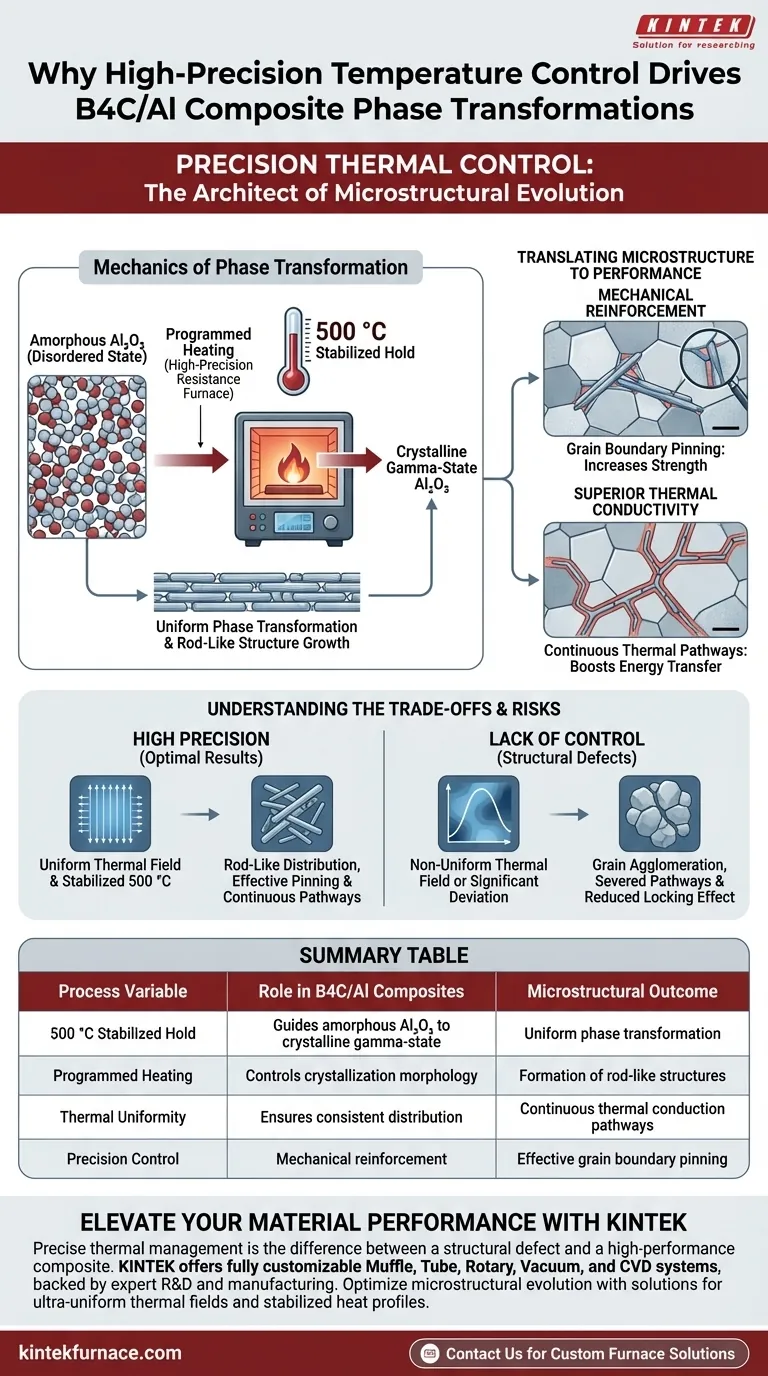
Precise temperature control serves as the critical architect of microstructural evolution. In the context of B4C/Al composites, a high-precision resistance furnace is essential because it utilizes programmed heating to accurately guide nano-alumina ($Al_2O_3$) from an amorphous state into a crystalline gamma-state. This transformation, specifically stabilized at a 500 °C hold, dictates the physical arrangement of the material's internal structure.
Core Insight: The uniform thermal field of a high-precision resistance furnace enables the growth of elongated, rod-like alumina structures along grain boundaries. This specific morphology provides a dual advantage: it mechanically pins grain boundaries to increase strength and simultaneously establishes continuous pathways for superior thermal conductivity.
