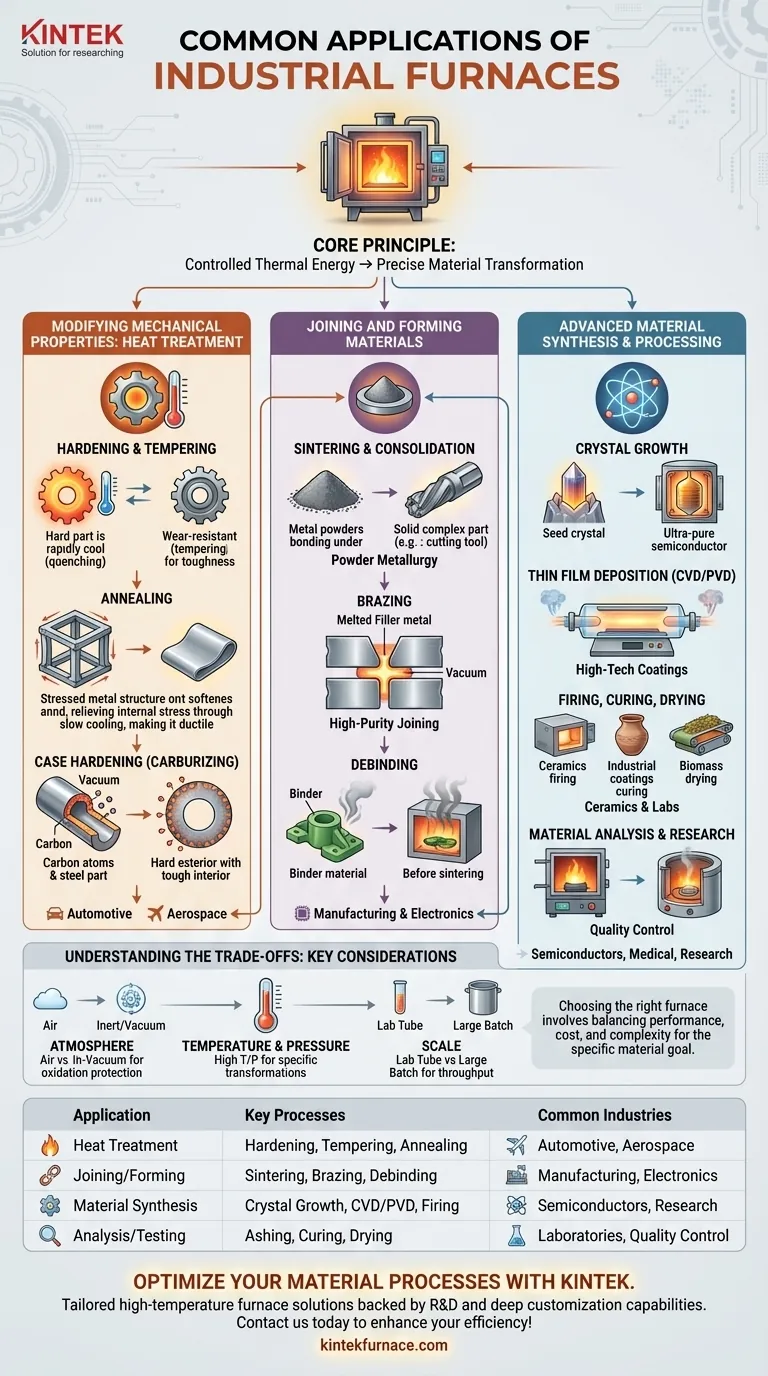
At their core, industrial furnaces use controlled thermal energy to fundamentally change the properties of materials. Their applications range from strengthening metals for automotive parts and creating ultra-pure crystals for semiconductors to testing the composition of petroleum products and firing advanced ceramics for aerospace.
The specific application of an industrial furnace isn't arbitrary; it is always chosen to achieve a precise material transformation. The required temperature, atmospheric conditions (like air, inert gas, or vacuum), and sometimes pressure dictate which process and furnace type are used.

Modifying Mechanical Properties: Heat Treatment
One of the most common uses for industrial furnaces is heat treatment, a group of processes designed to alter the internal structure of metals to improve their strength, toughness, and durability.
Hardening and Tempering
Hardening involves heating a metal (typically steel) to a high temperature and then cooling it rapidly. This process increases the material's hardness and wear resistance.
Tempering is a subsequent, lower-temperature treatment that reduces the brittleness created by hardening, thereby improving the material's overall toughness. These processes are foundational in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Annealing
Annealing is essentially the opposite of hardening. It involves heating a material and cooling it slowly to soften it, relieve internal stresses from manufacturing, and improve its ductility. This makes the material easier to work with in subsequent forming steps.
Case Hardening (Carburizing)
For components that need a highly wear-resistant surface but a tough, impact-resistant core, case hardening is used.
