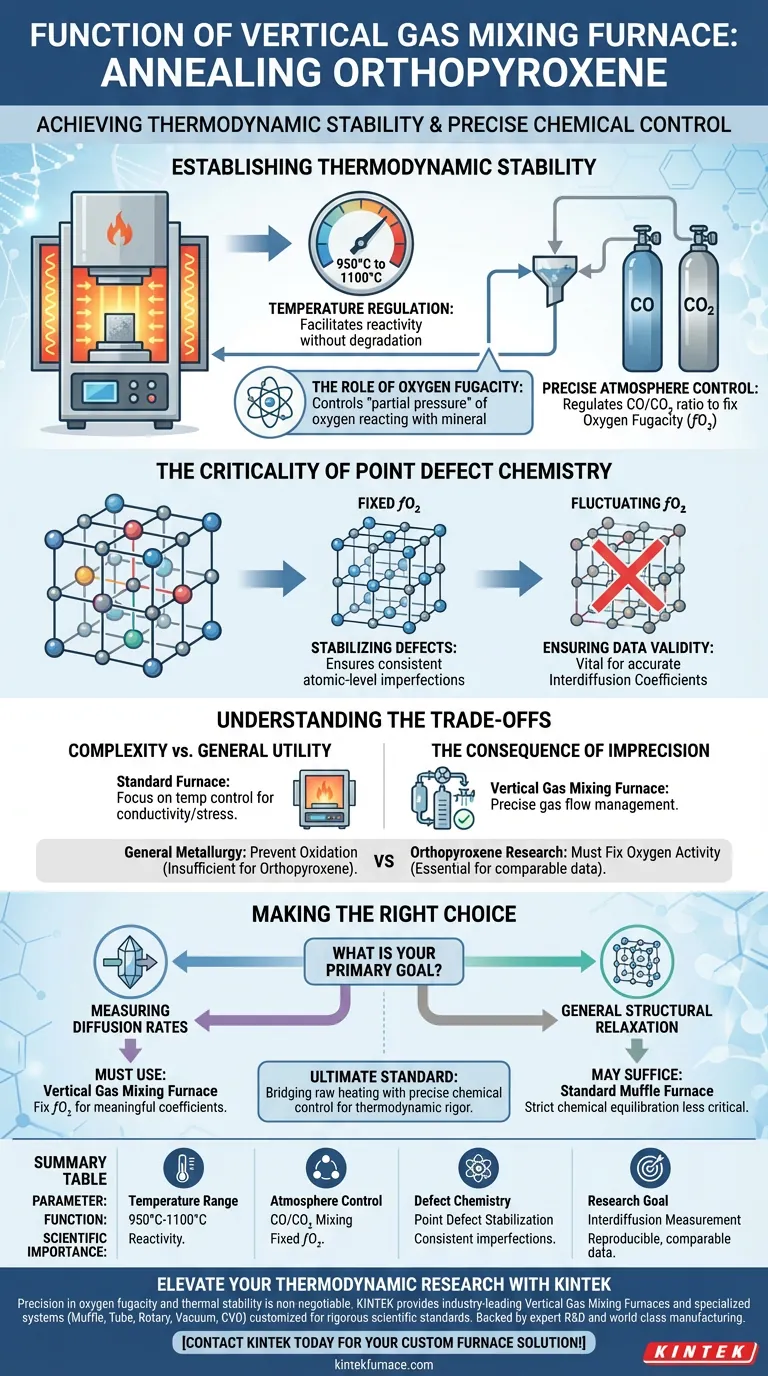
The primary function of a vertical gas mixing furnace during the annealing of orthopyroxene is to establish and maintain precise thermodynamic stability. This is achieved by regulating the temperature between 950°C and 1100°C while simultaneously controlling the flow ratio of CO and CO₂ gases to fix the oxygen fugacity ($fO_2$).
Core Takeaway While general annealing focuses on heat treatment, annealing orthopyroxene requires a strictly controlled chemical environment. The vertical gas mixing furnace is critical because it stabilizes point defect chemistry, ensuring that measured interdiffusion coefficients are accurate, reproducible, and scientifically comparable.

