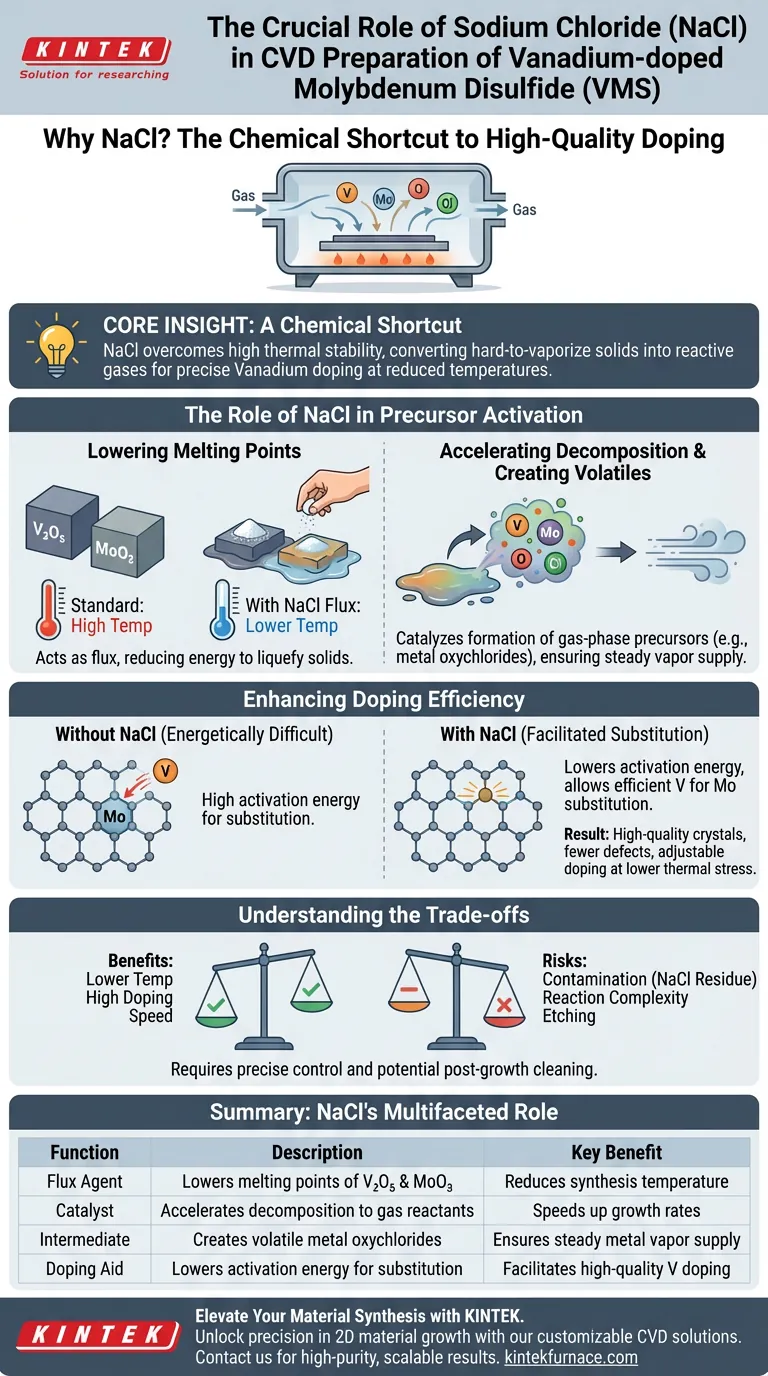
Sodium Chloride (NaCl) serves as a critical flux and catalyst in the synthesis of Vanadium-doped Molybdenum Disulfide (VMS). By significantly lowering the melting points of metal precursors like Vanadium Pentoxide ($V_2O_5$) and Molybdenum Trioxide ($MoO_3$), NaCl accelerates their decomposition into gas-phase reactants. This process enables Vanadium atoms to effectively substitute Molybdenum atoms at reduced temperatures, ensuring high-quality doping without the need for excessive thermal energy.
Core Insight: The addition of NaCl overcomes the high thermal stability of metal oxides, converting hard-to-vaporize solids into reactive gases. This creates a "chemical shortcut" that allows for precise, tunable Vanadium doping at temperatures that preserves the structural integrity of the material.
The Role of NaCl in Precursor Activation
The primary challenge in Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is converting solid source materials into a vapor that can react on the substrate. NaCl plays two distinct roles in overcoming this barrier.
Lowering Melting Points
Standard metal precursors, such as $V_2O_5$ and $MoO_3$, have naturally high melting points.