The Mechanics of Phase Transformation
Guiding the Alumina Transition
The primary function of the furnace's control system is to manage the phase change of nano-alumina ($Al_2O_3$). Initially present in an amorphous (disordered) state, the material requires a specific thermal profile to reorganize into a structured gamma-state.
The Role of Stabilized Heat
This transformation relies on a stabilized heat treatment, specifically at 500 °C. The high-precision resistance furnace maintains this temperature without significant fluctuation, ensuring the phase change occurs uniformly throughout the composite volume.
Creating Rod-Like Structures
Under these controlled conditions, the $Al_2O_3$ does not merely crystallize randomly. It distributes along the grain boundaries, forming distinct elongated or short rod-like structures.
Translating Microstructure to Performance
Grain Boundary Pinning
The formation of these rod-like structures is not cosmetic; it serves a mechanical purpose. These structures act as "pins" along the grain boundaries, restricting grain movement under stress.
Enhancing Mechanical Strength
By pinning the boundaries, the composite resists deformation more effectively. This microstructural reinforcement is the direct driver of the material's high-temperature strength.
Building Thermal Pathways
Simultaneously, these aligned structures function as bridges for energy transfer. They construct connected thermal conduction pathways within the matrix, significantly boosting the thermal conductivity of the final B4C/Al composite.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Consequence of Thermal Instability
While high precision yields optimal results, a lack of control leads to structural defects. If the thermal field is non-uniform, the alumina may fail to distribute evenly, creating weak points rather than a reinforced network.
Risks of Improper Temperature Settings
If temperatures deviate significantly from the programmed setpoint (e.g., exceeding the 500 °C target or fluctuating wildly), you risk grain agglomeration rather than the desired rod-like distribution. This can sever the thermal pathways and reduce the mechanical locking effect, rendering the heat treatment ineffective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the performance of B4C/Al composites, you must align your thermal processing strategy with your specific material objectives:
- If your primary focus is High-Temperature Strength: Ensure your furnace program emphasizes the stability of the 500 °C hold to maximize grain boundary pinning.
- If your primary focus is Thermal Conductivity: Prioritize the uniformity of the thermal field to guarantee continuous, unbroken conduction pathways throughout the matrix.
Ultimately, the precision of your thermal control is the single greatest determinant in converting raw potential into a high-performance composite.
Summary Table:
| Process Variable | Role in B4C/Al Composites | Microstructural Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 500 °C Stabilized Hold | Guides amorphous Al2O3 to crystalline gamma-state | Uniform phase transformation |
| Programmed Heating | Controls crystallization morphology | Formation of rod-like structures |
| Thermal Uniformity | Ensures consistent distribution | Continuous thermal conduction pathways |
| Precision Control | Mechanical reinforcement | Effective grain boundary pinning |
Elevate Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Precise thermal management is the difference between a structural defect and a high-performance composite. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-precision heating solutions required for complex phase transformations.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as other lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique B4C/Al composite research or production needs. Whether you require a ultra-uniform thermal field for thermal conductivity or stabilized heat profiles for grain boundary pinning, our systems deliver the accuracy your materials demand.
Ready to optimize your microstructural evolution? Contact us today to find your custom furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Chunfa Huang, Qiulin Li. Synergistic Optimization of High-Temperature Mechanical Properties and Thermal Conductivity in B4C/Al Composites Through Nano-Al2O3 Phase Transformation and Process Engineering. DOI: 10.3390/met15080874
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does an atmosphere box furnace contribute to the synthesis and preparation of new energy materials? Unlock Precision for Advanced Energy Solutions
- What is the function of a vertical gas mixing furnace during the annealing of orthopyroxene? Achieve Precise Stability
- What process environment does a tube atmosphere furnace provide for LMFP? Master Secondary Crystallization
- Why is a nitrogen environment necessary for Cu13Se52Bi35 thin film annealing? Protect Your Material Purity
- What are the technical advantages of using high-purity hydrogen for Cu-Al2O3 sintering? Enhance Bonding & Conductivity
- How do atmosphere furnaces contribute to electronic material manufacturing? Unlock Precision in Semiconductor and Component Production
- What energy-saving and environmental benefits do box type atmosphere furnaces provide? Boost Efficiency and Cut Waste
- What is the role of an atmosphere sintering furnace in the MLM process? Master CNT/Cu Composite Preparation



















