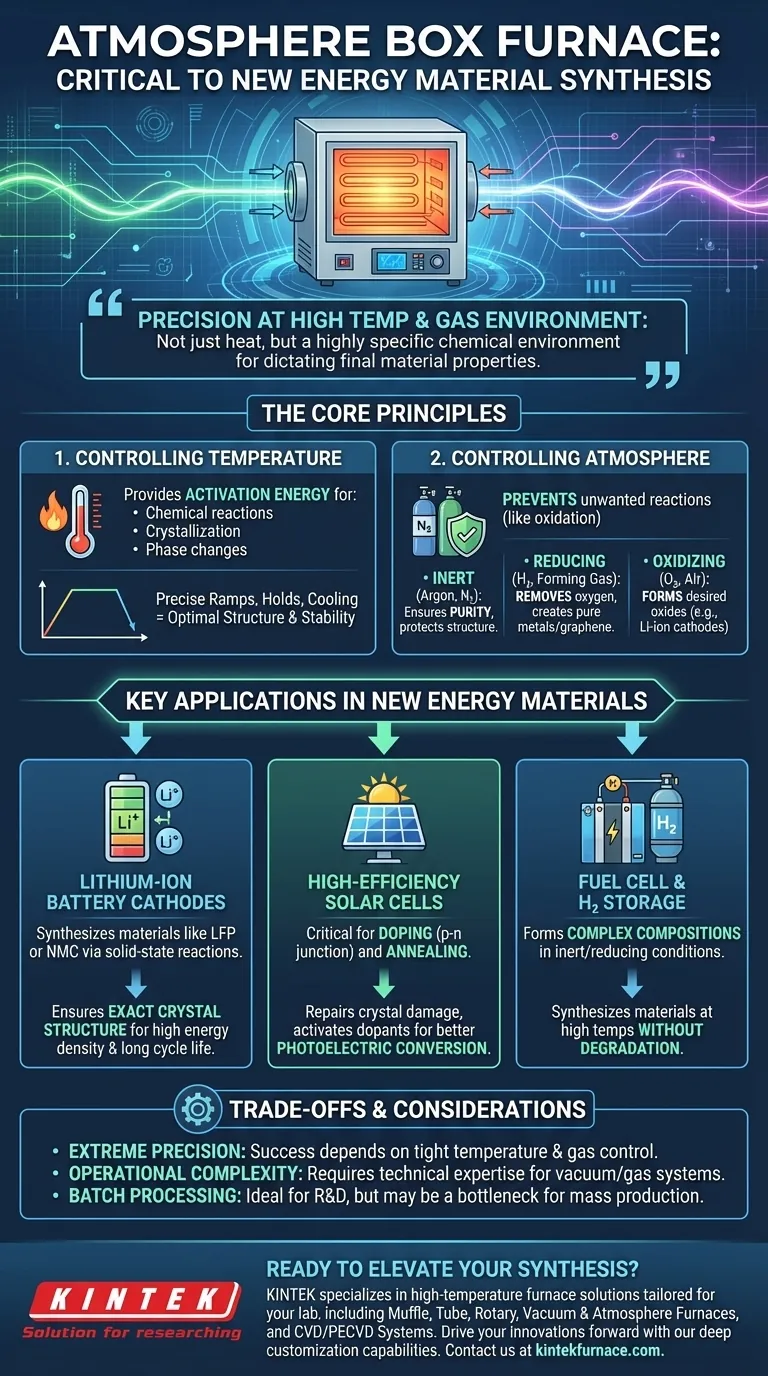
In the synthesis of new energy materials, an atmosphere box furnace is the critical tool that provides a precisely controlled high-temperature and gas environment. This control is essential for creating materials with the specific crystal structures, purity, and properties required for high-performance applications like lithium-ion batteries, solar cells, and fuel cells. It enables solid-state reactions, annealing, and doping processes that are impossible to conduct in open air.
The true function of an atmosphere box furnace is not just to provide heat, but to create a highly specific chemical environment. This control over the atmosphere at high temperatures is what allows researchers to dictate the final properties of a material, moving from a simple raw mixture to a high-performance energy component.

The Core Principles: Controlling Temperature and Atmosphere
The power of an atmosphere box furnace comes from its ability to manipulate the two most important variables in material synthesis: heat and the surrounding chemical environment.
