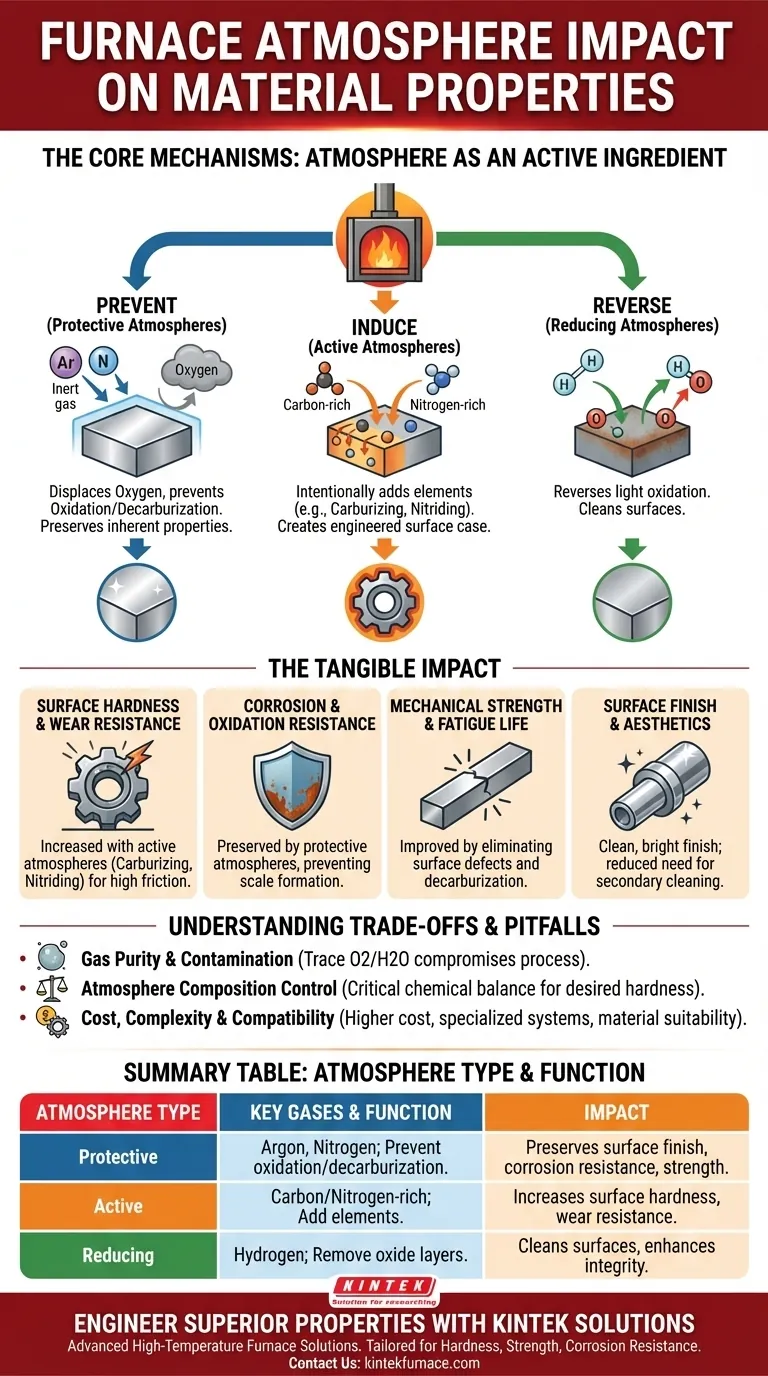
The atmosphere inside a furnace is not an inert background; it is an active ingredient in the heat treatment process. By controlling the gasses surrounding a material during heating, you are controlling the chemical reactions that occur on its surface. This directly dictates final material properties, including its hardness, strength, corrosion resistance, and surface finish.
A controlled furnace atmosphere is a precision tool. It moves beyond simply preventing damage like oxidation and allows you to intentionally add or remove elements at the material's surface, fundamentally engineering its final performance characteristics.
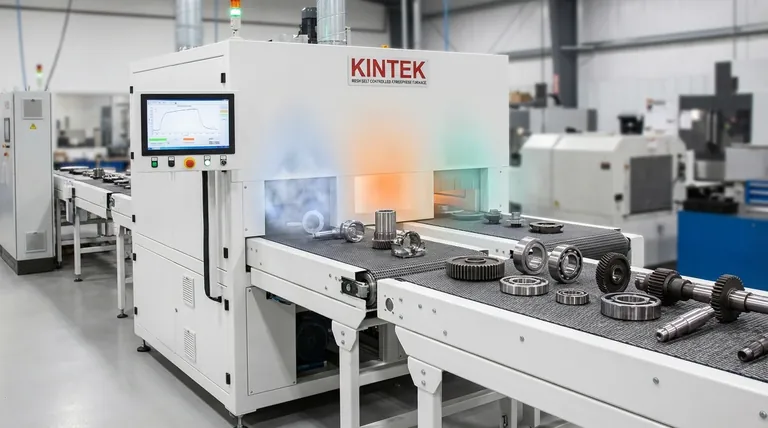

The Core Mechanisms: How Atmosphere Controls Reactions
To understand the impact, you must see the atmosphere as a source of chemical potential. The high temperatures inside a furnace act as a catalyst, accelerating reactions between the gas and the material.
