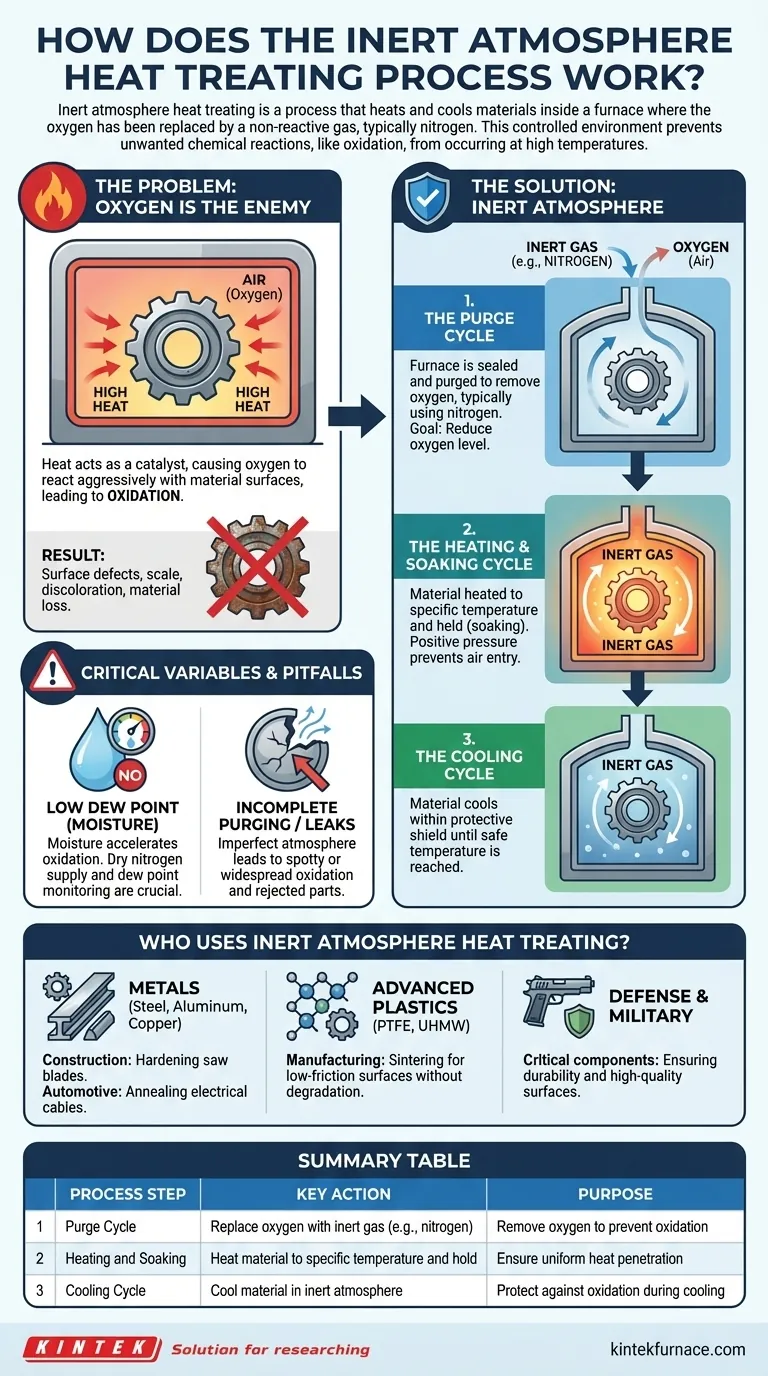
Inert atmosphere heat treating is a process that heats and cools materials inside a furnace where the oxygen has been replaced by a non-reactive gas, typically nitrogen. This controlled environment prevents unwanted chemical reactions, like oxidation, from occurring at high temperatures. The process ensures the material's surface quality and structural properties are preserved.
At its core, heat treating in an inert atmosphere is about creating a protective shield. By removing oxygen—the primary agent of corrosion and surface damage at high temperatures—you gain precise control over the final outcome of the material, from its appearance to its performance.

The Fundamental Problem: Why Oxygen Is the Enemy
At room temperature, the oxygen in the air is relatively harmless to most materials. However, introducing high heat dramatically changes this relationship, turning a benign environment into a destructive one.
Oxidation at High Temperatures
Heat acts as a catalyst for chemical reactions. When a material like steel or aluminum is heated in normal air, the elevated temperature causes the oxygen to react aggressively with its surface.
