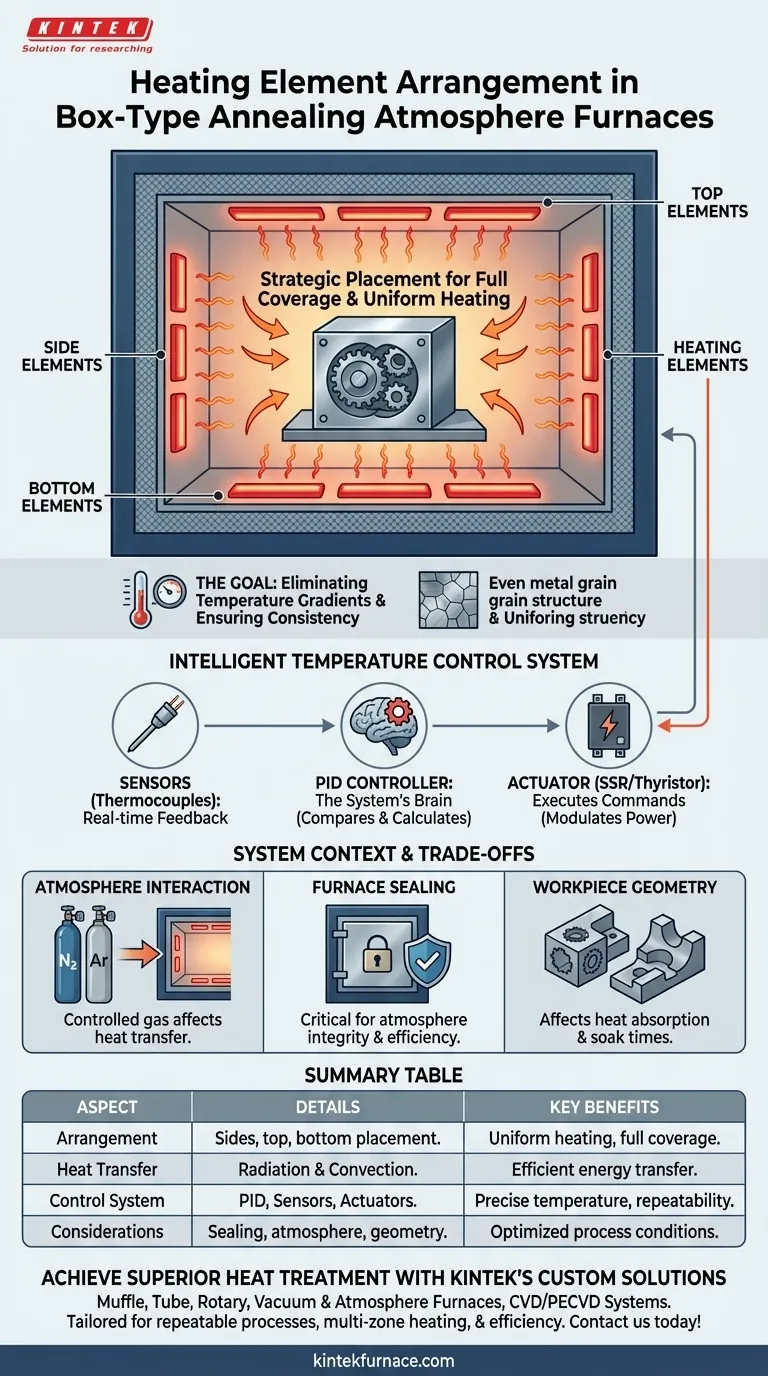
In a box-type annealing atmosphere furnace, the heating elements are strategically placed to surround the workload. They are arranged on the sides, at the top, and/or at the bottom of the furnace chamber. This distributed layout is the foundation for achieving the uniform temperature required for high-quality heat treatment.
The physical placement of heating elements is only the first step. True temperature uniformity is achieved by combining this distributed layout with a sophisticated, real-time temperature control system that constantly adjusts power based on sensor feedback.

