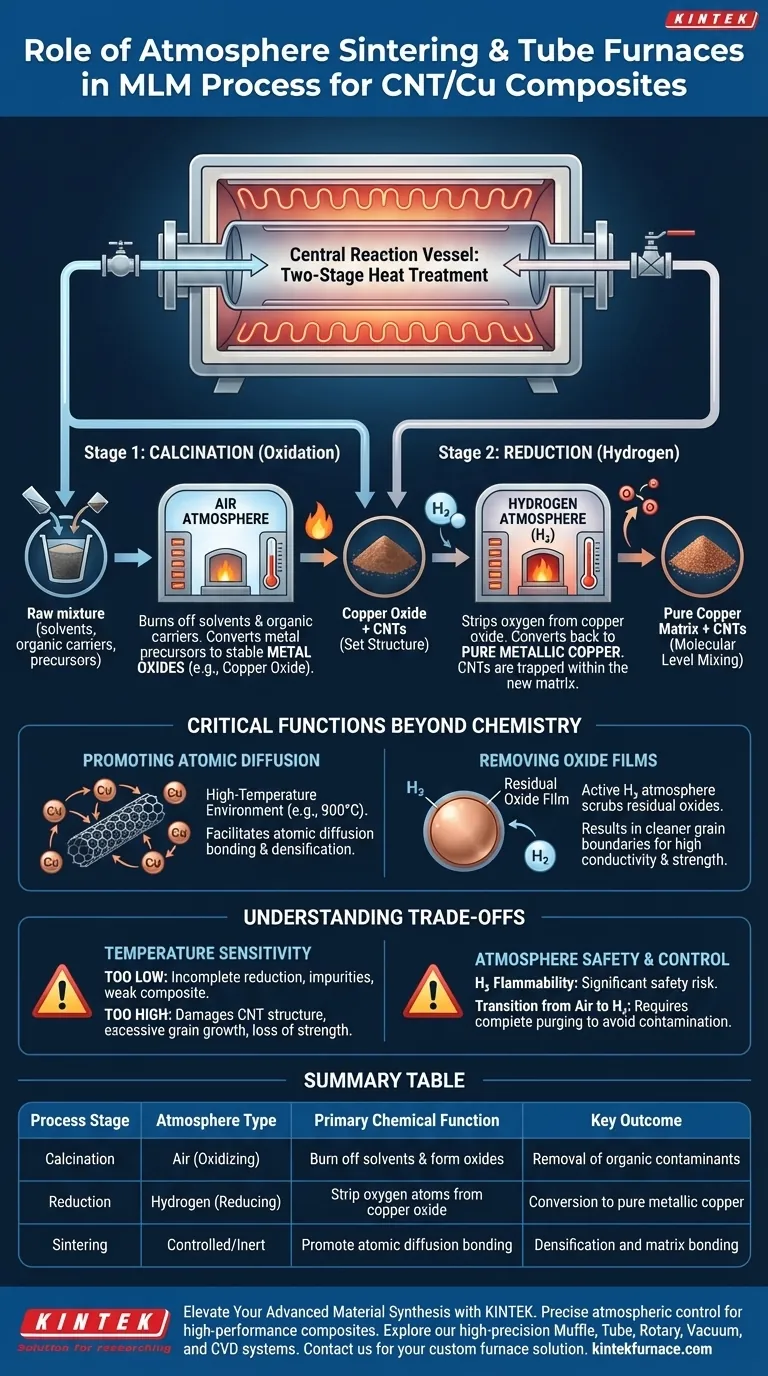
The atmosphere sintering or tube furnace acts as the central reaction vessel that drives the chemical conversion of raw precursors into usable composite materials. In the Molecular Level Mixing (MLM) process for Carbon Nanotube/Copper (CNT/Cu) composites, its specific role is to execute a two-stage heat treatment: first calcining the mixture in air to remove solvents and form oxides, and subsequently reducing those oxides in a hydrogen atmosphere to yield pure metallic copper reinforced with CNTs.
Core Takeaway The furnace is not merely a heating element; it is an atmospheric control system that dictates the chemical purity of the final powder. Its primary function is to eliminate organic contaminants and reduce copper oxides back to their metallic state, enabling atomic diffusion bonding between the copper matrix and the carbon nanotubes.

