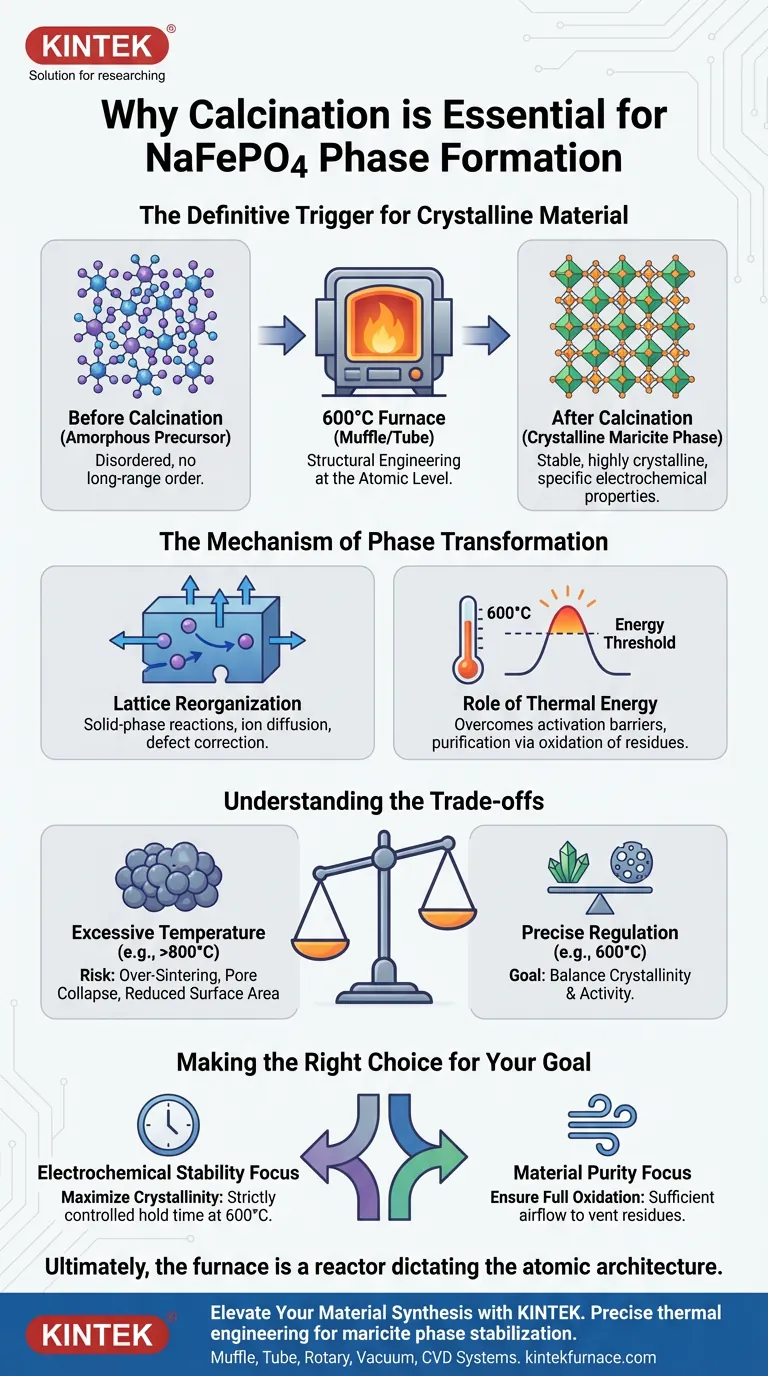
The calcination step is the definitive trigger that transforms sodium iron phosphate (NaFePO4) from a disordered, amorphous precursor into a functional, crystalline material. By subjecting the raw material to a sustained temperature of 600°C, the furnace drives the solid-phase reactions and atomic lattice reorganization necessary to stabilize the maricite phase.
The primary function of calcination is not merely drying, but structural engineering at the atomic level. It provides the thermodynamic energy required to reorganize the internal lattice of the material, ensuring high crystallinity and the specific electrochemical properties needed for performance.

The Mechanism of Phase Transformation
Transitioning from Amorphous to Crystalline
Before calcination, the sodium iron phosphate precursor exists as an amorphous mixture. In this state, the atoms lack the long-range order required for stable chemical behavior.