The Principle of Uniform Heating
The core engineering goal behind the heating element arrangement is to eliminate temperature variations within the furnace chamber. Any significant temperature difference, or "hot spot," can lead to inconsistent material properties in the final workpiece.
Strategic Placement for Full Coverage
By positioning heating elements on multiple faces of the furnace interior (sides, top, bottom), the design ensures that no part of the workload is too far from a heat source. This layout envelops the workpiece in heat.
Heat Transfer Mechanisms
This arrangement primarily uses two methods to transfer energy to the workpiece:
- Radiation: The elements glow at high temperatures, radiating thermal energy in all directions, which is absorbed by the workpiece surfaces.
- Convection: The elements heat the controlled atmosphere gas inside the furnace, which then circulates and transfers heat to the workpiece.
The Goal: Eliminating Temperature Gradients
For processes like annealing, even a small temperature gradient across a metal part can result in uneven grain growth or incomplete stress relief. The multi-sided element arrangement is specifically designed to deliver equal heating from all directions, ensuring the entire workpiece reaches and holds the target temperature uniformly.
How Precise Temperature is Maintained
The physical layout of the elements works in tandem with an intelligent control system. This system acts as the furnace's brain, ensuring the temperature doesn't just get hot, but stays precisely at the setpoint.
The Role of Temperature Sensors
Thermocouples or other sensors are placed inside the furnace chamber to provide constant, real-time temperature data. This feedback is the critical input for the control system.
The PID Controller: The System's Brain
The temperature controller, typically using a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) algorithm, processes the data from the sensors. It compares the actual temperature to the desired setpoint and calculates the precise amount of power needed to correct any deviation.
Actuators: Executing Commands
The controller sends its commands to an actuator, such as a thyristor regulator or solid-state relay (SSR). This device modulates the electrical power flowing to the heating elements, increasing or decreasing their output to maintain the exact temperature required by the process.
Understanding the System Context and Trade-offs
The heating element arrangement does not operate in a vacuum. Its effectiveness is directly tied to the furnace's overall design and the specific application.
Interaction with the Controlled Atmosphere
The type of gas used for the controlled atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen, argon) has its own thermal properties. The control system must account for how this gas helps or hinders heat transfer to ensure accurate temperature management.
The Importance of Furnace Sealing
A reliable seal on the furnace door is critical. Any leak allows the controlled atmosphere to escape and outside air to enter, which not only compromises the material treatment but also causes heat loss and temperature instability, forcing the heating system to work harder.
Workpiece Geometry Matters
While the furnace provides a uniform heating environment, the size and shape of the workpiece itself can affect how it absorbs heat. Large or complex parts may require longer soak times or specialized loading racks to ensure their core temperature matches the surface temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The design of the heating and control system should align with your specific material processing needs.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: Prioritize a furnace with a high-quality PID controller and multiple, well-placed temperature sensors for the most accurate feedback and control.
- If your primary focus is treating complex shapes: Inquire about furnaces with multi-zone heating, where different banks of elements can be controlled independently to deliver tailored heat to different areas.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Closely evaluate the quality of the furnace's insulation and door seals, as this directly impacts energy consumption and atmosphere usage.
Understanding this interplay between physical design and intelligent control is key to achieving optimal results in your heat treatment processes.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Heating Element Arrangement | Placed on sides, top, and/or bottom of furnace chamber for full coverage |
| Heat Transfer Mechanisms | Radiation and convection from elements to workpiece |
| Temperature Control System | Uses PID controllers, thermocouples, and thyristor regulators for real-time adjustments |
| Key Benefits | Uniform heating, elimination of temperature gradients, improved process repeatability |
| Considerations | Affected by furnace sealing, atmosphere type, and workpiece geometry |
Achieve Superior Heat Treatment with KINTEK's Custom Solutions
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need precise temperature control for repeatable processes, multi-zone heating for complex shapes, or energy-efficient designs, we can tailor a furnace to your needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your heat treatment results and boost your lab's efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment



















