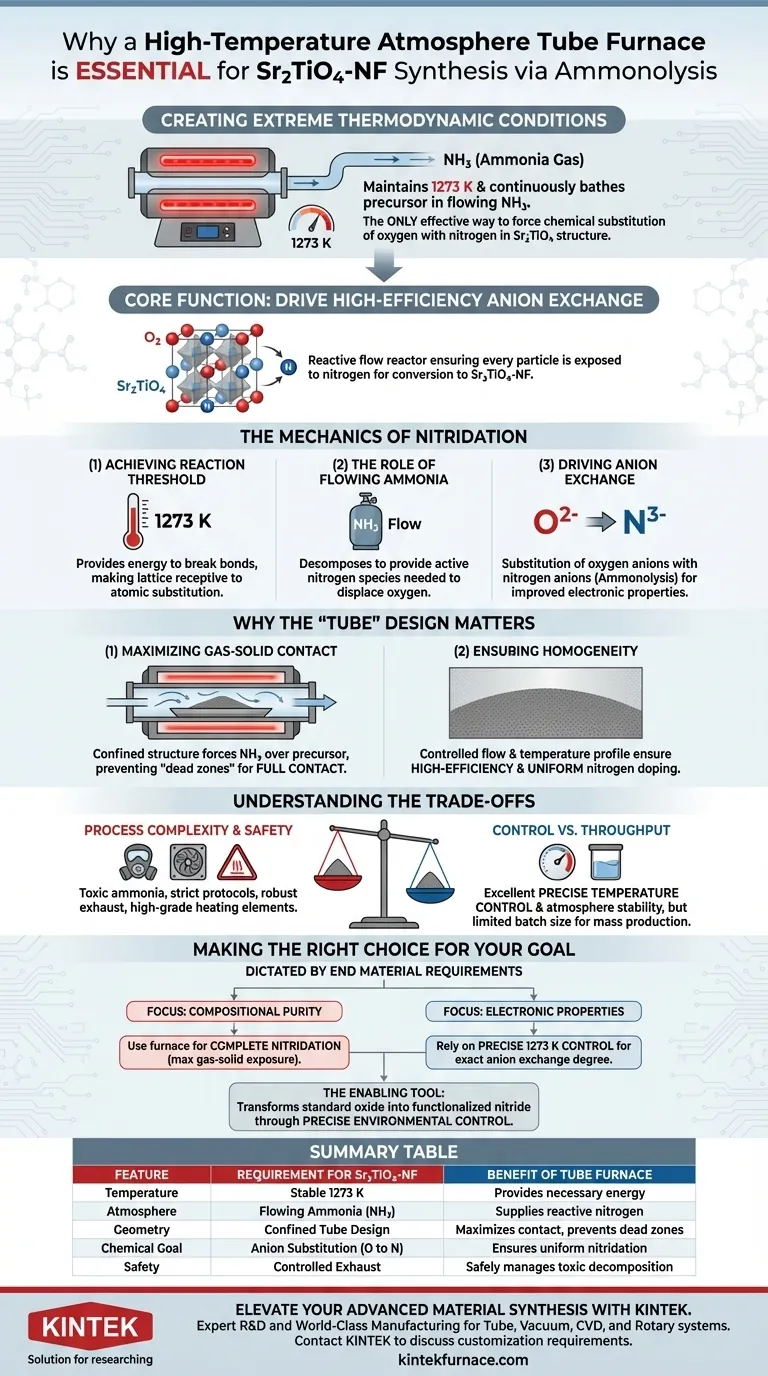
A high-temperature atmosphere tube furnace is required to create the extreme thermodynamic conditions necessary for ammonolysis. Specifically, it maintains a precise temperature of 1273 K while ensuring the precursor powder is continuously bathed in a flowing stream of ammonia (NH3) gas. This combination of high heat and controlled atmosphere is the only effective way to force the chemical substitution of oxygen anions with nitrogen anions in the Sr2TiO4 structure.
The core function of this equipment is to drive high-efficiency anion exchange. The furnace does not merely heat the material; it creates a reactive flow reactor that ensures every particle of the precursor is exposed to nitrogen, facilitating the conversion of Sr2TiO4 into nitrogen-doped Sr2TiO4-NF.

The Mechanics of Nitridation
Achieving the Reaction Threshold
Synthesizing Sr2TiO4-NF requires breaking strong chemical bonds to modify the crystal lattice.
The tube furnace provides the necessary energy by maintaining a stable environment at 1273 K. At this temperature, the lattice becomes receptive to atomic substitution, allowing the modification of the material's electronic structure.
