaces help prevent the formation of dangerous bacterial biofilms, a leading cause of implant failure.
Enhancing Durability and Wear Resistance
Many medical implants, particularly artificial joints, are subject to significant mechanical stress and wear over time.
CVD is an established industrial process for creating exceptionally hard and low-friction coatings. This same technology can be applied to medical implants to increase their durability and extend their functional lifespan.
Beyond Implants: Advanced Biomedical Functions
While coating implants is the primary use, the precise control offered by CVD furnaces enables other cutting-edge biomedical applications.
Developing Advanced Drug Delivery Systems
CVD can be used to construct microscopic structures or porous coatings designed to hold and release a therapeutic agent over time.
This allows for highly localized and controlled drug delivery. For example, a drug-eluting stent can be coated to slowly release medication that prevents the artery from re-narrowing.
Supporting Tissue Engineering Research
The field of tissue engineering aims to grow replacement tissues and organs. This often requires a "scaffold" material that cells can grow on.
CVD furnaces provide the controlled heat treatment and material deposition necessary to create and modify these complex biomaterial scaffolds, supporting research in regenerative medicine.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the CVD process is not a universal solution and comes with inherent complexities.
Process Complexity and Cost
CVD is a sophisticated, high-temperature vacuum process that requires significant capital investment and technical expertise to operate. It is not a simple or inexpensive coating method.
Adhesion and Uniformity are Critical
The success of a medical coating depends entirely on its perfect adhesion and uniformity. Any flaw, crack, or delamination in the coating can expose the underlying material, negating its benefit and potentially creating a site for failure.
Material and Precursor Constraints
The process relies on volatile precursor chemicals that can be expensive, hazardous, and difficult to handle. The selection of materials that are both suitable for the CVD process and safe for the human body is limited.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective determines which CVD application is most relevant.
- If your primary focus is implant safety and longevity: The key is to leverage CVD for biocompatible, antibacterial, and wear-resistant coatings.
- If your primary focus is developing novel therapeutics: Explore the use of CVD to create porous films and structures for controlled drug delivery systems.
- If your primary focus is advancing regenerative medicine: Use the furnace's precise control for the heat treatment and surface modification of biomaterial scaffolds.
Ultimately, the CVD furnace serves as a critical tool for bridging the gap between synthetic materials and living biological systems.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Biocompatible Coatings | Reduces inflammation, blood clots, and tissue rejection for implants like stents and joints |
| Antibacterial Properties | Prevents infections by resisting or killing bacteria on implant surfaces |
| Wear Resistance | Increases durability and lifespan of implants under mechanical stress |
| Drug Delivery Systems | Enables controlled, localized release of therapeutics for targeted treatment |
| Tissue Engineering | Supports creation of biomaterial scaffolds for regenerative medicine research |
Ready to elevate your biomedical innovations with precision CVD solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're developing safer implants, advanced drug delivery systems, or regenerative scaffolds, we can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored CVD furnaces can drive your biomedical projects forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
People Also Ask
- What future trends are expected in the development of CVD tube furnaces? Discover Smarter, More Versatile Systems
- What is the process for synthesizing transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) using CVD tube furnaces? Master High-Quality Thin Film Growth
- What are the operational benefits of using a CVD Tube Furnace? Enhance Precision and Efficiency in Your Lab
- What are the practical applications of gate media prepared by CVD tube furnaces? Unlock Advanced Electronics and More
- What are 2D heterostructures and how are they created using CVD tube furnaces? Unlock Atomic-Scale Material Engineering



















