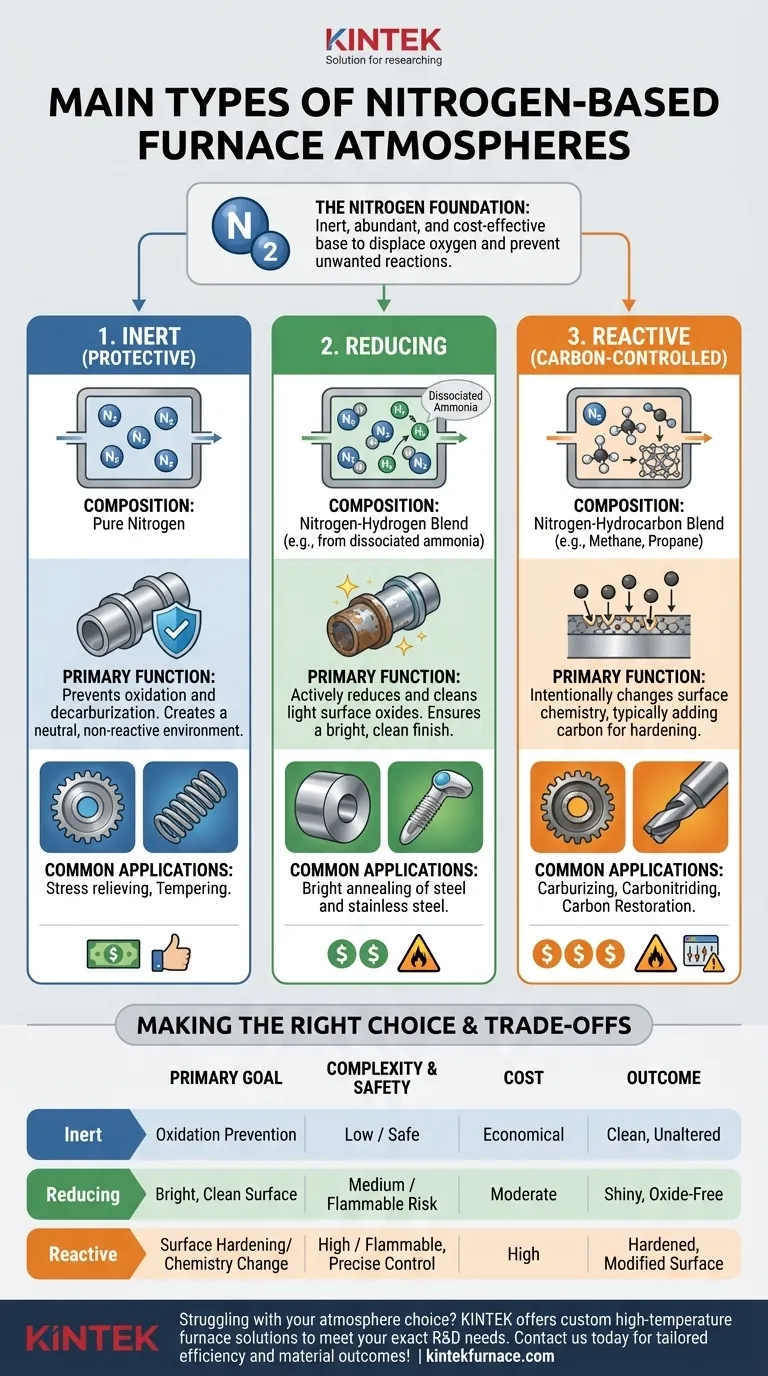
At their core, the main types of nitrogen-based furnace atmospheres are categorized by what is mixed with the nitrogen to achieve a specific outcome. These fall into three primary groups: pure nitrogen for inert protection, nitrogen-hydrogen blends for creating a reducing atmosphere, and nitrogen-hydrocarbon blends for actively changing the material's surface chemistry.
The choice of a nitrogen-based atmosphere is a decision between passive protection and active treatment. While pure nitrogen simply prevents unwanted reactions, adding gases like hydrogen or hydrocarbons allows you to actively clean a material's surface or fundamentally alter its properties.

Why Nitrogen is the Foundation
The Role of an Inert Base Gas
Furnace atmospheres are used to control the environment during heat treatment, primarily to prevent unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation (rusting) and decarburization (carbon loss from steel).
