In industrial heat treatment, a hydrogen atmosphere is a highly effective but specialized tool used for its powerful chemical reactivity. It serves as an exceptional reducing agent, meaning it actively removes oxygen from metal surfaces, but this same reactivity creates significant risks, particularly the decarburization of high-carbon steels.
Hydrogen's primary value lies in its unparalleled ability to reduce surface oxides, producing exceptionally clean and bright metal parts. However, this benefit must be weighed against its tendency to remove carbon from certain steels and the strict safety protocols required for its handling.

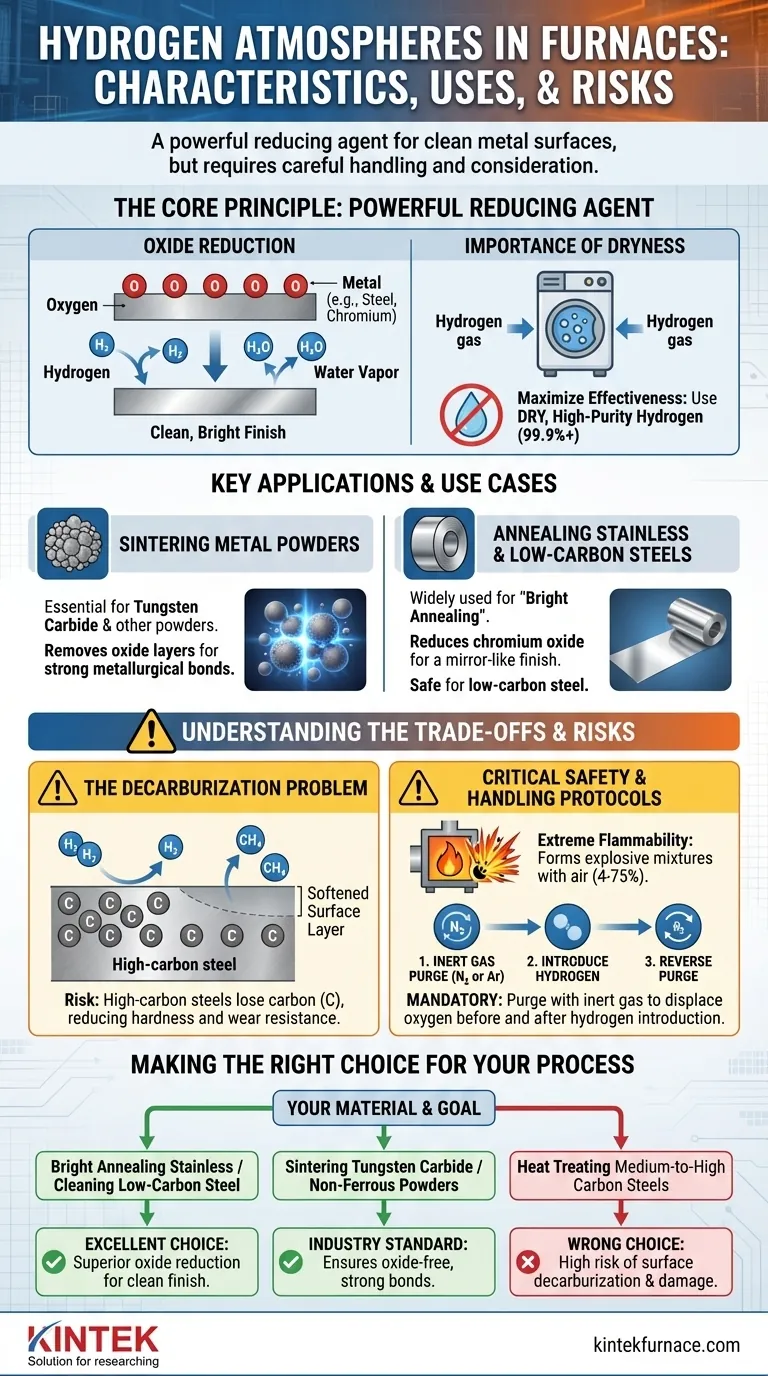
The Core Principle: A Powerful Reducing Agent
Hydrogen's role in a furnace is not to be inert, but to be actively and chemically involved in the process. Its small molecular size and high reactivity make it uniquely suited for surface cleaning at a chemical level.
How Hydrogen Reduces Oxides
The fundamental purpose of a hydrogen atmosphere is to reverse oxidation. At high temperatures, hydrogen gas (H₂) readily reacts with metal oxides (like iron oxide or chromium oxide) present on the surface of a part.