Without a catalyst, volatilizing these materials requires extremely high temperatures.
NaCl acts as a flux, reducing the thermal energy required to liquefy and evaporate these solids.
Accelerating Decomposition
Beyond simply melting the precursors, NaCl actively catalyzes their decomposition.
It promotes the formation of gas-phase precursors much faster than thermal evaporation alone.
While standard heating might slowly sublime the source, the presence of NaCl triggers a reaction that rapidly releases the metal atoms needed for growth.
Creation of Volatile Intermediates
Drawing on similar CVD chemistry (such as in tungsten synthesis), NaCl likely reacts with the metal oxides to form metal oxychlorides.
These intermediate compounds are significantly more volatile than the original oxides.
This increased volatility ensures a steady, abundant supply of Vanadium and Molybdenum vapor reaching the substrate.
Enhancing Doping Efficiency
The goal of VMS synthesis is not just to grow a crystal, but to substitute specific atoms within the lattice. NaCl is essential for achieving this "substituted doping."
Facilitating Atomic Substitution
For Vanadium-doped Molybdenum Disulfide, Vanadium atoms must replace Molybdenum atoms within the crystal structure.
This substitution is energetically difficult.
NaCl lowers the activation energy for this replacement, allowing Vanadium to substitute Molybdenum efficiently.
Improving Material Quality
Because NaCl lowers the required reaction temperature, the synthesis places less thermal stress on the substrate and the growing crystal.
This results in high-quality crystals with fewer defects compared to those grown at the extreme temperatures required without a flux.
It allows researchers to achieve adjustable doping concentrations, tailoring the material's properties by simply controlling the process parameters.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While NaCl is highly effective, introducing a salt into a high-purity environment introduces specific variables that must be managed.
Contamination Risks
The most immediate trade-off is the potential for residual contamination.
If the NaCl does not fully evaporate or react, salt residues may remain on the substrate or within the sample.
This often necessitates a post-growth cleaning step or precise calibration of the precursor ratios to ensure the salt is fully consumed or vented.
Reaction Complexity
Adding a third chemical species (the salt) adds complexity to the reaction thermodynamics.
It creates a more dynamic environment where the flow rates and temperature zones must be precisely controlled.
Improper control can lead to etching of the substrate or unintended chemical byproducts if the salt concentration is too high.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The use of NaCl is a strategic decision based on the specific requirements of your material synthesis.
- If your primary focus is reducing synthesis temperature: Use NaCl to lower the melting point of your precursors, preserving delicate substrates and saving energy.
- If your primary focus is high doping concentration: Rely on NaCl to increase the supply of gas-phase Vanadium, forcing higher rates of atomic substitution.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high purity: Be aware that using a salt flux requires strict optimization to prevent sodium or chlorine contamination in the final lattice.
NaCl transforms the CVD process from a brute-force thermal evaporation into a chemically assisted, efficient substitution reaction.
Summary Table:
| Role of NaCl | Function Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Flux Agent | Lowers melting points of $V_2O_5$ and $MoO_3$ precursors | Reduces required synthesis temperature |
| Catalyst | Accelerates decomposition into gas-phase reactants | Speeds up growth and reaction rates |
| Intermediate | Creates volatile metal oxychlorides | Ensures steady supply of metal vapor |
| Doping Aid | Lowers activation energy for atomic substitution | Facilitates high-quality Vanadium doping |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Unlock precision in your 2D material growth with our advanced CVD solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique doping and temperature requirements. Whether you are optimizing Vanadium-doped MoS2 or pioneering new semiconductor alloys, our technical team provides the equipment and expertise needed for high-purity, scalable results.
Ready to refine your CVD process? Contact us today to find your custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Krishna Rani Sahoo, Tharangattu N. Narayanan. Vanadium Doped Magnetic MoS<sub>2</sub> Monolayers of Improved Electrical Conductivity as Spin‐Orbit Torque Layer. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202502408
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How can customers maximize the quality of CVD coatings? Master Pre-Coating Prep for Superior Results
- When is CVD the preferred choice? Achieve Superior Thin Films for Complex Applications
- What are the technical advantages of using an LPCVD system for WS2-MoS2? Achieve Atomic Seamless Precision
- What are the benefits of CVD coatings in aerospace and automotive industries? Boost Durability and Efficiency
- What are the key differences between PVD and CVD processes? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of physical Vapour deposition? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Films
- What is the specific function of a thermal evaporation system in IPSLS growth? Precision Precursor Deposition
- What future trends are expected in the development of CVD tube furnaces? Discover Smarter, More Versatile Systems



