Vacuum carburizing, for example, introduces carbon into the surface layer of a steel part in a vacuum environment, creating an exceptionally hard exterior without compromising the integrity of the interior.
Joining and Forming Materials
Furnaces are also critical for manufacturing solid components, whether by joining separate parts or by consolidating powders into a dense mass.
Sintering and Consolidation
Sintering is a process that uses heat to bond powder-based materials—like metals or ceramics—into a solid, coherent object without melting them.
This technique is central to powder metallurgy for creating complex parts like carbide cutting tools. Hot press furnaces apply both heat and pressure simultaneously for maximum densification.
Brazing
Brazing is a metal-joining process where a filler metal is melted and flows into the gap between two closely fitted parts, creating an exceptionally strong bond upon cooling.
Vacuum brazing is a high-purity version of this process, essential for manufacturing sensitive components like vacuum-sealed switches for the electrical industry.
Debinding
In processes like metal injection molding (MIM), a "binder" material is mixed with metal powder to help form a "green" part. Debinding is the crucial furnace step where this binder is carefully burned or evaporated away before the final sintering phase.
Advanced Material Synthesis and Processing
High-technology industries rely on furnaces for creating and refining the specialized materials that power modern electronics, medical devices, and research.
Crystal Growth
The manufacturing of semiconductors and optical components depends on the ability to grow large, single, ultra-pure crystals. Specialized vacuum furnaces provide the stable, contamination-free environment necessary for this precise process.
Thin Film Deposition (CVD/PVD)
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) are processes that deposit extremely thin layers of material onto a substrate.
Tube and vacuum furnaces are often used to create the high-temperature, controlled-atmosphere environments needed for these coatings, which can provide wear resistance, electrical conductivity, or other special properties.
Firing, Curing, and Drying
Ceramic firing is a classic furnace application used to permanently harden pottery, tiles, and advanced technical ceramics. Box furnaces are common in both labs and production for this purpose.
At lower temperatures, furnaces are also used for drying materials like biomass or food products and for curing industrial coatings and composites.
Material Analysis and Research
In laboratory settings, furnaces are indispensable analytical tools. Ashing furnaces, for instance, are used to burn a sample completely to determine its non-combustible ash content, a key quality metric for materials like coal and oil.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The vast array of furnace applications exists because each process involves a unique set of compromises between performance, cost, and complexity.
The Need for a Controlled Atmosphere
Many standard heat treatments can occur in air. However, at high temperatures, oxygen can react with and damage a material's surface, a process known as oxidation.
Using an inert gas (like argon) or a vacuum prevents this oxidation. Vacuum furnaces provide the ultimate protection against contamination but are significantly more complex and costly than air-fired furnaces. This trade-off is necessary for high-performance aerospace alloys or sensitive electronic materials.
General Purpose vs. Specialized Equipment
A box furnace is a versatile workhorse, capable of performing annealing, hardening, and ceramic firing. However, it may not be the most efficient or precise tool for any single task.
In contrast, a hot press furnace is highly specialized for sintering under pressure. It does one job perfectly but lacks the flexibility of a box furnace. The choice depends on whether the user needs a multi-tool or a scalpel.
Scale and Throughput
The physical design of a furnace dictates its application. A small tube furnace is ideal for processing a few small samples with high uniformity in a research lab.
Conversely, a large batch furnace is designed for the high-throughput heat treatment of thousands of automotive parts at once. The application must match the required production scale.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right furnace application, you must first define the desired change in your material.
- If your primary focus is improving metal performance: You will likely use heat treatment processes like hardening, annealing, or case hardening.
- If your primary focus is creating solid parts from powders: Sintering is your key process, often preceded by debinding in a controlled atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is advanced electronics or aerospace: You will require processes in high-purity environments, such as vacuum brazing, crystal growth, or CVD.
- If your primary focus is general lab research or testing: Versatile box or tube furnaces provide an essential platform for a wide range of analytical and synthesis tasks.
Ultimately, selecting the right industrial furnace application begins with a clear understanding of the material transformation you need to achieve.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Common Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Hardening, Tempering, Annealing | Automotive, Aerospace |
| Joining and Forming | Sintering, Brazing, Debinding | Manufacturing, Electronics |
| Material Synthesis | Crystal Growth, CVD/PVD, Firing | Semiconductors, Research |
| Analysis and Testing | Ashing, Curing, Drying | Laboratories, Quality Control |
Ready to optimize your material processes with the right furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements in industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a Quartz Tube Furnace and what is its primary function? Essential for Real-Time Material Observation
- What is the necessity of using vacuum-sealed quartz tubes? Ensuring Integrity in Ti-Cu Alloy Heat Treatment
- What are the key features of a quartz tube furnace? Discover High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- What is a quartz tube furnace and what is its primary use? Essential for Controlled High-Temp Processing
- How does the work process of a quartz tube furnace typically proceed? Master Precision Heating for Advanced Materials



















