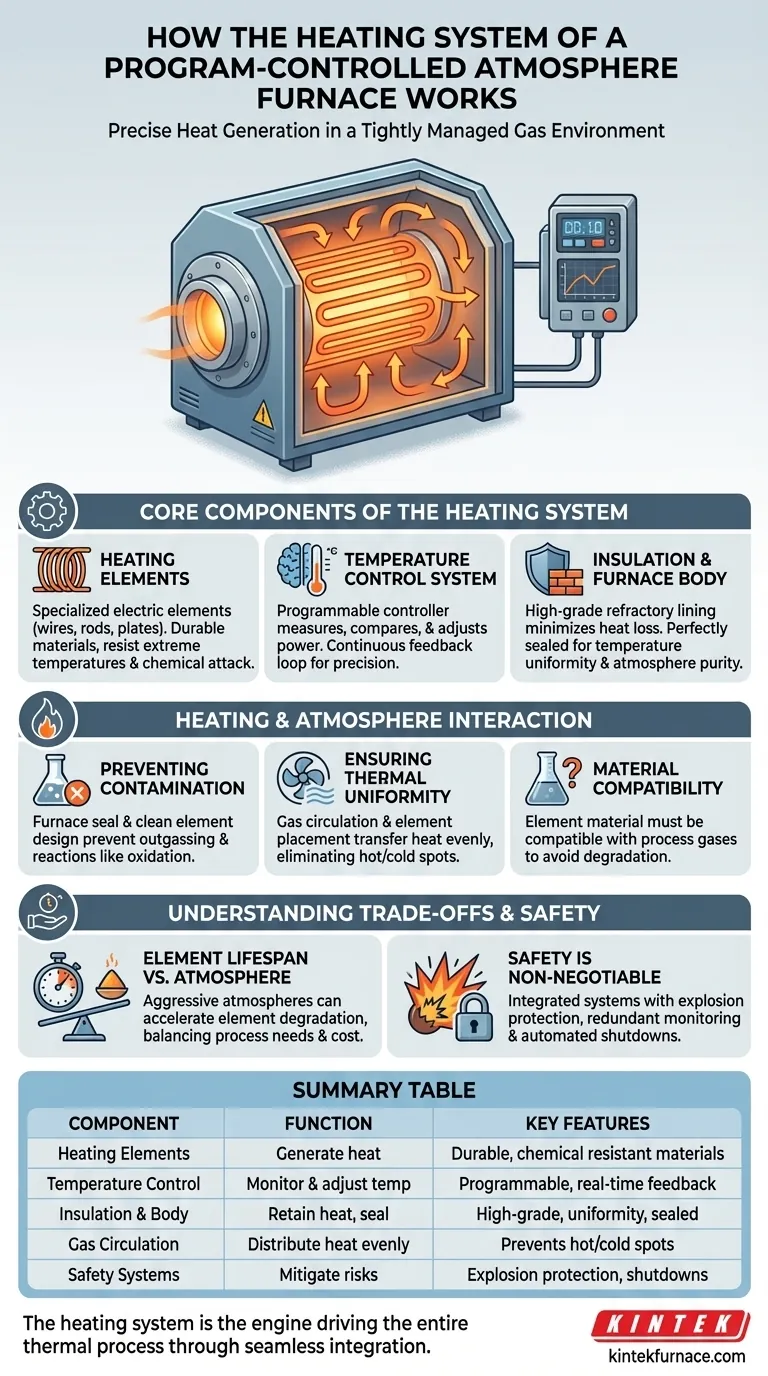
At its core, the heating system in a program-controlled atmosphere furnace uses specialized electric heating elements to generate heat. A sophisticated control system continuously monitors the internal temperature and precisely adjusts the power supplied to these elements, ensuring the workload follows a predefined temperature profile within a tightly managed gas environment.
The challenge is not simply to generate heat, but to do so with extreme precision inside a controlled, often reactive, chemical atmosphere. Therefore, the heating system cannot be viewed in isolation; it is an integrated part of the furnace's atmosphere, control, and safety architecture.
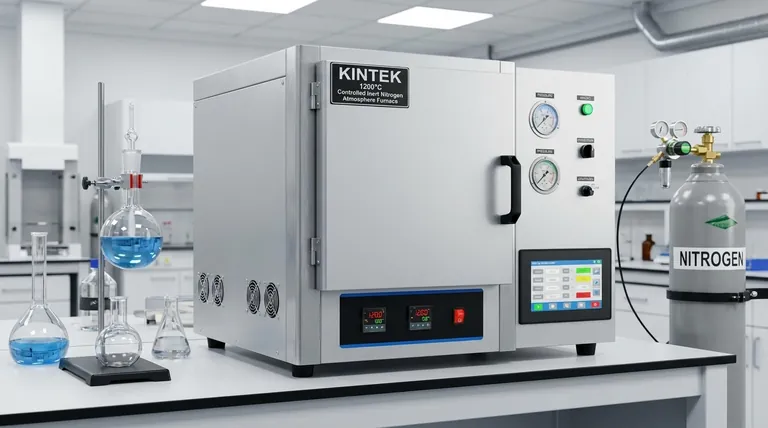

The Core Components of the Heating System
A furnace's ability to perform its function reliably depends on the synergy between three key heating-related components.
