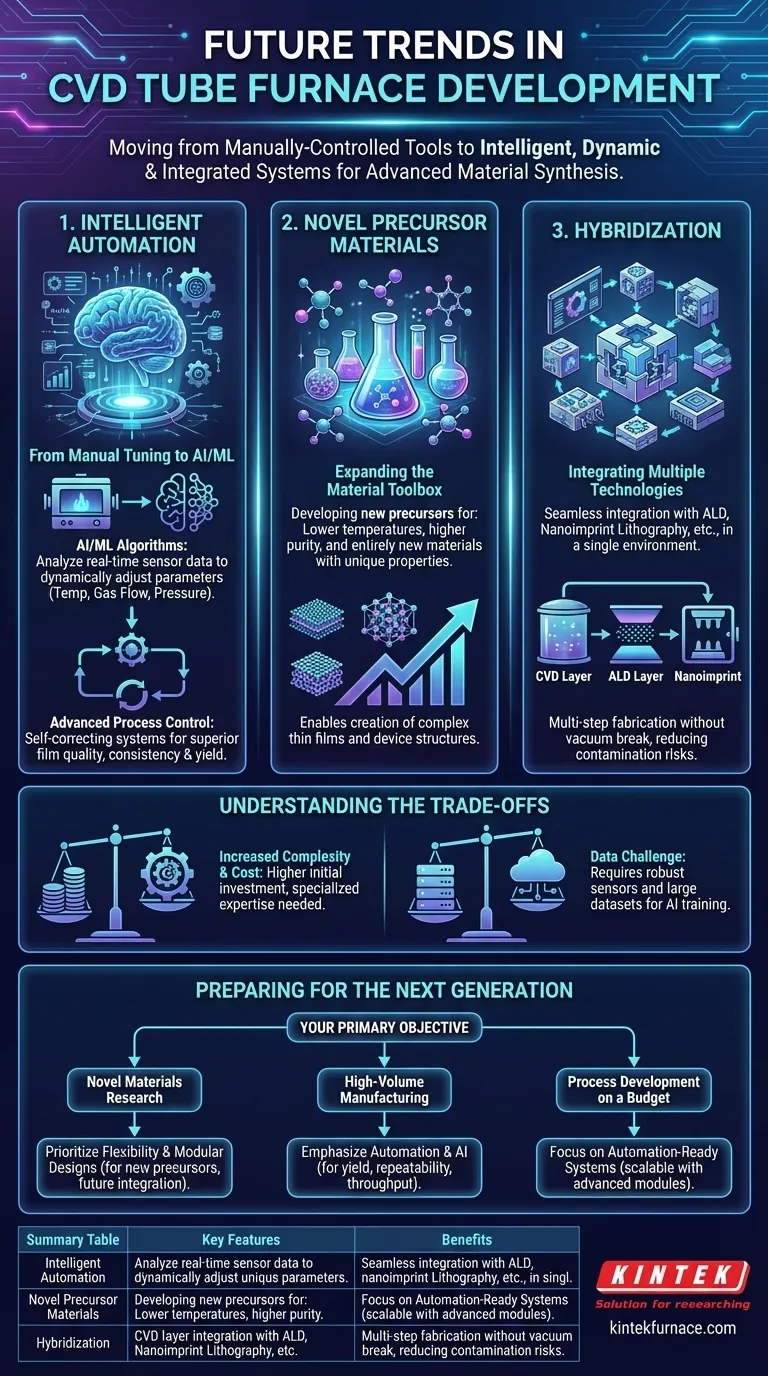
In short, the future of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) tube furnaces is defined by three core advancements: the integration of intelligent automation, the development of novel precursor materials, and the hybridization with other fabrication technologies. These trends are moving the technology from a manually-controlled tool to a dynamic, precise, and highly integrated system for advanced material synthesis.
The core evolution is a shift away from static, pre-programmed recipes. Future CVD furnaces are becoming intelligent, self-optimizing systems designed for higher precision, greater material diversity, and more sustainable operation.

