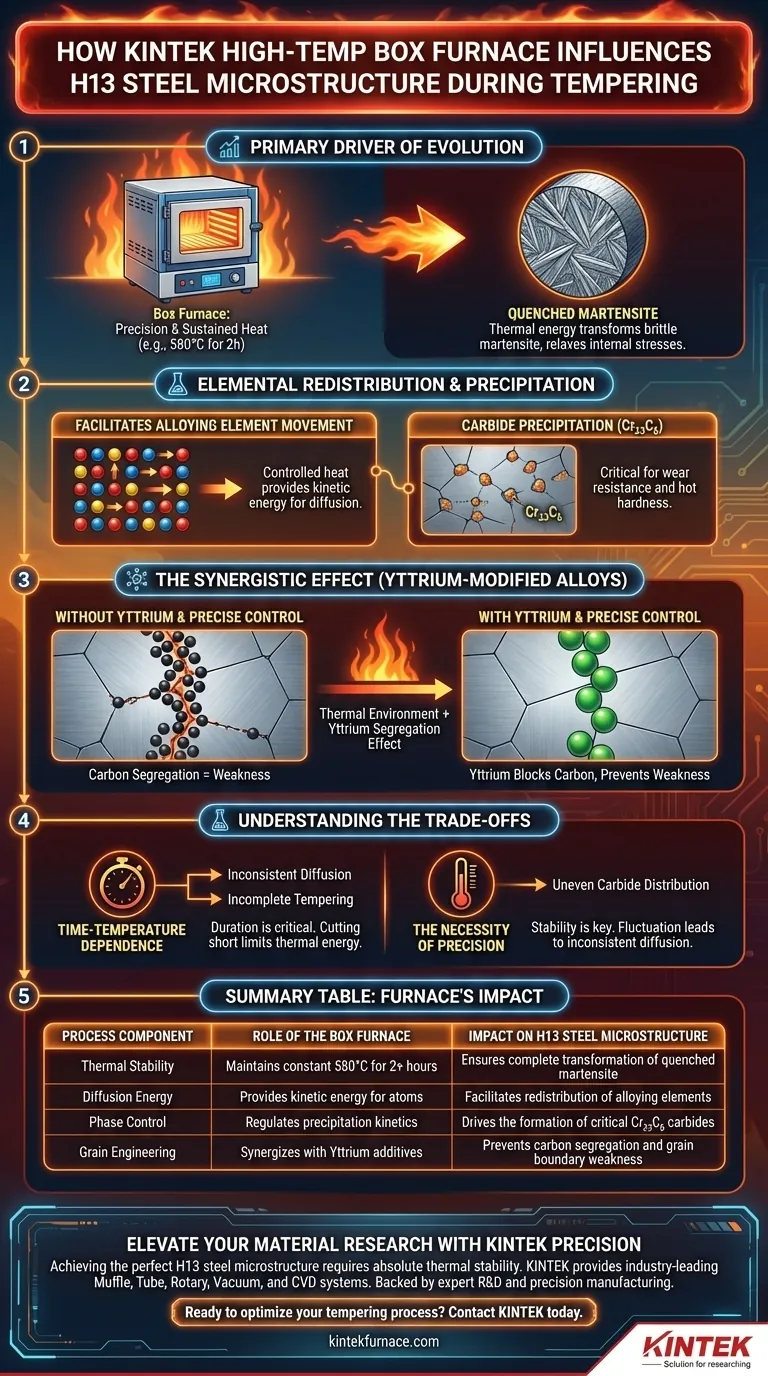
A laboratory high-temperature box furnace acts as the primary driver of microstructural evolution in H13 steel by providing the precise, sustained thermal environment required to transform brittle quenched martensite. By maintaining a constant temperature, such as 580°C for two hours, the furnace supplies the specific thermal energy necessary to redistribute alloying elements and precipitate essential carbides like $Cr_{23}C_{6}$.
The furnace serves as a critical control vessel for diffusion, allowing thermal energy to facilitate the redistribution of elements while working synergistically with additives like Yttrium to prevent microstructural defects at the grain boundaries.

Driving Microstructural Transformation
The Role of Sustained Thermal Energy
The primary function of the box furnace is to provide a precise and sustained constant temperature environment.
For H13 steel, a typical regimen involves holding the material at approximately 580°C for two hours. This duration and stability are essential to fully activate the tempering transformation process.