The Heating Elements
The actual work of generating heat is done by electric heating elements, often in the form of wires, rods, or plates. These are not ordinary heaters; they are fabricated from durable materials designed to withstand extreme temperatures and resist chemical attack from the specific process atmosphere inside the furnace.
The Temperature Control System
This is the brain of the operation. A sensor, such as a thermocouple, measures the temperature inside the furnace in real-time. This data is fed to a programmable controller, which compares the actual temperature to the desired setpoint in the program and constantly adjusts the electrical power sent to the heating elements to correct any deviation. This creates a continuous feedback loop for precise control.
The Insulation and Furnace Body
The furnace chamber is lined with high-grade refractory and insulating materials. This thermal insulation is critical for minimizing heat loss, ensuring temperature uniformity across the workload, and improving energy efficiency. The furnace body must also be perfectly sealed to prevent the external environment from contaminating the internal atmosphere.
How Heating Interacts with the Furnace Atmosphere
In an atmosphere furnace, the heating system does not operate in a vacuum or simple air. It must function in perfect harmony with the carefully managed gas environment.
Preventing Contamination
The primary purpose of an atmosphere furnace is to prevent unwanted reactions, like oxidation. The furnace's tight seal is the first line of defense. The heating system supports this by being designed to operate cleanly, without outgassing or introducing contaminants that would compromise the controlled atmosphere.
Ensuring Thermal Uniformity
Consistent product quality requires that every part of the workload experiences the same thermal cycle. The placement of heating elements and the design of the gas circulation system must work together. The gas flow helps transfer heat evenly throughout the chamber, eliminating hot or cold spots that could lead to inconsistent results.
Material Compatibility
The material of the heating elements must be chemically compatible with the process gases being used. For example, a heating element that works perfectly in an inert nitrogen atmosphere might degrade rapidly in a carbon-rich or hydrogen atmosphere. This selection is a critical design consideration.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety
Operating a high-temperature system with specialized gases involves inherent challenges and requires a focus on safety.
Element Lifespan vs. Atmosphere
Even the most robust heating elements have a finite lifespan. Aggressive or fluctuating atmospheres can accelerate their degradation. This creates a trade-off between the desired chemical process and the operational cost and maintenance schedule of the heating elements.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
The heating system design differs for batch furnaces, where a single load is heated and cooled, versus continuous furnaces, where material moves steadily through different temperature zones. Batch systems require controls that can manage rapid temperature changes, while continuous systems need stable, consistent heat in each zone.
Safety is Non-Negotiable
Many controlled atmospheres use flammable or hazardous gases. The heating system is a potential ignition source, making its integration with the safety system paramount. This includes explosion protection devices, redundant temperature monitoring, and automated shutdown procedures that activate if gas flow or temperature deviates from safe limits.
Applying This to Your Process
Your specific goals will determine which aspects of the heating system are most critical for you to focus on.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: The precision of the temperature control system and the design for thermal uniformity are your most important considerations.
- If your primary focus is working with reactive atmospheres: Pay closest attention to the material compatibility of the heating elements and the integrity of the furnace's seals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: The efficiency and durability of a continuous furnace's zoned heating system will be key to your operational success.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Ensure the furnace has a fully integrated safety system that links the heating controls directly to the gas management and monitoring hardware.
Ultimately, the heating system is the engine that drives the entire thermal process, and its successful operation depends on its seamless integration with the furnace's other critical systems.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Elements | Generate heat | Durable materials, resistant to chemical attack |
| Temperature Control System | Monitor and adjust temperature | Programmable controller, real-time feedback |
| Insulation and Furnace Body | Retain heat and seal atmosphere | High-grade refractory, ensures uniformity |
| Gas Circulation System | Distribute heat evenly | Prevents hot/cold spots, supports atmosphere control |
| Safety Systems | Mitigate risks | Explosion protection, automated shutdowns |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's thermal processing with precision and safety? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on process repeatability, reactive atmospheres, high-volume production, or operational safety, our furnaces deliver reliable performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications and drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity



















