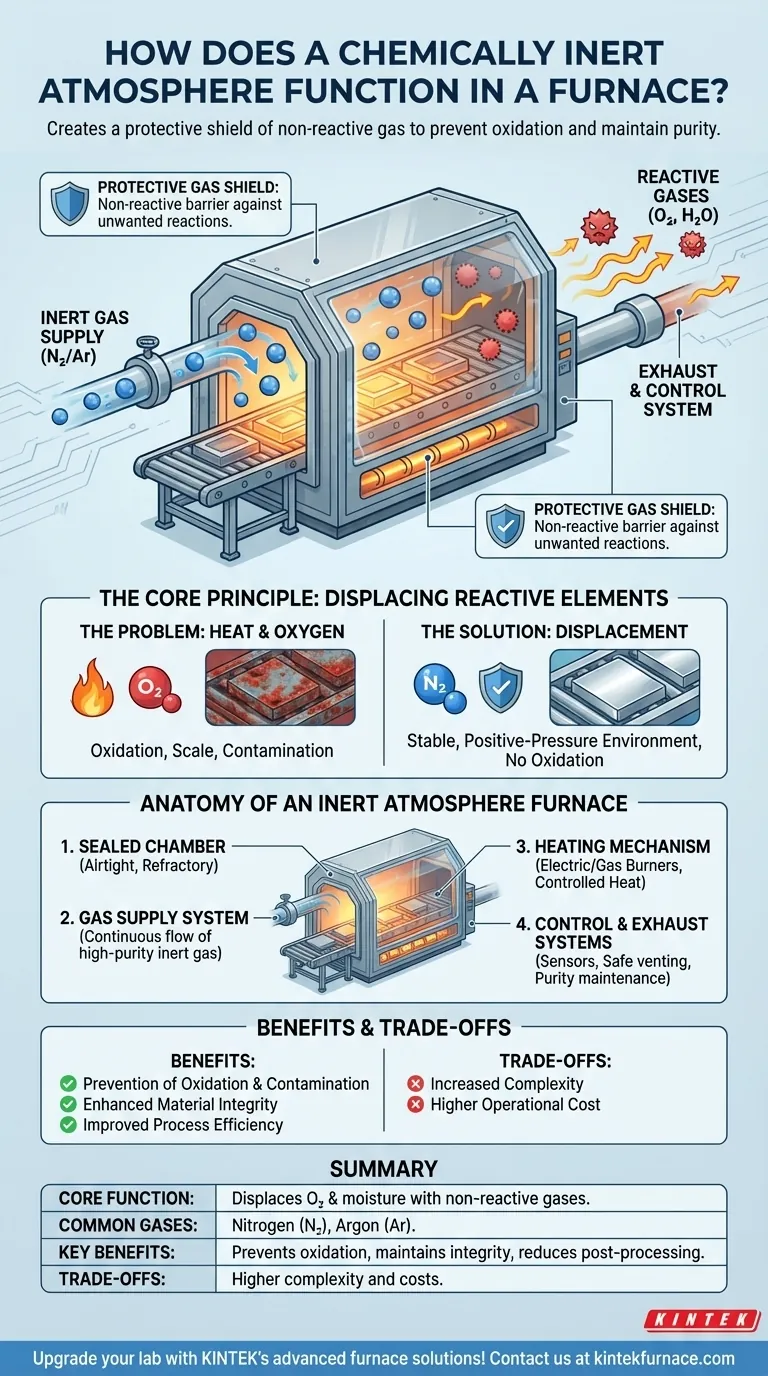
At its core, a chemically inert atmosphere functions by using a non-reactive gas, such as nitrogen or argon, to physically displace and purge reactive gases like oxygen and moisture from a sealed furnace chamber. This creates a protective shield around the material being heat-treated, preventing unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation and ensuring the material's purity and integrity are maintained at high temperatures.
An inert atmosphere's function is not to chemically interact with the material. Instead, it acts as a high-purity barrier, creating a controlled environment that prevents the material from reacting with the air that would normally be present.