The Two-Stage Chemical Transformation
The MLM process relies on the furnace to manipulate the chemical state of the powder through precise atmospheric changes.
Stage 1: Calcination via Oxidation
Initially, the furnace operates in an air atmosphere. This stage is critical for burning off residual solvents and organic carriers used during the mixing phase.
During this process, the metal precursors are converted into stable metal oxides (specifically copper oxide in this context). This ensures that the physical structure of the precursor is set before the final reduction.
Stage 2: Reduction via Hydrogen
Once calcination is complete, the furnace atmosphere is switched to a reducing environment, typically using hydrogen gas.
This step strips the oxygen atoms from the copper oxide, converting it back into pure metallic copper. Because the CNTs are already mixed at a molecular level, this reduction traps the CNTs within the newly formed copper matrix.
Critical Functions Beyond Chemistry
Beyond simple chemical conversion, the furnace creates the physical conditions necessary for material performance.
Promoting Atomic Diffusion
The tube furnace provides a controlled high-temperature environment (often around 900 °C for sintering applications).
At these temperatures, the furnace facilitates atomic diffusion bonding. This allows the copper particles to bond with one another and interact mechanically with the CNTs, leading to densification.
Removing Oxide Films
Even after the initial reduction, trace oxide films can remain on particle surfaces.
Operating under a hydrogen atmosphere actively scrubs these residual oxide films. This results in cleaner grain boundaries, which is essential for high electrical conductivity and mechanical strength in the final composite.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the tube furnace is essential, improper management of the process parameters can lead to critical defects.
Temperature Sensitivity
Precise temperature control is mandatory. If the temperature is too low, the reduction of copper oxide will be incomplete, leaving impurities that weaken the composite.
Conversely, if the temperature is too high, you risk damaging the structural integrity of the carbon nanotubes or causing excessive grain growth in the copper, which negates the strengthening benefits of the MLM process.
Atmosphere Safety and Control
The use of hydrogen for reduction introduces significant safety considerations regarding flammability.
Furthermore, the transition from air (calcination) to hydrogen (reduction) must be managed carefully. Incomplete purging of the chamber between stages can lead to inconsistent reduction or contamination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your CNT/Cu composite powders, align your furnace operations with your specific material requirements.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Prioritize the hydrogen reduction phase. Ensure sufficient time and gas flow to completely reduce copper oxides and remove all residual oxygen.
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Strength: Focus on the sintering temperature profile. You need a temperature high enough to promote diffusion bonding and densification, but low enough to preserve the CNT structure.
Ultimately, the success of the Molecular Level Mixing process depends on using the furnace to strictly control the chemical interface between the copper matrix and the carbon nanotubes.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Atmosphere Type | Primary Chemical Function | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Air (Oxidizing) | Burn off solvents & form oxides | Removal of organic contaminants |
| Reduction | Hydrogen (Reducing) | Strip oxygen atoms from copper oxide | Conversion to pure metallic copper |
| Sintering | Controlled/Inert | Promote atomic diffusion bonding | Densification and matrix bonding |
Elevate Your Advanced Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise atmospheric control is the difference between a contaminated sample and a high-performance composite. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-precision Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of Molecular Level Mixing (MLM).
Whether you are refining CNT/Cu composites or developing next-generation alloys, our customizable lab high-temp furnaces provide the thermal stability and gas safety protocols your research requires. Contact us today to find the perfect furnace solution for your unique needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does atmosphere control affect defect formation in graphitic carbon nitride? Master Atmosphere Engineering
- What are the main types of nitrogen-based furnace atmospheres? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- What are the thermal insulation properties of argon in furnace applications? Unlock Material Purity and Efficiency
- Why is a high-temperature atmosphere tube furnace required for the synthesis of Sr2TiO4-NF through ammonolysis?
- Why use a resistance heating furnace for Hf chlorination? Ensure Stable HfO2 Coating Growth & Precursor Flow
- What factors determine the specific parameters of a box-type atmosphere furnace? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- In what settings are controlled atmosphere furnaces commonly used? Essential for High-Purity Material Processing
- What is the role of a reducing atmosphere in foundry operations? Prevent Oxidation and Control Metal Quality



















