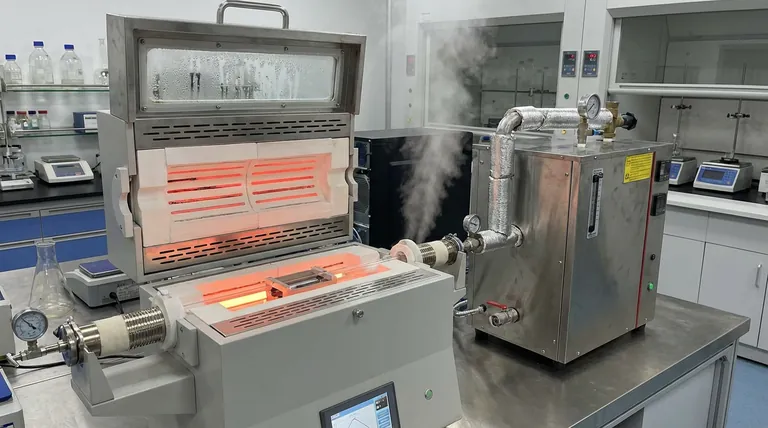
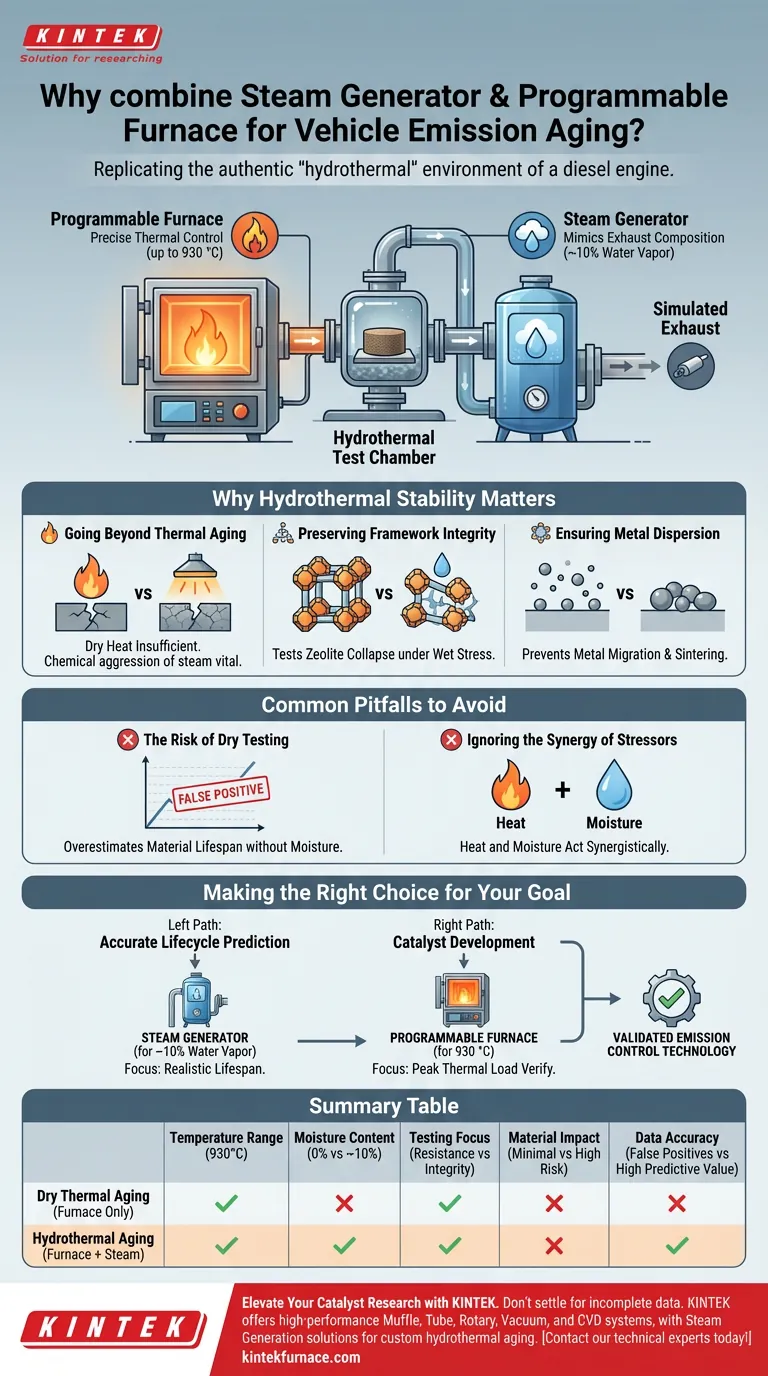
The combination of a steam generator and a programmable furnace is strictly necessary because it replicates the authentic "hydrothermal" environment of a diesel engine. While the programmable furnace provides precise thermal stress testing up to 930 °C, the steam generator introduces the approximately 10% water vapor content inherent in actual exhaust. Without the introduction of moisture via the steam generator, the experiment would only test thermal resistance, failing to capture the far more destructive chemical reality of vehicle emissions.