Preventing Unwanted Reactions (Protective Atmospheres)
The most basic function of a controlled atmosphere is to protect the material from air. Heating in ambient air, which is rich in oxygen, causes oxidation (scaling or rust) and, for steels, decarburization (loss of surface carbon).
An inert atmosphere, using gases like argon or nitrogen, displaces the oxygen. This prevents these harmful reactions, preserving the material's inherent properties and ensuring a clean, bright surface finish.
Inducing Desired Reactions (Active Atmospheres)
Active atmospheres are designed to intentionally change the surface chemistry of a part. By introducing specific gases, you can diffuse new elements into the material's surface layer.
Common examples include carburizing (adding carbon to increase surface hardness) or nitriding (adding nitrogen for wear resistance). This creates a composite material: a tough, hard case over a more ductile core.
Creating a Reducing Environment
A reducing atmosphere, typically containing hydrogen, can reverse light oxidation. It actively strips oxygen atoms from the material's surface, which can be useful for cleaning parts that may have been slightly oxidized before treatment.
The Tangible Impact on Final Material Properties
Controlling these surface reactions has a direct and predictable effect on the component's final performance.
Surface Hardness and Wear Resistance
Active atmospheres that add carbon (carburizing) or nitrogen (nitriding) create an extremely hard surface layer, or "case." This is critical for components like gears and bearings that experience high friction and wear.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Using a protective atmosphere prevents the formation of an oxide scale. This not only results in a better surface finish but also preserves the material's natural resistance to corrosion, as the protective base metal is not consumed.
Mechanical Strength and Fatigue Life
Surface defects like oxidation pits or a soft decarburized layer act as stress concentrators. By preventing these defects, a controlled atmosphere ensures the material's full bulk strength is realized and significantly improves its fatigue life by eliminating potential crack initiation sites.
Surface Finish and Aesthetics
For many applications, appearance matters. A part treated in a protective atmosphere emerges from the furnace clean, bright, and free of scale. This often eliminates the need for secondary cleaning operations like sandblasting or chemical pickling.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
While powerful, atmosphere control is not without its challenges. Success requires precision and an understanding of the potential downsides.
Gas Purity and Contamination
The effectiveness of an atmosphere depends on its purity. Trace amounts of oxygen or water vapor in an inert gas supply can still cause discoloration and oxidation, compromising the entire process.
Atmosphere Composition Control
In active atmospheres, the chemical balance is critical. Too much carbon potential in a carburizing atmosphere can lead to soot formation on the part surface. Too little will fail to achieve the desired hardness.
Cost and Complexity
Atmosphere furnaces are more complex and expensive to operate than simple air furnaces. The cost of inert or specialized process gases, along with the required monitoring and safety systems, must be factored into the decision.
Material-Atmosphere Compatibility
Not all atmospheres are suitable for all materials. For example, while nitrogen is often considered inert, it can react with certain alloys like those containing titanium or aluminum at high temperatures, forming undesirable nitrides.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct atmosphere is determined entirely by the desired outcome for the material.
- If your primary focus is preserving existing material properties and achieving a clean surface: Use a protective, inert atmosphere like high-purity nitrogen or argon to prevent all surface reactions.
- If your primary focus is increasing surface hardness and wear resistance: Use an active atmosphere for carburizing or nitriding to diffuse hardening elements into the surface.
- If your primary focus is cleaning a slightly oxidized surface during processing: Use a reducing atmosphere containing hydrogen to remove the existing oxide layer.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive processing where surface finish is not critical: Heating in ambient air may be acceptable, but you must account for material loss to scale and potential degradation of mechanical properties.
Mastering the furnace atmosphere transforms heat treatment from a simple heating process into a precise material engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Key Gases | Primary Function | Impact on Material Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protective | Argon, Nitrogen | Prevent oxidation and decarburization | Preserves surface finish, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength |
| Active | Carbon-rich, Nitrogen-rich | Add elements via carburizing/nitriding | Increases surface hardness and wear resistance |
| Reducing | Hydrogen | Remove oxide layers | Cleans surfaces and enhances material integrity |
Ready to engineer superior material properties with precision furnace atmospheres? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure we meet your unique experimental needs, delivering enhanced hardness, strength, and corrosion resistance for your materials. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your heat treatment processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance



