Transforming Quenched Martensite
The initial microstructure of the steel, quenched martensite, is hard but brittle.
The thermal energy provided by the furnace drives the phase transformation of this martensite. This process relaxes internal stresses and prepares the matrix for the precipitation of secondary phases.
Elemental Redistribution and Precipitation
Facilitating Alloying Element Movement
The heat generated by the box furnace facilitates the redistribution of alloying elements within the steel matrix.
Without this controlled thermal input, the atoms would lack the kinetic energy required to diffuse to their optimal positions. This diffusion is the mechanism that alters the mechanical properties of the steel.
Carbide Precipitation
A specific outcome of this thermal treatment is the precipitation of carbides, specifically $Cr_{23}C_{6}$.
These carbides form as a result of the element redistribution enabled by the furnace. Their presence is critical for establishing the wear resistance and hot hardness characteristic of H13 steel.
The Synergistic Effect in Modified Alloys
Controlling Grain Boundary Segregation
In Yttrium-modified H13 steel, the furnace's environment plays a distinct role in grain boundary engineering.
The thermal environment works in tandem with the segregation effect of Yttrium. This combination is responsible for inhibiting the excessive segregation of carbon atoms at the grain boundaries.
Preventing Microstructural Weakness
Uncontrolled carbon segregation can lead to brittleness at the grain boundaries.
By maintaining a controlled thermal environment, the furnace ensures that Yttrium can effectively block this carbon pile-up. This results in a more uniform and robust microstructure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of Precision
The benefits of Yttrium modification and carbide precipitation rely heavily on the stability of the furnace.
If the furnace cannot maintain a precise constant temperature (e.g., fluctuating significantly from 580°C), the diffusion of elements will be inconsistent. This can lead to incomplete tempering or uneven carbide distribution.
Time-Temperature Dependence
The process is strictly bound by time; the cited two-hour duration is not arbitrary.
Cutting the furnace time short limits the thermal energy available for element redistribution. Conversely, excessive time could potentially alter the precipitation kinetics, though the primary risk here is insufficient diffusion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the performance of H13 steel, you must align your thermal processing with your material composition.
- If your primary focus is Standard Tempering: Ensure your furnace can hold 580°C without fluctuation to drive the complete transformation of quenched martensite.
- If your primary focus is Modified Alloy Performance (Yttrium): distinct attention must be paid to the sustained duration of heating to allow Yttrium to segregate effectively and inhibit carbon buildup.
The laboratory box furnace is not merely a heater, but a precision instrument that dictates the final arrangement of atoms in your steel.
Summary Table:
| Process Component | Role of the Box Furnace | Impact on H13 Steel Microstructure |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Maintains constant 580°C for 2+ hours | Ensures complete transformation of quenched martensite |
| Diffusion Energy | Provides kinetic energy for atoms | Facilitates redistribution of alloying elements |
| Phase Control | Regulates precipitation kinetics | Drives the formation of critical $Cr_{23}C_{6}$ carbides |
| Grain Engineering | Synergizes with Yttrium additives | Prevents carbon segregation and grain boundary weakness |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect H13 steel microstructure requires more than just heat—it requires absolute thermal stability. KINTEK provides industry-leading, customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the rigorous demands of laboratory heat treatment.
Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, our high-temperature furnaces empower researchers to control diffusion and precipitation with unmatched accuracy.
Ready to optimize your tempering process? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique needs and find the ideal high-temp solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Y. Q. Wang, Bin Yang. Improved Corrosion Resistance of Yttrium-Bearing H13 Steel for Shield Machine Cutter Ring. DOI: 10.3390/met15090935
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What temperature information is displayed simultaneously on the controls? Monitor Real-Time and Target Temperatures for Precision
- What is the role of a laboratory high-temperature furnace in LLZO crystal phase regulation? Optimize Li-Ion Electrolytes
- What process conditions does a high-temperature muffle furnace provide for biomass briquette ash analysis?
- Why is precise temperature control in a muffle furnace critical during the conversion of FeOOH to Fe2O3?
- What role does a muffle furnace play in analyzing the combustion residues? Optimize Your Composite Char Analysis
- What is the function of a vacuum box resistance furnace in the preparation of Pine Nut Shell Biochar (PBC)?
- What design features enhance the versatility of box furnaces? Boost Your Lab's Thermal Processing Flexibility
- How is the temperature controlled in a muffle furnace? Master Precise Heating for Your Lab



