Establishing Thermodynamic Stability
Precise Atmosphere Control
The furnace does not simply heat the sample; it creates a specific chemical atmosphere.
By manipulating the ratio of CO (Carbon Monoxide) and CO₂ (Carbon Dioxide) gases, the system creates a constant oxygen fugacity ($fO_2$).
Temperature Regulation
The process operates within a specific thermal window, typically between 950°C and 1100°C.
At these temperatures, the mineral is chemically reactive enough to equilibrate with the gas atmosphere without melting or degrading unexpectedly.
The Role of Oxygen Fugacity
Oxygen fugacity is effectively the "partial pressure" of oxygen available to react with the mineral.
Controlling this variable is the defining feature of this furnace type, distinguishing it from standard muffle furnaces used in broader applications like semiconductor manufacturing.
The Criticality of Point Defect Chemistry
Stabilizing Defects
Orthopyroxene contains atomic-level imperfections known as point defects.
The concentration and behavior of these defects are highly sensitive to the surrounding oxygen environment.
Ensuring Data Validity
To measure interdiffusion coefficients (how atoms move within the crystal lattice), the defect structure must remain constant.
If the furnace fails to maintain a specific $fO_2$, the defect chemistry changes, rendering the diffusion data inconsistent and scientifically invalid.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Complexity vs. General Utility
A standard annealing furnace (often used for metals or silicon) focuses primarily on temperature control to optimize conductivity or remove stress.
In contrast, the vertical gas mixing furnace introduces significant complexity by requiring precise gas flow management.
The Consequence of Imprecision
In general metallurgy or semiconductor processing, the goal is often simply "preventing oxidation."
However, for orthopyroxene research, preventing oxidation is not enough; the oxygen activity must be fixed to a specific thermodynamic value. Failure to do so results in data that cannot be compared across different studies.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
To determine if this equipment is necessary for your specific application, consider your end goals:
- If your primary focus is measuring diffusion rates: You must use a gas mixing furnace to fix the oxygen fugacity, or your calculated coefficients will be meaningless due to fluctuating defect chemistry.
- If your primary focus is general structural relaxation: A standard muffle furnace (controlled heating and cooling) may suffice, as strict chemical equilibration with the atmosphere is less critical.
Ultimately, the vertical gas mixing furnace is the standard for thermodynamic rigor in mineral physics, bridging the gap between raw heating and precise chemical control.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Function in Orthopyroxene Annealing | Scientific Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 950°C to 1100°C | Facilitates reactivity without mineral degradation. |
| Atmosphere Control | CO/CO₂ Gas Mixing | Establishes fixed oxygen fugacity ($fO_2$). |
| Defect Chemistry | Point Defect Stabilization | Ensures consistent atomic-level imperfections. |
| Research Goal | Interdiffusion Measurement | Provides reproducible, scientifically comparable data. |
Elevate Your Thermodynamic Research with KINTEK
Precision in oxygen fugacity and thermal stability is non-negotiable for mineral physics and interdiffusion studies. KINTEK provides industry-leading Vertical Gas Mixing Furnaces, alongside our specialized Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all designed to meet the most rigorous scientific standards.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our high-temperature lab furnaces are fully customizable to your unique research needs. Ensure your data's validity with a system built for thermodynamic rigor.
Ready to stabilize your research environment? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Maria A. Dias, Ralf Dohmen. Experimental determination of Fe–Mg interdiffusion in orthopyroxene as a function of Fe content. DOI: 10.1007/s00410-024-02110-7
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature furnace facilitate the molten salt synthesis of CoNb2O6? Precision Thermal Control Guide
- How are the heating elements arranged in the box type annealing atmosphere furnace? For Uniform Heating and Precise Control
- What is the primary purpose of an inert oven? Protect Materials from Oxidation in Heating
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- How does a heating furnace contribute to the simulated pre-oxidation of alloy powders? Optimize Your Material Research
- What critical protective roles does argon serve for AA7150-Al2O3 composites? Ensure Purity & Density
- What is the primary function of an air oxidation furnace in carbon chain synthesis? Optimize SWCNT Pretreatment
- What protective role does a constant flow of inert gas play in dynamic atmosphere sintering? Enhance Material Integrity



















