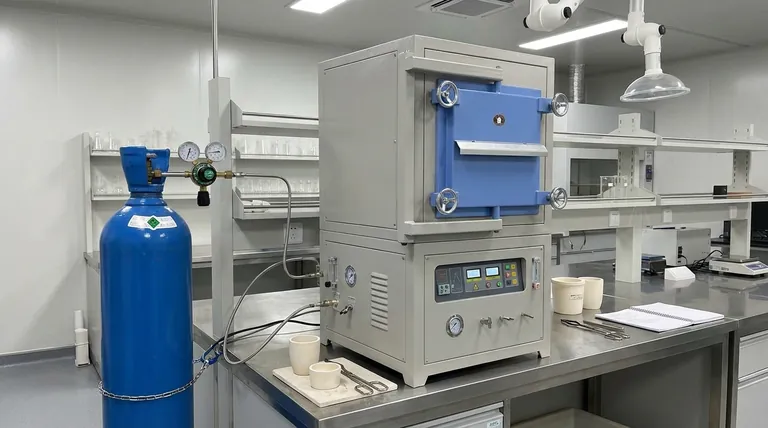
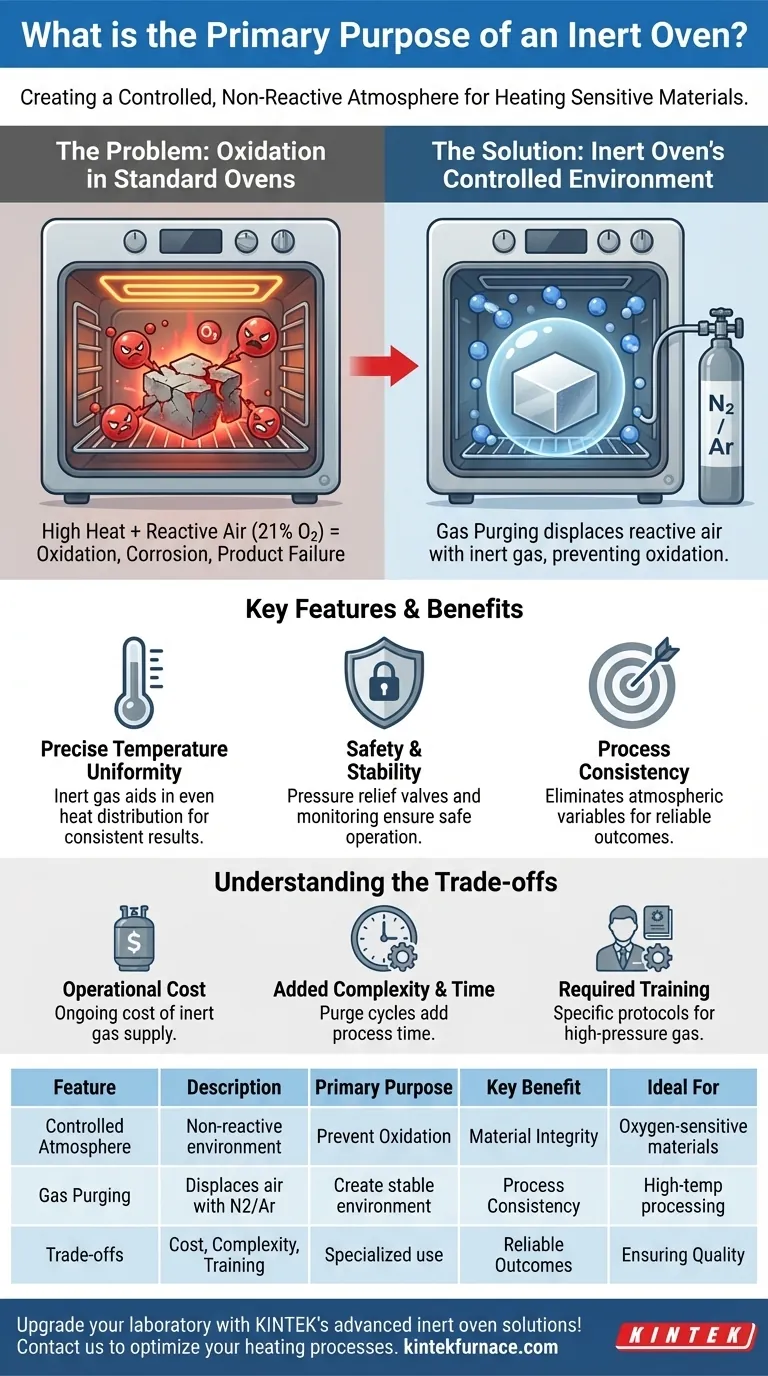
At its core, an inert oven serves one critical function: to create a controlled, non-reactive atmosphere for heating processes. Its primary purpose is to heat sensitive materials without allowing them to be damaged by oxidation, contamination, or other unwanted chemical reactions that occur in the presence of normal air.
