In a furnace, nitrogen is primarily used to create a controlled, non-reactive (inert) atmosphere. Its main function is to displace atmospheric oxygen and moisture, which prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation and scaling that would otherwise damage the material being heat-treated.
Using nitrogen in a furnace isn't about adding something to the process; it's about removing something destructive: oxygen. By replacing the reactive air with inert nitrogen, you create a protective shield that preserves the integrity and surface quality of the metal during high-temperature treatment.

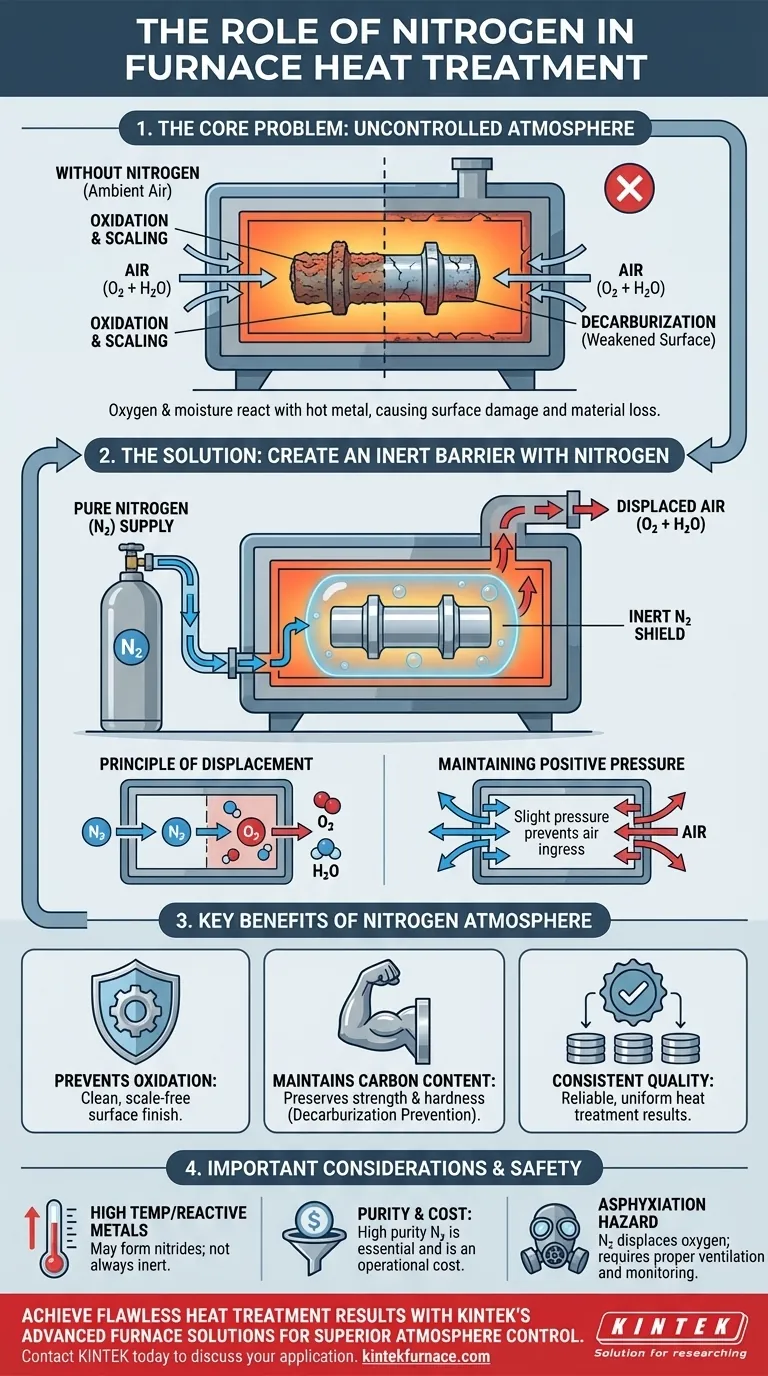
The Core Problem: Uncontrolled Furnace Atmospheres
When a material like steel is heated to several hundred degrees, its chemical reactivity increases dramatically. The normal air we breathe becomes a significant threat to the quality of the final product.
The Threat of Oxidation
At high temperatures, oxygen in the air aggressively reacts with metals, especially ferrous alloys like steel. This reaction, oxidation, forms a layer of scale or oxide on the metal's surface.
This oxide layer is detrimental. It leads to material loss, a poor surface finish, and can interfere with subsequent processes like coating or welding.