The high-temperature environment of a muffle or tube furnace forces these atoms to align into a repeating geometric pattern. This transition creates the stable maricite phase, which is the specific crystalline structure required for the material's intended application.
Lattice Reorganization
Heat treatment induces solid-phase reactions. This process allows ions to diffuse and rearrange themselves within the solid structure without melting the material.
This reorganization corrects defects in the atomic lattice. The result is a material with high structural integrity and the specific electronic pathways necessary for electrochemical activity.
The Role of Thermal Energy
Overcoming Activation Barriers
Phase transformation requires a specific energy threshold. The furnace provides a controlled environment at 600°C, which supplies the necessary activation energy to break initial bonds and form new, stable crystalline bonds.
Without reaching this specific temperature, the material would remain kinetically trapped in a disordered state. The extended duration of the heating process ensures the reaction propagates through the entire bulk of the material, not just the surface.
Purification via Thermal Oxidation
While the primary goal is crystallization, the high-temperature environment also serves a purification role. It facilitates the removal of volatile components and residual organic impurities trapped in the precursor.
By burning off these residues, the furnace ensures that the final crystal lattice is pure. This prevents foreign substances from interfering with the material's electrochemical performance or structural stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Over-Sintering
While heat is essential, excessive temperature can be detrimental. As seen in general catalyst preparation, temperatures significantly higher than the optimal set point (e.g., 800°C) can lead to severe sintering.
Sintering causes particles to fuse together aggressively, leading to a collapse of the pore structure. This reduces the specific surface area and can degrade the active sites required for reactivity.
Balancing Crystallinity and Activity
There is often a tension between achieving perfect crystallinity and maintaining surface activity. Higher temperatures generally improve crystal perfection but may reduce surface area.
Precise temperature regulation within the furnace is the only way to navigate this trade-off. It ensures the material is crystalline enough to be stable, but not so densified that it loses its functional surface characteristics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the successful synthesis of NaFePO4, you must tailor your furnace parameters to your specific performance metrics.
- If your primary focus is Electrochemical Stability: Prioritize a strictly controlled hold time at 600°C to maximize crystallinity and fully stabilize the maricite phase.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Ensure the furnace allows for sufficient airflow or atmosphere control to fully oxidize and vent organic residues from the precursor.
Ultimately, the furnace is not just a heater; it is a reactor that dictates the fundamental atomic architecture of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Process Component | Role in NaFePO4 Synthesis | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (600°C) | Overcomes activation barriers for bonding | Formation of stable crystalline bonds |
| Lattice Reorganization | Solid-phase ion diffusion and alignment | Stabilization of the maricite phase |
| Impurity Removal | Thermal oxidation of volatile organics | High material purity and lattice integrity |
| Thermal Control | Prevention of aggressive sintering | Maintenance of surface area and active sites |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise thermal engineering is the difference between an amorphous precursor and a high-performance crystalline material. KINTEK provides the advanced heating technology required to stabilize the maricite phase of NaFePO4 with uncompromising accuracy.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your laboratory's unique high-temperature needs.
Ready to optimize your calcination process?
Contact our specialists today to find the perfect furnace solution for your research.
Visual Guide
References
- Krishna Dagadkhair, Paresh H. Salame. Electronic Transport Properties of Carbon‐Encapsulated Maricite NaFePO<sub>4</sub> as Cathode Material for Sodium‐Ion Batteries. DOI: 10.1002/adsu.202500188
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of applying secondary artificial aging heat treatment to aluminum alloy parts? Boost Yield Strength
- Why is a laboratory constant temperature drying oven necessary for biomass adsorbents? Ensure Precision & Integrity
- How does a high-temperature furnace enhance the availability of phosphorus? Unlock 97.5% Solubility via Calcination
- How does a blast drying oven support the preparation of rubidium-doped mesoporous bioactive glass? Optimized Synthesis
- Why is a laboratory drying oven used for cottonseed oil extraction? Achieve Maximum Yield and Accuracy
- Why is 10^-6 mbar pressure required for CZTS PLD? Ensure Pure, High-Efficiency Thin Film Deposition
- What role does thermal processing with precise temperature control and tensile stress play in PVDF fiber stabilization?
- How does temperature control precision affect c-BAs crystal growth? Ensure Lattice Integrity in Two-Week Cycles



















