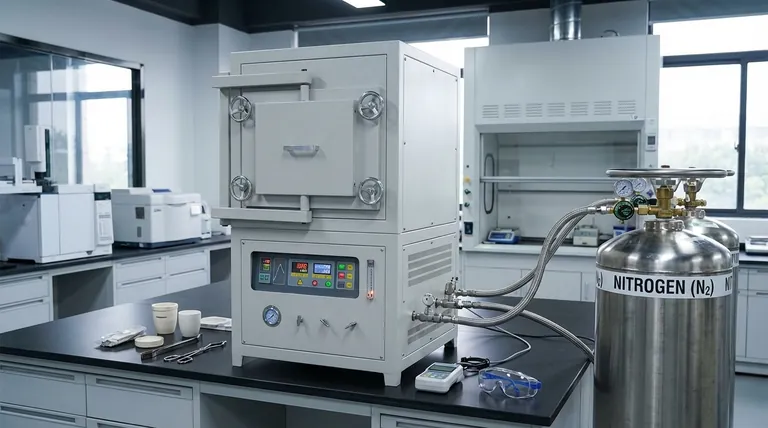
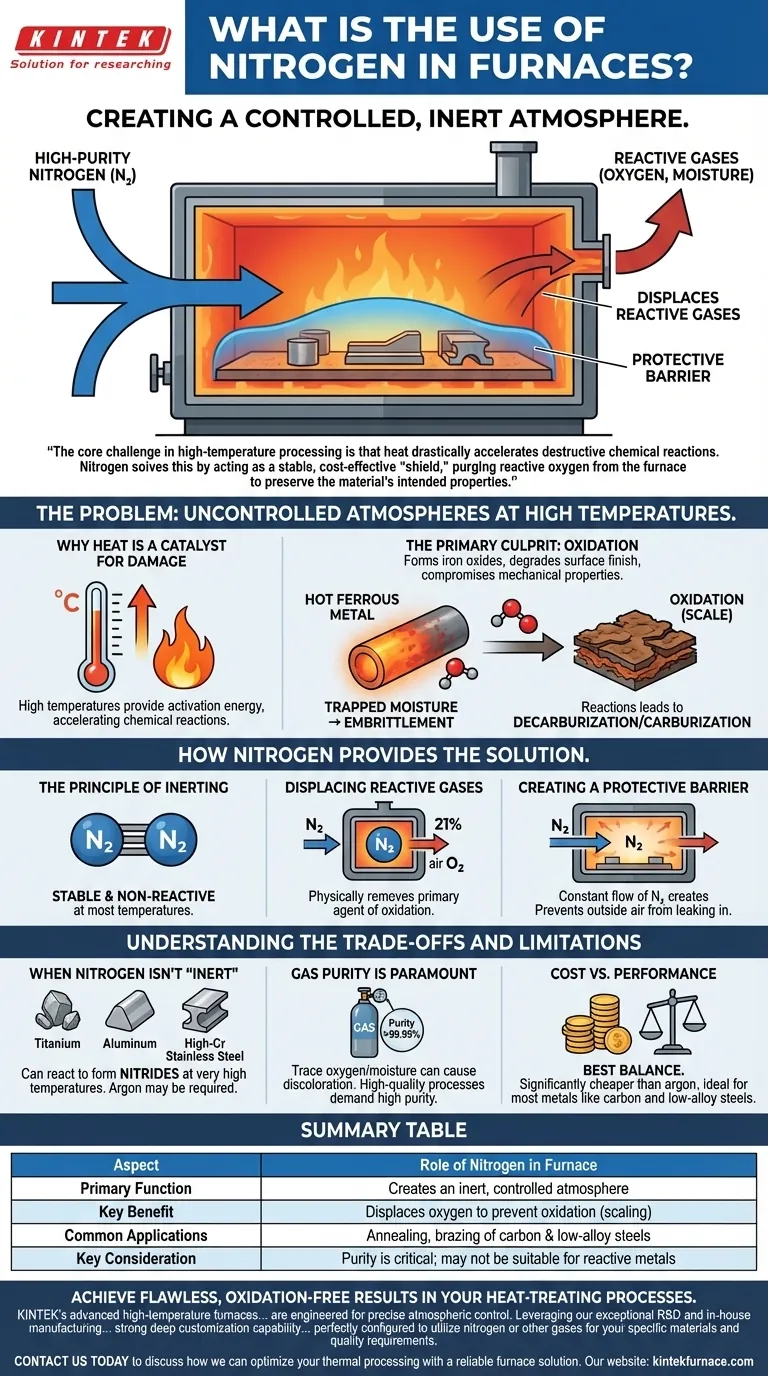
In industrial furnaces, nitrogen's primary role is to create a controlled, inert atmosphere. This engineered environment is critical for high-temperature processes, as it displaces reactive gases like oxygen and moisture. By doing so, it protects the materials being processed from unwanted chemical reactions, chiefly oxidation, which would otherwise degrade their quality and integrity.
