The fundamental environmental benefit of using inert gases in furnaces is the proactive prevention of oxidation. This single act eliminates the need for subsequent, environmentally damaging processes, such as chemical cleaning, which in turn reduces energy consumption, lowers emissions, and prevents the generation of toxic waste.
By shifting from a reactive strategy of cleaning up oxidation after it forms to a proactive one of preventing it from ever occurring, manufacturers can eliminate entire categories of hazardous materials and energy-intensive processes from their operations.

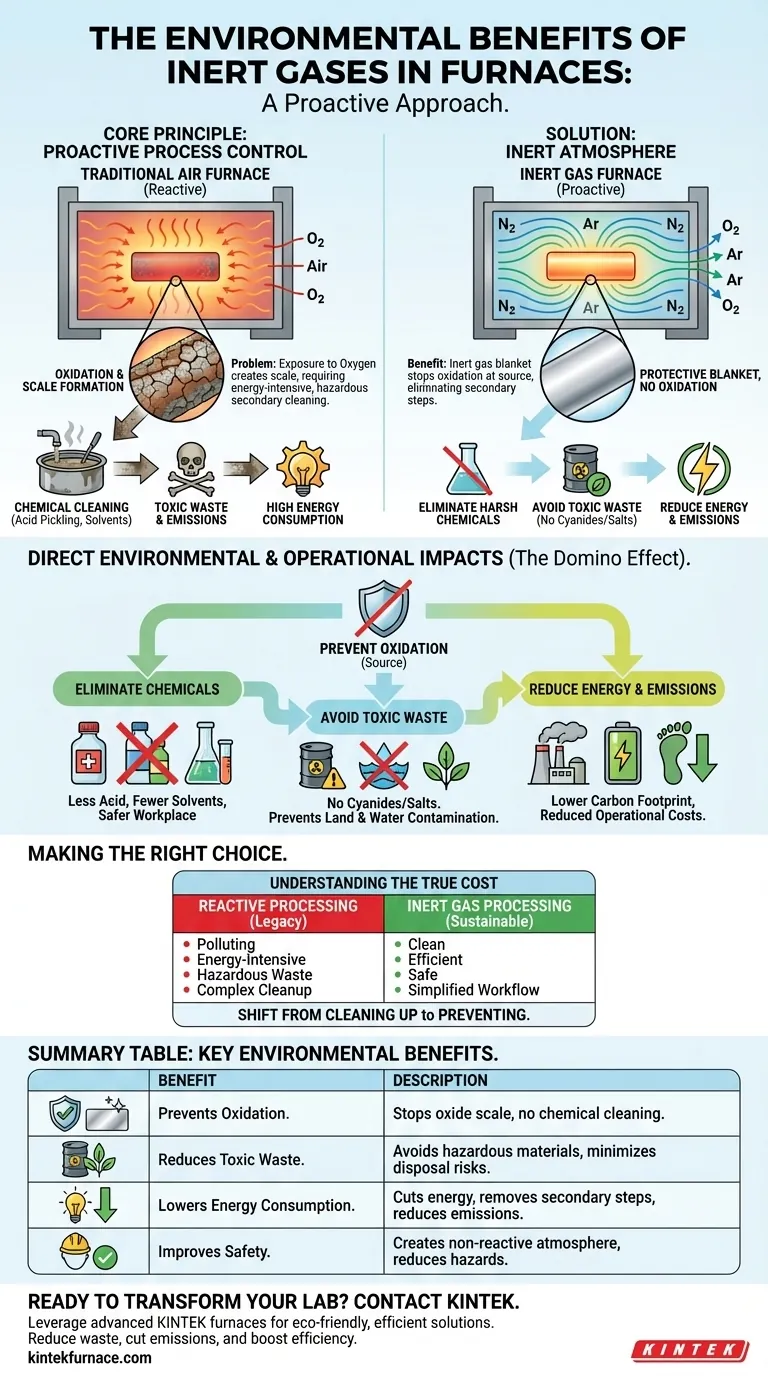
The Core Principle: Proactive Process Control
Industrial furnaces operating with ambient air expose heated materials to oxygen, causing undesirable chemical reactions. Inert gas atmospheres fundamentally change this dynamic by creating a controlled, non-reactive environment.