The Role of High Temperature in Material Synthesis
High temperature provides the activation energy needed to drive chemical reactions and physical changes in solid materials. This is essential for processes like crystallization, where atoms arrange themselves into a highly ordered structure.
For new energy materials, a well-defined crystal structure is directly linked to performance. A furnace allows for precise temperature ramps, holds (soaks), and cooling rates, ensuring the material achieves its optimal structure and stability.
The Critical Importance of a Controlled Atmosphere
The gas environment inside the furnace is just as important as the temperature. A controlled atmosphere prevents unwanted reactions, primarily oxidation from the air, which can contaminate the material and ruin its properties.
By introducing specific gases, you can create different environments:
- Inert Atmosphere (e.g., Argon, Nitrogen): This prevents any reaction from occurring, ensuring the material's purity during heat treatment. It's used when you only want the heat to affect the material's structure, not its chemical composition.
- Reducing Atmosphere (e.g., Hydrogen, Forming Gas): This environment actively removes oxygen. It is used to reduce metal oxides into pure metals or to synthesize specific materials like graphene from carbon-based precursors.
- Oxidizing Atmosphere (e.g., Oxygen, Air): In some cases, a specific, controlled amount of oxygen is required to form the desired oxide material, such as the cathode materials in lithium-ion batteries.
Key Applications in New Energy Materials
The precise control offered by these furnaces is fundamental to the development of today's most promising energy technologies.
Synthesizing Lithium-Ion Battery Cathodes
The performance of a lithium-ion battery is heavily dependent on the quality of its cathode material. An atmosphere furnace facilitates the high-temperature solid-state reaction needed to form materials like Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) or Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC).
Controlling the oxygen level and temperature profile ensures the final material has the exact crystal structure and stoichiometry required for high energy density and long cycle life.
Fabricating High-Efficiency Solar Cells
For silicon-based solar cells, the furnace is used for critical steps like doping and annealing. Doping involves introducing impurities into the silicon wafer to create the necessary p-n junction, which is the heart of the solar cell.
Annealing is a heat treatment process that repairs crystal damage from manufacturing and helps activate the dopants. Both steps must be done in a controlled atmosphere to improve the photoelectric conversion efficiency.
Developing Fuel Cell and Hydrogen Storage Materials
New materials for fuel cell electrolytes and solid-state hydrogen storage often have complex compositions that can only be formed under specific conditions. An atmosphere furnace provides the inert or reducing environment needed to synthesize these materials at high temperatures without degradation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While indispensable, atmosphere box furnaces are specialized tools with practical considerations.
The Demand for Extreme Precision
The success of a synthesis process often depends on maintaining temperature stability within a few degrees and precise control over gas flow rates. Any deviation can lead to a batch of material with substandard or inconsistent properties, wasting time and valuable resources.
Operational Complexity and Cost
These are not simple ovens. Operating an atmosphere furnace requires technical expertise to manage vacuum pumps, gas mixing systems, and programmable temperature controllers safely and effectively. They represent a significant capital investment for any research lab or production facility.
Batch Processing vs. Scalability
A "box" furnace is inherently a batch-processing tool. While perfect for research, development, and small-scale production, it can be a bottleneck for mass manufacturing. Large-scale industrial production often requires more complex and expensive continuous or tunnel furnaces.
Applying This to Your Project
Your approach will depend entirely on the final goal for your material.
- If your primary focus is maximizing electrochemical performance (batteries): Concentrate on achieving high crystallinity and phase purity by carefully controlling the temperature profile and oxygen partial pressure during synthesis.
- If your primary focus is improving photoelectric efficiency (solar): Use the furnace to optimize the annealing and doping cycles to reduce defects in the silicon crystal lattice.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research and development: Leverage the furnace's versatility to experiment with novel material compositions under a wide range of atmospheric and thermal conditions.
Ultimately, mastering the controlled environment within an atmosphere furnace is fundamental to innovating the next generation of energy materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in New Energy Material Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Controlled Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation, enables inert/reducing/oxidizing environments for purity and specific reactions |
| High Temperature Control | Drives solid-state reactions, crystallization, and annealing for optimal material structure |
| Applications | Used in lithium-ion battery cathodes, solar cell doping, and fuel cell material development |
| Key Benefits | Enhances crystal structure, purity, and performance in energy storage and conversion devices |
Ready to elevate your new energy material synthesis? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for your lab's needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet unique experimental requirements for lithium-ion batteries, solar cells, and more. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.



