The core challenge in high-temperature processing is that heat drastically accelerates destructive chemical reactions. Nitrogen solves this by acting as a stable, cost-effective "shield," purging reactive oxygen from the furnace to preserve the material's intended properties.

The Problem: Uncontrolled Atmospheres at High Temperatures
Why Heat Is a Catalyst for Damage
High temperatures provide the activation energy needed for chemical reactions to occur rapidly. While this heat is necessary for processes like annealing or brazing, it also makes materials, especially metals, highly susceptible to reacting with the surrounding air.
The Primary Culprit: Oxidation
The most common and damaging reaction is oxidation. When hot ferrous metals are exposed to oxygen, they form iron oxides, a brittle layer known as scale. This scale degrades the surface finish, alters the part's dimensions, and can compromise its mechanical properties.
Beyond Simple Rust
An uncontrolled atmosphere can cause other issues besides oxidation. Trapped moisture can introduce hydrogen, leading to embrittlement, and reactions with carbon in the air or on the material can lead to unintended decarburization or carburization, weakening the final product.
How Nitrogen Provides the Solution
The Principle of Inerting
Nitrogen gas (N₂) is composed of two nitrogen atoms joined by a very strong triple bond. This bond makes the molecule exceptionally stable and non-reactive (inert) at the temperatures used for most common heat-treating applications.
Displacing Reactive Gases
The fundamental strategy is gas displacement. By continuously feeding high-purity nitrogen into a sealed furnace, the lighter, ambient air—which is about 21% oxygen—is purged and forced out. This physically removes the primary agent of oxidation from the part's environment.
Creating a Protective Barrier
This constant flow of nitrogen creates a positive pressure inside the furnace, forming a protective blanket around the materials. This barrier prevents any outside air from leaking back in, ensuring the parts remain in a non-reactive environment throughout the entire heating and cooling cycle.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
When Nitrogen Isn't 'Inert'
While highly stable, nitrogen can react with certain elements at very high temperatures. Metals like titanium, aluminum, and some high-chromium stainless steels can form nitrides on their surface. In these specific cases, a more truly inert gas like argon may be required.
Gas Purity Is Paramount
The effectiveness of a nitrogen atmosphere is directly tied to its purity. Even trace amounts of residual oxygen or moisture in the nitrogen supply can be enough to cause discoloration or light oxidation on sensitive materials. High-quality processes demand high-purity nitrogen.
Cost vs. Performance
Nitrogen is overwhelmingly the most common choice for furnace atmospheres because it provides the best balance of cost and performance. It is significantly less expensive than argon, making it the economical solution for processing the vast majority of common metals, particularly carbon and low-alloy steels.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Controlling the furnace atmosphere is not an afterthought; it is a fundamental process variable. Your choice of gas depends entirely on your materials and quality requirements.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation on common ferrous metals: Nitrogen is the industry-standard and most cost-effective solution for creating a protective atmosphere.
- If you are working with reactive metals like titanium or at extreme temperatures: You must evaluate the risk of nitride formation and consider using a more inert gas like argon.
- If final product quality and consistency are critical: Always specify and monitor the purity of your nitrogen supply to control residual oxygen and moisture levels.
Mastering your furnace atmosphere is essential for achieving repeatable, high-quality results in any thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role of Nitrogen in Furnace |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Creates an inert, controlled atmosphere |
| Key Benefit | Displaces oxygen to prevent oxidation (scaling) |
| Common Applications | Annealing, brazing of carbon & low-alloy steels |
| Key Consideration | Purity is critical; may not be suitable for reactive metals (e.g., titanium) |
Achieve flawless, oxidation-free results in your heat-treating processes. KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces, including our Atmosphere and Tube Furnaces, are engineered for precise atmospheric control. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide robust solutions for diverse laboratories. Our strong deep customization capability ensures your furnace is perfectly configured to utilize nitrogen or other gases for your specific materials and quality requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processing with a reliable furnace solution. Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality



