This chemical reaction strips the oxygen atom from the metal, forming water vapor (H₂O) and leaving behind a pure, clean metal surface. This process is critical for achieving a bright, unblemished finish.
The Importance of Dryness
The effectiveness of hydrogen as a deoxidizer is maximized when it is dry. Any moisture (water vapor) introduced into the furnace can itself be a source of oxygen, working against the desired reducing effect.
For this reason, high-purity (99.9%+) hydrogen is often passed through a dryer before entering the furnace to ensure maximum oxide reduction.
Key Applications and Use Cases
The choice to use a hydrogen atmosphere is driven by the material being processed and the desired final surface quality. It excels in applications where surface oxides are a primary concern.
Sintering Metal Powders
Hydrogen is essential for sintering, particularly for materials like tungsten carbide and other metal powders. It removes the thin oxide layer on each individual powder grain before they are fused together.
This oxide removal is crucial for allowing strong, direct metallurgical bonds to form between the particles, resulting in a dense and robust final part.
Annealing Stainless and Low-Carbon Steels
Hydrogen is widely used for the "bright annealing" of stainless steels. The chromium in stainless steel readily forms a passive chromium oxide layer, which hydrogen effectively reduces, resulting in a bright, mirror-like finish.
It is also safe and effective for annealing low-carbon steels, as it cleans the surface without a significant risk of detrimental reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Using a hydrogen atmosphere requires a clear understanding of its downsides. Its high reactivity is both its greatest strength and its most significant liability.
The Decarburization Problem
This is the most critical risk when working with steel. At elevated temperatures, hydrogen can react with the carbon (C) within high-carbon steels to form methane gas (CH₄).
This reaction effectively pulls carbon out of the steel's surface, a phenomenon known as decarburization. This loss of carbon softens the surface layer and compromises the material's intended hardness and wear resistance, making pure hydrogen unsuitable for many tool steels and high-carbon alloys.
Critical Safety and Handling Protocols
Hydrogen is extremely flammable and can form an explosive mixture with air (oxygen) over a very wide range of concentrations (4-75%). It cannot be introduced into or removed from a hot furnace that contains air.
Therefore, a strict purging procedure is mandatory. The furnace must first be purged with an inert gas, such as nitrogen or argon, to displace all oxygen. Only then can hydrogen be safely introduced. At the end of the cycle, the process is reversed: inert gas purges the hydrogen before the door is opened to the air.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace atmosphere is a critical decision based on your material and engineering goals.
- If your primary focus is bright annealing stainless steel or cleaning low-carbon steel: Hydrogen is an excellent choice for its superior ability to reduce surface oxides and produce a clean finish.
- If your primary focus is sintering tungsten carbide or other non-ferrous metal powders: Dry hydrogen is the industry standard for ensuring oxide-free surfaces that promote strong metallurgical bonds.
- If your primary focus is heat treating medium-to-high carbon steels: Pure hydrogen is generally the wrong choice due to the high risk of surface decarburization, which will damage the part's properties.
Mastering hydrogen's dual nature as a powerful deoxidizer and a potential decarburizer is the key to leveraging it effectively and safely in your heat treatment operations.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic/Use | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Acts as a powerful reducing agent to remove oxygen from metal surfaces, producing clean, bright finishes |
| Key Applications | Sintering metal powders (e.g., tungsten carbide), bright annealing stainless and low-carbon steels |
| Main Risks | Decarburization of high-carbon steels, flammability requiring strict safety protocols (e.g., inert gas purging) |
| Safety Measures | Use of dry, high-purity hydrogen; mandatory purging with inert gases like nitrogen or argon to prevent explosions |
Optimize your laboratory's heat treatment processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, whether you're sintering powders or annealing metals. Contact us today to enhance efficiency and safety in your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of the circulation fan in a full-hydrogen bell-type furnace? Boost Heat Transfer Efficiency
- What is the function of a hydrogenation furnace in U-6Nb powder production? Master Chemical Embrittlement
- How is the sealing performance of an experimental box type atmosphere furnace enhanced? Boost Purity with Advanced Sealing Systems
- Why are high-temperature annealing furnaces and H2-N2 atmospheres required for oriented silicon steel research?
- How is a box furnace used in sintering of metal powders? Achieve Dense, High-Strength Metal Parts



