Real-world combustion exhaust is a harsh mixture of extreme heat and significant moisture. By pairing steam generation with high-temperature furnaces, researchers can test the hydrothermal stability of catalysts, ensuring they maintain their structure and effectiveness under realistic operating conditions.

The Components of Realistic Simulation
Mimicking Exhaust Composition
Combustion byproducts are rarely dry. In diesel engines specifically, the exhaust gas typically contains around 10% water vapor.
To derive valid experimental data, you must replicate this specific atmospheric composition. A steam generator is the only way to introduce this required moisture in a controlled, measurable capacity.
Precision Thermal Control
The programmable furnace serves as the thermal engine of the experiment. It allows researchers to apply precise heating profiles, reaching temperatures as high as 930 °C.
This capability simulates the intense heat spikes an engine experiences under heavy load or during regeneration cycles.
Why Hydrothermal Stability Matters
Going Beyond Thermal Aging
Simple thermal aging (dry heat) is often insufficient for testing emission control materials.
The addition of water vapor creates a hydrothermal environment, which is chemically more aggressive than dry air. Materials that survive dry heat may fail rapidly when moisture facilitates structural degradation.
Preserving Framework Integrity
The primary subject of these tests is often metal zeolites. These materials rely on a specific crystalline structure, or framework, to function.
The steam-furnace combination rigorously tests whether this framework remains intact or collapses under the stress of hot steam.
Ensuring Metal Dispersion
Catalysts rely on active metals being well-distributed (dispersed) across their surface.
Under hydrothermal conditions, these metals can migrate and clump together (sinter), rendering the catalyst ineffective. This experimental setup confirms the material's ability to maintain metal dispersion despite extreme environmental stress.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The Risk of Dry Testing
The most significant error in emission simulation is relying solely on dry thermal treatment.
Data derived without water vapor often yields "false positives," suggesting a material is stable when it would actually fail in a real engine.
Ignoring the Synergy of Stressors
Heat and moisture act synergistically to degrade materials.
Isolating these variables often hides the true degradation mechanism. The programmable furnace and steam generator must be used simultaneously to observe the cumulative effect on the zeolite.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When designing your experimental validation protocols, consider the specific requirements of your material application:
- If your primary focus is accurate lifecycle prediction: You must utilize the steam generator to replicate the ~10% water vapor found in real exhaust, as dry testing will overestimate material lifespan.
- If your primary focus is catalyst development: You should prioritize the programmable furnace's ability to ramp to 930 °C to verify that metal dispersion holds up under peak thermal loads.
Validating emission control technology requires testing against the reality of the engine, where heat and moisture always work together.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Dry Thermal Aging (Furnace Only) | Hydrothermal Aging (Furnace + Steam) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Up to 930 °C | Up to 930 °C |
| Moisture Content | 0% (Dry Air) | ~10% Water Vapor (Simulated Exhaust) |
| Testing Focus | Thermal Resistance | Framework Integrity & Chemical Stability |
| Material Impact | Minimal Structural Stress | High Risk of Zeolite Collapse/Sintering |
| Data Accuracy | Potential "False Positives" | High Real-World Predictive Value |
Elevate Your Catalyst Research with KINTEK
Don't settle for incomplete data from dry thermal testing. To accurately predict the lifespan and efficiency of emission control materials, you need a setup that replicates the harsh reality of diesel exhaust.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized Steam Generation solutions. Our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique hydrothermal aging requirements, ensuring your zeolites and catalysts maintain structural integrity and metal dispersion under peak thermal loads.
Ready to build a more realistic simulation environment? Contact our technical experts today to customize your high-temperature furnace system!
Visual Guide
References
- Konstantin Khivantsev, János Szanyi. Increasing Al-Pair Abundance in SSZ-13 Zeolite via Zeolite Synthesis in the Presence of Alkaline Earth Metal Hydroxide Produces Hydrothermally Stable Co-, Cu- and Pd-SSZ-13 Materials. DOI: 10.3390/catal14010056
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of adding phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5) as a desiccant? Ensure Deep Electrolyte Regeneration
- What industries commonly use batch furnaces? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Electronics
- What is the purpose of coating aluminum electrodes with Au80Pd20? Enhancing Precision in Nanoparticle Characterization
- What are some common applications of industrial furnaces? Discover Key Uses in Manufacturing and Research
- What thermochemical environment does an entrained flow reactor provide? Simulate Industrial Biomass Combustion
- What role does an oscillating furnace play in the synthesis of quaternary Ge-Se-Tl-Sb glass alloys? Ensure Homogeneity
- Why is it necessary to preheat the mold for Mg-8Li-3Al-0.3Si alloy? Unlock Peak Casting Integrity
- What role does a laboratory drying oven play in the formation of polymer colloidal crystal templates? Mastering 3DOM Foundations



