The Core Principle: Displacing Reactive Elements
The Problem: Heat and Oxygen
Most materials, especially metals, will readily react with oxygen when heated. This process, known as oxidation, can form a layer of scale on the surface, alter the material's properties, and compromise the final product's quality.
Heat acts as a catalyst, dramatically accelerating these unwanted chemical reactions. Even trace amounts of oxygen or moisture can cause significant contamination at the high temperatures used in many furnace processes.
The Solution: A Protective Gas Shield
An inert atmosphere furnace solves this problem through displacement. By continuously pumping an inert gas into a sealed chamber, the lighter, ambient air containing oxygen and water vapor is pushed out.
This establishes a stable, positive-pressure environment composed almost entirely of the non-reactive gas. The material inside is therefore shielded from any elements that could cause oxidation or other contamination.
Common Inert Gases
The most common gases used are nitrogen (N₂) and argon (Ar). Nitrogen is often chosen for its cost-effectiveness, while argon, being denser and even more inert, is used for highly sensitive materials where absolute purity is critical.
Anatomy of an Inert Atmosphere Furnace
The Sealed Chamber: The First Line of Defense
The foundation of the system is an airtight heating chamber, often a muffle furnace design. It is constructed from refractory materials like ceramics or specialized metals to withstand extreme temperatures while preventing outside air from leaking in.
The Gas Supply System: Creating the Atmosphere
This system delivers a continuous, controlled flow of high-purity inert gas into the chamber. It is critical for both purging the initial air and maintaining a slight positive pressure throughout the heating and cooling cycle to prevent any contamination.
The Heating Mechanism: Applying Controlled Heat
Electric heating elements or gas burners provide the required temperature. These are managed by advanced control systems that work in concert with the gas flow to ensure the material undergoes the precise thermal process required.
Control and Exhaust Systems: Maintaining Purity
Sophisticated sensors monitor and regulate both temperature and gas flow rates. An exhaust system safely vents the purged gases and any potential byproducts, maintaining a clean and stable atmosphere inside the furnace.
Understanding the Benefits and Trade-offs
Benefit: Prevention of Oxidation and Contamination
The primary advantage is a clean, bright finish on the material, free from scale or discoloration. This is essential for applications in electronics, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing.
Benefit: Enhanced Material Integrity
By preventing unwanted chemical reactions, the fundamental properties of the material are preserved. This ensures the final product meets its specified mechanical, electrical, and chemical performance standards.
Benefit: Improved Process Efficiency
Materials treated in an inert atmosphere often require no secondary cleaning steps like sandblasting, grinding, or acid pickling. This reduction in post-processing saves time, labor, and cost.
The Trade-off: Complexity and Operational Cost
The main trade-off is increased complexity and cost compared to a standard air furnace. These systems require sealed chambers, gas management hardware, and a continuous supply of inert gas, which represents an ongoing operational expense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Deciding whether to use an inert atmosphere depends entirely on the material and the desired outcome of your heat-treatment process.
- If your primary focus is material purity and preventing oxidation: An inert atmosphere is essential for processes like annealing, brazing, or sintering sensitive metals and advanced materials.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment where surface oxidation is acceptable: A standard air furnace may be a more cost-effective solution, especially if a subsequent cleaning step is already part of your workflow.
- If your primary focus is to induce a specific surface reaction: You need a reactive atmosphere (e.g., hydrogen for reduction or methane for carburizing), not an inert one.
Ultimately, mastering your thermal process begins with mastering its atmosphere.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Uses non-reactive gases to displace oxygen and moisture, creating a protective shield. |
| Common Gases | Nitrogen (cost-effective), Argon (high purity for sensitive materials). |
| Key Benefits | Prevents oxidation, maintains material integrity, reduces post-processing needs. |
| Trade-offs | Higher complexity and operational costs due to sealed chambers and gas supply. |
Upgrade your lab's thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance material purity and efficiency in your heat-treatment processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity



