What is Oxidation in a Furnace?
When metals are heated in the presence of oxygen, they form a layer of oxide scale on their surface. This scale is a form of corrosion that can compromise the material's integrity, dimensions, and finish.
Removing this oxide scale requires secondary processes, such as acid pickling or abrasive blasting, which have significant environmental and financial costs.
How Inert Gases Create a Protective Atmosphere
Inert gases, most commonly nitrogen and argon, are used to purge oxygen from the furnace chamber. Because these gases are chemically non-reactive, they form a protective blanket around the workpiece.
This inert atmosphere prevents oxygen from reaching the hot metal surface, thereby stopping oxidation before it can even begin.
Direct Environmental and Operational Impacts
Preventing oxidation at the source creates a domino effect of positive environmental outcomes by simplifying the entire manufacturing workflow.
Eliminating Harsh Chemical Use
The most significant benefit is the reduced or eliminated need for harsh chemicals to remove oxide scale. This means less acid, fewer solvents, and a safer workplace.
Avoiding Toxic Waste Disposal
Older heat-treatment methods sometimes relied on processes involving toxic salts, such as cyanides. Using an inert atmosphere completely avoids these hazardous materials.
This eliminates the immense challenge and liability associated with disposing of waste salts, contaminated water, and even contaminated equipment like jigs and fixtures.
Reducing Energy Consumption and Emissions
Post-treatment cleaning processes are energy-intensive. By producing a clean part directly from the furnace, you eliminate the energy required for secondary cleaning, washing, and drying steps.
This reduction in energy use directly translates to a lower carbon footprint and reduced operational costs.
Understanding the True Cost of Reactive Processing
The decision to use an inert atmosphere is not just an upgrade; it is a strategic move away from a legacy of environmental hazards. The "trade-off" is between a clean, preventative method and a dirty, reactive one.
The Problem of Land and Water Contamination
The disposal of waste from chemical cleaning and salt bath processes poses a direct threat to the environment. Accidental spills or improper disposal of cyanides and acidic waste can lead to long-term land and water contamination.
The Burden of Secondary Waste Streams
Reactive processing creates multiple waste streams that must be managed. This includes not only the toxic chemicals themselves but also contaminated rinse water and "pack carburising" waste.
Each of these streams adds complexity, cost, and environmental risk to the operation. Inert gas processing, by its nature, generates virtually none of this secondary waste.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Adopting an inert gas atmosphere is a strategic decision that aligns operational efficiency with environmental responsibility.
- If your primary focus is eliminating hazardous waste: Using an inert atmosphere is the most effective way to remove toxic salts and corrosive acids from your process entirely.
- If your primary focus is reducing your carbon footprint: Preventing oxidation eliminates the energy-intensive secondary cleaning steps, directly lowering your energy consumption and associated emissions.
- If your primary focus is product quality and efficiency: An inert atmosphere produces cleaner parts with superior material properties, reducing rework and simplifying the entire production line.
Ultimately, using an inert atmosphere allows you to build a cleaner, safer, and more efficient process from the ground up.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Prevents Oxidation | Stops oxide scale formation, eliminating need for chemical cleaning. |
| Reduces Toxic Waste | Avoids hazardous materials like cyanides and acids, minimizing disposal risks. |
| Lowers Energy Consumption | Cuts energy use by removing secondary cleaning processes, reducing emissions. |
| Improves Safety | Creates a non-reactive atmosphere, reducing workplace hazards and contamination. |
Ready to transform your lab with eco-friendly furnace solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, helping you reduce waste, cut emissions, and boost efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your sustainability goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.



