The Role of Flowing Ammonia
Heat alone is insufficient; a reactive nitrogen source is required.
The furnace facilitates the introduction of ammonia (NH3) gas flow. As the ammonia decomposes at high temperatures, it provides the active nitrogen species needed to displace oxygen atoms within the material.
Driving Anion Exchange
The primary chemical goal is substitution.
In this environment, oxygen anions ($O^{2-}$) in the precursor are replaced by nitrogen anions ($N^{3-}$). This process, known as ammonolysis, is critical for achieving the specific electronic properties of Sr2TiO4-NF, such as improved conductivity or catalytic activity.
Why the "Tube" Design Matters
Maximizing Gas-Solid Contact
The physical geometry of the furnace is as important as the temperature.
The confined structure of the tube forces the ammonia gas to flow directly over and through the precursor powder. This ensures full contact between the gas and the solid, preventing "dead zones" where the reaction might fail to occur.
Ensuring Homogeneity
Uniformity is critical for functional materials.
By controlling the flow rate and temperature profile within the tube, the system ensures that the nitrogen doping is high-efficiency and uniform throughout the entire sample. This prevents the formation of a heterogeneous mixture where some parts of the powder are nitrided and others remain pure oxides.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Complexity and Safety
While effective, using a tube furnace with ammonia introduces significant handling risks.
Ammonia is toxic and reactive, requiring strict safety protocols and robust exhaust systems. Furthermore, operating at 1273 K places immense thermal stress on the equipment, requiring high-grade heating elements and thermal insulation.
Control vs. Throughput
Tube furnaces offer precision but often lack volume.
They are excellent for achieving the precise temperature control and atmosphere stability needed for high-quality synthesis. However, the batch size is often limited by the diameter of the tube, making mass production more challenging compared to other furnace types.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The use of a high-temperature atmosphere tube furnace is dictated by the specific requirements of your end material.
- If your primary focus is Compositional Purity: Use this furnace to ensure complete nitridation, as the tube design maximizes the exposure of the powder to the reactive ammonia gas.
- If your primary focus is Electronic Properties: Rely on the precise 1273 K temperature control to achieve the exact degree of anion exchange required to tune the material's conductivity.
Ultimately, the tube furnace is the enabling tool that transforms a standard oxide into a functionalized nitride through precise environmental control.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Requirement for Sr2TiO4-NF Synthesis | Benefit of Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Stable 1273 K | Provides necessary energy to break lattice bonds |
| Atmosphere | Flowing Ammonia (NH3) gas | Supplies reactive nitrogen for anion exchange |
| Geometry | Confined Tube Design | Maximizes gas-solid contact and prevents dead zones |
| Chemical Goal | Anion Substitution (O to N) | Ensures uniform nitridation and electronic tuning |
| Safety | Controlled Exhaust | Safely manages toxic ammonia decomposition at high heat |
Elevate Your Advanced Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise nitridation of materials like Sr2TiO4-NF requires more than just heat; it demands the perfect synergy of atmosphere control and thermal stability. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Tube, Vacuum, CVD, and Rotary systems designed to handle the rigorous demands of ammonolysis and high-temp reactions.
Whether you need customizable lab-scale furnaces or robust high-temperature systems, our equipment ensures uniform anion exchange and high-efficiency results for your unique research needs. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your customization requirements and see how our expertise can drive your innovation forward.
Visual Guide
References
- Jinxing Yu, Xiaoxiang Xu. Fluorine-expedited nitridation of layered perovskite Sr2TiO4 for visible-light-driven photocatalytic overall water splitting. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55748-z
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the primary purpose of using a constant temperature drying oven in sugarcane bagasse pretreatment? Find Out Why
- What negative consequences can occur without proper furnace atmosphere control? Avoid Costly Failures and Ensure Safety
- How does the furnace atmosphere impact the final properties of a material? Master Material Engineering with Controlled Atmospheres
- How does the heating system of a program-controlled atmosphere furnace work? Unlock Precision Heating for Your Lab
- Why is a high-precision annealing furnace necessary for optical fibers? Control Nanoparticle Growth for Peak Performance
- What are the maximum temperature and dew point specifications for retort furnaces? Key Specs for High-Purity Processing
- What are the characteristics and uses of hydrogen atmospheres in furnaces? Unlock Clean Metal Processing
- What is the pressure range of an atmosphere box furnace under vacuum conditions? Find the Right Vacuum Level for Your Lab



