The Danger of Decarburization
For many steels, the carbon content is critical to its strength and hardness. Oxygen in a hot furnace atmosphere can react with the carbon within the steel itself, pulling it out of the surface.
This process, known as decarburization, leaves a soft, weakened layer on the component's exterior, potentially leading to premature part failure.
Why Ambient Air is the Enemy
Ambient air is approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and contains variable amounts of water vapor. Both oxygen and water vapor are powerful oxidizing agents at the temperatures used in heat treatment, making an uncontrolled furnace a highly corrosive environment.
How Nitrogen Solves the Problem
Introducing pure nitrogen into the furnace directly counteracts the threats posed by ambient air. It works through a simple but effective principle.
Creating an Inert Barrier
Nitrogen gas (N₂) is exceptionally stable and non-reactive at most heat-treating temperatures due to the strong triple bond holding its two atoms together. This inert quality means it won't react with the metal being processed.
The Principle of Displacement
By continuously feeding nitrogen gas into a sealed furnace, you physically push out, or displace, the ambient air. This purge removes the problematic oxygen and moisture from the environment surrounding the hot metal parts.
Maintaining Positive Pressure
Once the furnace is purged, a low flow of nitrogen is maintained. This creates a slight positive pressure inside the furnace. If any minor leaks exist in the furnace seals, the positive pressure ensures that nitrogen flows out, preventing destructive oxygen from leaking in.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While highly effective, using nitrogen is not without its own set of considerations. An objective analysis requires understanding its limitations.
Not Always Perfectly Inert
At very high temperatures, or with highly reactive metals like titanium, aluminum, or certain high-chromium stainless steels, nitrogen can cease to be inert. It can react to form nitrides on the metal's surface, which can sometimes cause embrittlement.
Purity and Cost
The effectiveness of a nitrogen atmosphere depends on its purity. Even a small percentage of oxygen contamination can be enough to cause surface discoloration or light oxidation. Achieving and maintaining high-purity nitrogen, whether from bulk liquid tanks or on-site generation, represents a significant operational cost.
Critical Safety Considerations
Nitrogen is a colorless, odorless gas that displaces oxygen. In a confined space, a nitrogen leak can create an oxygen-deficient atmosphere, posing a severe asphyxiation hazard to personnel. Proper ventilation, sealing, and oxygen monitoring are non-negotiable safety requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The goal of your furnace atmosphere dictates its composition. Nitrogen is a foundational tool for achieving specific outcomes.
- If your primary focus is preventing general oxidation and decarburization on carbon steels: A high-purity nitrogen atmosphere is the industry-standard solution for a clean, protective environment.
- If your primary focus is treating highly sensitive alloys or achieving the brightest possible finish: You may need a nitrogen-hydrogen blend (a "reducing" atmosphere) to actively scavenge any trace amounts of remaining oxygen.
- If your primary focus is intentionally hardening the surface of a part: You will use a specialized reactive atmosphere, such as in a nitriding process, where nitrogen is a key ingredient intended to react with the steel.
Ultimately, controlling the furnace atmosphere with nitrogen gives you direct command over the quality, consistency, and final properties of your product.
Summary Table:
| Purpose of Nitrogen in a Furnace | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Displaces Oxygen & Moisture | Prevents oxidation and scaling on metal surfaces |
| Creates an Inert Atmosphere | Protects material integrity during high-temperature processing |
| Prevents Decarburization | Maintains critical carbon content in steel for strength and hardness |
| Maintains Positive Pressure | Ensures a consistent, protective environment by preventing air ingress |
Achieve Flawless Heat Treatment Results with KINTEK
Precise atmosphere control is the key to consistent, high-quality outcomes in your heat treatment processes. Just as this article explains the critical role of nitrogen, having the right furnace technology is equally important.
KINTEK delivers advanced furnace solutions designed for superior atmosphere control:
- Precision-Engineered Furnaces: Our Muffle, Tube, Vacuum, and Atmosphere Furnaces are built with exceptional sealing and gas flow management to maintain the exact environment your materials require.
- Strong In-House Customization: Leveraging our exceptional R&D and manufacturing capabilities, we tailor furnace systems to your unique process needs, whether you require high-purity inert atmospheres or complex gas mixtures.
Stop letting uncontrolled atmospheres compromise your product quality. Let our experts help you select or custom-build a furnace solution that guarantees the results you need.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and discover the perfect furnace for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance



