This reaction is known as oxidation. It leads to the formation of an oxide layer, which can range from simple discoloration to a thick, flaky scale on the surface of the part.
The Consequences of Oxidation
Oxidation is rarely desirable. For aluminum, a thickening oxide layer can make the part unsuitable for its intended application. For steel, it results in surface defects and material loss.
These unwanted surface changes often mean the part will be rejected or require costly and time-consuming secondary operations like grinding, polishing, or chemical cleaning to remove the damaged layer.
The Inert Atmosphere Solution: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Inert atmosphere heat treating directly solves the oxidation problem by systematically removing oxygen from the equation. The process follows three critical phases.
Step 1: The Purge Cycle
Before any heating begins, the furnace is sealed and purged with an inert gas. Nitrogen is the most common choice due to its availability and cost-effectiveness.
This "cover gas" is pumped into the furnace, displacing the oxygen-rich air. The goal is to reduce the internal oxygen level to a point where it can no longer react with the material during heating.
Step 2: The Heating and Soaking Cycle
Once the oxygen is sufficiently purged, the heating cycle begins. The material is brought to a specific temperature and often held there for a set period—a process known as soaking—to ensure the heat penetrates the entire part.
Throughout this phase, a slight positive pressure of the inert gas is maintained inside the furnace. This prevents any outside air from leaking in and re-contaminating the environment.
Step 3: The Cooling Cycle
The protective atmosphere is maintained even as the material cools. A part is often most vulnerable to oxidation at high temperatures, so removing it from the inert environment while still hot would undo the benefits of the process.
The material is cooled within the nitrogen shield until it reaches a temperature where it will no longer react with air.
Common Pitfalls and Critical Variables
Simply using an inert gas is not enough. The success of the process depends on carefully controlling variables that can compromise the protective atmosphere.
The Importance of a Low Dew Point
Moisture is a hidden accelerant for oxidation. The amount of water vapor in the atmosphere, measured as the dew point, can significantly impact the final surface quality.
Even with very low oxygen levels, high moisture content can increase the reactivity of any remaining oxygen. For this reason, using a dry nitrogen supply and monitoring the dew point is critical for achieving the best results.
Incomplete Purging or Furnace Leaks
The most common failure point is an imperfect atmosphere. If the initial purge cycle is too short or the furnace has leaks in its seals, oxygen can remain in or re-enter the chamber.
This leads to spotty or widespread oxidation, defeating the purpose of the treatment and often resulting in rejected parts.
Who Uses Inert Atmosphere Heat Treating?
This process is vital across numerous industries where material integrity is non-negotiable. It is highly versatile and applicable to both metals and advanced polymers.
Metals: Steel, Aluminum, and Copper
For metals, the goal is often to preserve a clean, bright surface finish or protect specific properties.
- Construction: Hardening steel for saw blades without creating scale.
- Automotive: Annealing (softening) aluminum electrical cables without compromising their conductive surface.
Advanced Plastics: PTFE and UHMW
Certain plastics, such as PTFE (Teflon) and Ultra-High Molecular Weight (UHMW) polyethylene, are damaged by oxygen when heated.
- Manufacturing: Sintering these plastics in a nitrogen atmosphere is essential to create parts with a low-friction surface without degrading the polymer's structure.
Defense and Military Applications
The process is also used for critical components where performance and reliability are paramount, such as finishing gun barrels to ensure durability and a high-quality surface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
Your specific goal will determine which aspects of the process require the most attention.
- If your primary focus is preserving a pristine surface finish: You must ensure a thorough purge cycle and maintain a low dew point to prevent any and all discoloration.
- If your primary focus is maintaining specific mechanical or electrical properties: Controlling both the temperature profile and the purity of the inert atmosphere is equally critical to prevent unwanted surface reactions.
- If your primary focus is processing temperature-sensitive plastics like PTFE: An inert atmosphere is not optional; it is essential to prevent material degradation and achieve the desired characteristics.
By controlling the environment, you gain complete control over your material's final properties and quality.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Purge Cycle | Replace oxygen with inert gas (e.g., nitrogen) | Remove oxygen to prevent oxidation |
| Heating and Soaking | Heat material to specific temperature and hold | Ensure uniform heat penetration |
| Cooling Cycle | Cool material in inert atmosphere | Protect against oxidation during cooling |
Ready to enhance your material processing with precise heat treating? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, tailored for industries like automotive, construction, and defense. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring optimal performance and quality. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can benefit your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.



