For materials that would be damaged by oxygen when heated, a standard oven is a liability. An inert oven solves this by systematically replacing reactive air with an unreactive gas like nitrogen or argon, creating a safe environment for high-temperature processing.

The Fundamental Problem: Oxidation in Standard Ovens
To understand the value of an inert oven, you must first understand the problem it solves. The air we breathe is a liability in many industrial and scientific heating applications.
Why Normal Air Is a Problem
The atmosphere is roughly 21% oxygen, a highly reactive gas. While essential for life, this reactivity becomes a significant issue at elevated temperatures.
When heated in the presence of oxygen, many materials undergo oxidation. This chemical reaction can degrade, damage, or completely alter the properties of the material being processed.
The Impact of an Uncontrolled Atmosphere
Heating in a standard, air-filled oven can lead to a range of undesirable outcomes. Metals can corrode, electronic components can fail, and polymers can become brittle.
This lack of atmospheric control introduces variables that reduce the quality and consistency of the final product, leading to higher failure rates and unreliable results.
How Inert Ovens Create a Controlled Environment
An inert oven is a specialized piece of equipment engineered to counteract the threat of atmospheric reactivity through several key features.
The Role of Gas Purging
The defining feature of an inert oven is its gas purging system. The process begins by sealing the oven chamber.
An inert gas, most commonly nitrogen or argon, is then introduced into the chamber. This new gas displaces, or "purges," the reactive oxygen and moisture, leaving behind a stable, non-reactive environment for the heating process.
Maintaining Precise Temperature
Beyond atmospheric control, these ovens provide precise temperature uniformity. The inert gas itself can aid in distributing heat more evenly throughout the chamber than air alone.
This combination of atmospheric and thermal control ensures that the material is processed under exact, repeatable conditions.
Ensuring Safety and Stability
Operating with pressurized gas requires robust safety measures. Inert ovens are equipped with pressure relief valves to prevent over-pressurization and gas monitoring systems to ensure the integrity of the inert atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, an inert oven is a specialized tool with specific considerations. It is not a universal replacement for all heating applications.
The Operational Cost of Inert Gas
The primary trade-off is the ongoing cost of the inert gas. Unlike a standard oven that uses free ambient air, an inert oven consumes nitrogen or argon, which must be supplied from tanks or an on-site generator.
Added Complexity and Cycle Time
The gas purging cycle adds time and complexity to the overall process. Operators cannot simply open the door and place a part inside; they must run the purge cycle before heating and often must wait for the oven to cool before safely opening it.
Required Training and Safety Protocols
Handling high-pressure gas cylinders and monitoring a sealed system requires specific training. The safety protocols are more involved than those for a standard convection oven, which must be factored into any operational plan.
Is an Inert Oven Right for Your Process?
Choosing the right heating equipment depends entirely on the sensitivity of your materials and the goals of your process.
- If your primary focus is working with oxygen-sensitive materials: An inert oven is not just beneficial—it is essential to prevent oxidation and ensure material integrity.
- If your primary focus is ensuring maximum product consistency: The controlled atmosphere of an inert oven eliminates a major process variable, leading to more repeatable and reliable outcomes.
- If your primary focus is simple drying or curing of non-reactive materials: A standard convection or vacuum oven is likely a more cost-effective and straightforward solution.
Ultimately, an inert oven provides absolute control over the heating environment, protecting your most sensitive processes from the invisible threat of atmospheric reaction.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Creates a controlled, non-reactive atmosphere for heating sensitive materials |
| Key Benefit | Prevents oxidation, contamination, and unwanted chemical reactions |
| Common Gases Used | Nitrogen, Argon |
| Ideal For | Oxygen-sensitive materials, high-temperature processing, and ensuring product consistency |
| Trade-offs | Higher operational costs due to gas usage, added process complexity, and need for safety training |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced inert oven solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, protecting sensitive materials from oxidation and enhancing process reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heating processes and deliver tailored solutions for your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance



