Nitrogen (N₂) is the most common foundation for these atmospheres because it is relatively inert. It effectively displaces oxygen, which is the primary cause of oxidation at high temperatures.
Cost and Availability
Nitrogen is also used because it is abundant, making up roughly 78% of the air we breathe. This makes it a highly cost-effective and readily available choice for industrial processes compared to more expensive inert gases like argon.
The Functional Categories of Nitrogen Atmospheres
While nitrogen provides the protective base, it's the gas mixed with it that defines the atmosphere's function.
1. Inert (Protective) Atmospheres
This is the simplest form, consisting palavras-chave of high-purity nitrogen. Its sole purpose is to create a non-reactive environment.
By displacing oxygen, it prevents surface scaling and other oxidative reactions. It is a neutral atmosphere, meaning it does not react with the metal's surface.
2. Reducing Atmospheres (Nitrogen-Hydrogen)
These atmospheres are a mixture of nitrogen and hydrogen (H₂) gas. The addition of hydrogen transforms the atmosphere from merely protective to actively reducing.
A reducing atmosphere can chemically "reduce" or clean light surface oxides that may already be present on the parts. This is critical for processes લોકો needing a bright, clean finish, such as bright annealing of steel and stainless steel.
A common source for this mixture is dissociated ammonia. When ammonia (NH₃) is heated, it breaks down (dissociates) into a pre-mixed atmosphere of 75% hydrogen and 25% nitrogen.
3. Reactive (Carbon-Controlled) Atmospheres
These are the most complex nitrogen-based atmospheres. They involve adding a reactive gas, typically a hydrocarbon like methane (CH₄) or propane, to the nitrogen base.
The goal is to intentionally change the surface chemistry of the material. This is used for processes like:
- Carburizing: Adding carbon to the surface of low-carbon steel to harden it.
- Carbonitriding: Adding both carbon and nitrogen.
- Carbon Restoration: Restoring carbon to a surface that was previously decarburized.
Control of these atmospheres is critical, as sitzt in an incorrect mixture can lead to sooting or improper carbon levels in the part.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an atmosphere requires balancing process goals with cost and safety considerations.
Safety and Complexity
Pure nitrogen is safe and simple to manage. However, the addition of other gases introduces risks.
Hydrogen is highly flammable and poses an explosion risk if not handled with strict safety protocols. Hydrocarbon gases are also flammable and require precise control systems to prevent sooting and ensure the correct chemical reactions occur.
Cost vs. Desired Finish
A pure nitrogen atmosphere is the most economical option. It is sufficient for many general-purpose heat treatments like stress relieving or tempering where a bright finish is not the primary goal.
Achieving a bright, oxide-free surface with a nitrogen-hydrogen blend costs more due to the price of hydrogen and the required safety infrastructure.
Process Control
Reactive atmospheres for carburizing are the most complex and require sophisticated atmosphere control systems. These systems continuously monitor gas composition to maintain the desired carbon potential, ensuring consistent and repeatable results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection depends entirely on the desired outcome for your material.
- If your primary focus is simple oxidation prevention: Use a pure nitrogen atmosphere for its safety and low cost.
- If your primary focus is achieving a bright, clean, oxide-free surface: Use a nitrogen-hydrogen blend, which actively reduces surface oxides.
- If your primary focus is increasing surface hardness or altering surface chemistry: You must use a reactive, carbon-controlled atmosphere with a hydrocarbon gas.
Ultimately, understanding your material's end-use requirements is the key to selecting the correct and most cost-effective furnace atmosphere.
Summary Table:
| Type | Composition | Primary Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert (Protective) | Pure Nitrogen | Prevents oxidation and decarburization | Stress relieving, tempering |
| Reducing | Nitrogen-Hydrogen Blend | Cleans surface oxides for bright finish | Bright annealing of steel and stainless steel |
| Reactive (Carbon-Controlled) | Nitrogen-Hydrocarbon Blend | Alters surface chemistry for hardening | Carburizing, carbonitriding, carbon restoration |
Struggling to select the right furnace atmosphere for your lab's heat treatment needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, helping you achieve optimal results with the perfect nitrogen-based atmosphere. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your process efficiency and material outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance



