The Drive for Smarter, More Precise Deposition
The primary driver for innovation is the need for greater control and repeatability in creating complex thin films for semiconductors, solar cells, and advanced coatings. This requires moving beyond simple, timed process steps.
From Manual Tuning to Intelligent Automation
Future systems will increasingly rely on Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). Instead of just executing a pre-set recipe, the furnace will use sensors to monitor conditions in real-time.
AI algorithms will analyze this data to dynamically adjust parameters like temperature, gas flow, and pressure. This ensures the optimal conditions are maintained throughout the deposition, dramatically improving film quality, consistency, and yield.
The Role of Advanced Process Control
This automation is enabled by more sophisticated process control modules. These are the hardware and software systems that translate the AI's decisions into physical actions.
Think of it as the furnace's nervous system. It allows for a closed-loop feedback mechanism where the system constantly self-corrects, compensating for minor fluctuations that would ruin a deposition in a traditional, less-responsive furnace.
Expanding the Material and Process Toolbox
The applications for CVD are growing, and with them, the demand for new materials and more complex device structures. The furnace itself is evolving to become a more versatile and capable platform.
The Search for Novel Precursor Materials
Significant research is focused on developing new precursor materials—the gaseous chemical compounds that supply the elements for the thin film.
The goal is to find precursors that work at lower temperatures, have higher purity, or enable the deposition of entirely new materials with unique electronic or physical properties. This expands the range of what can be created in a CVD system.
Hybridization: Integrating Multiple Technologies
CVD is becoming one step in a larger, integrated workflow. Furnaces are being designed to integrate seamlessly with other technologies like Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) or nanoimprint lithography.
This allows for multi-step fabrication of complex devices within a single, controlled environment. A process might involve depositing a base layer with CVD, followed by an atomically precise layer using ALD, all without breaking the vacuum or risking contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While these advancements promise significant benefits, they also introduce new considerations that must be weighed carefully.
Increased Complexity and Cost
Intelligent systems with integrated AI and hybrid capabilities are inherently more complex. This translates to a higher initial investment cost for the equipment.
Furthermore, operating and maintaining these systems will require more specialized technical expertise. Labs and manufacturing facilities will need to invest in training to fully leverage these advanced features.
The Data Challenge of AI/ML
Implementing AI-driven process control is not a simple "plug-and-play" solution. It requires a robust sensor infrastructure to generate high-quality data.
More importantly, the machine learning models must be trained on large datasets from previous depositions. Acquiring and managing this data can be a significant undertaking, representing a hidden cost and technical hurdle.
How to Prepare for the Next Generation of CVD
Your approach to adopting these future technologies should be guided by your primary objective, whether it's fundamental research, process development, or high-volume production.
- If your primary focus is novel materials research: Prioritize systems offering flexibility for new precursor materials and modular designs that allow for future integration with other technologies like ALD.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: Emphasize automation and AI-driven process control to maximize yield, repeatability, and throughput while considering sustainability features to lower long-term operational costs.
- If your primary focus is process development on a budget: Look for fundamentally sound systems with good vacuum and gas control that are "automation-ready," allowing you to add more advanced control modules as your needs and budget evolve.
By understanding these trends, you can make strategic decisions that position your work at the forefront of material science and engineering.
Summary Table:
| Trend | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Intelligent Automation | AI/ML, real-time sensors, dynamic parameter adjustment | Improved film quality, consistency, and yield |
| Novel Precursor Materials | Lower temperature, higher purity, new material deposition | Expanded material range and unique properties |
| Hybridization with Other Technologies | Integration with ALD, nanoimprint lithography | Multi-step fabrication in controlled environments |
Ready to elevate your material synthesis with cutting-edge CVD tube furnaces? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're in research, process development, or high-volume production, our intelligent and versatile systems can enhance precision, efficiency, and sustainability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your innovation goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth
- Why are CVD tube furnace sintering systems indispensable for 2D material research and production? Unlock Atomic-Scale Precision



















