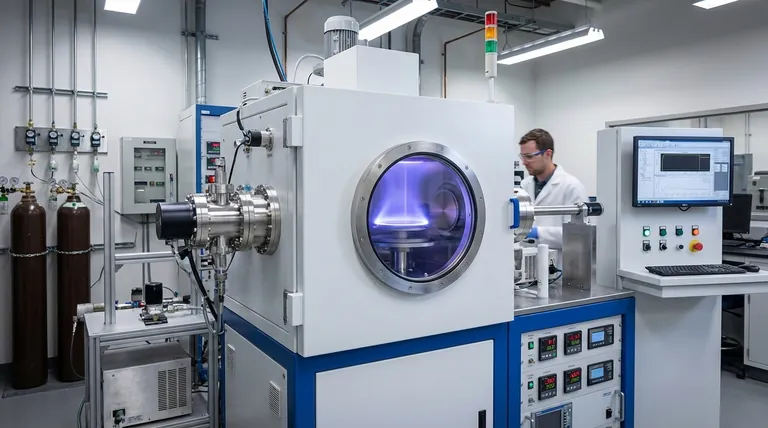
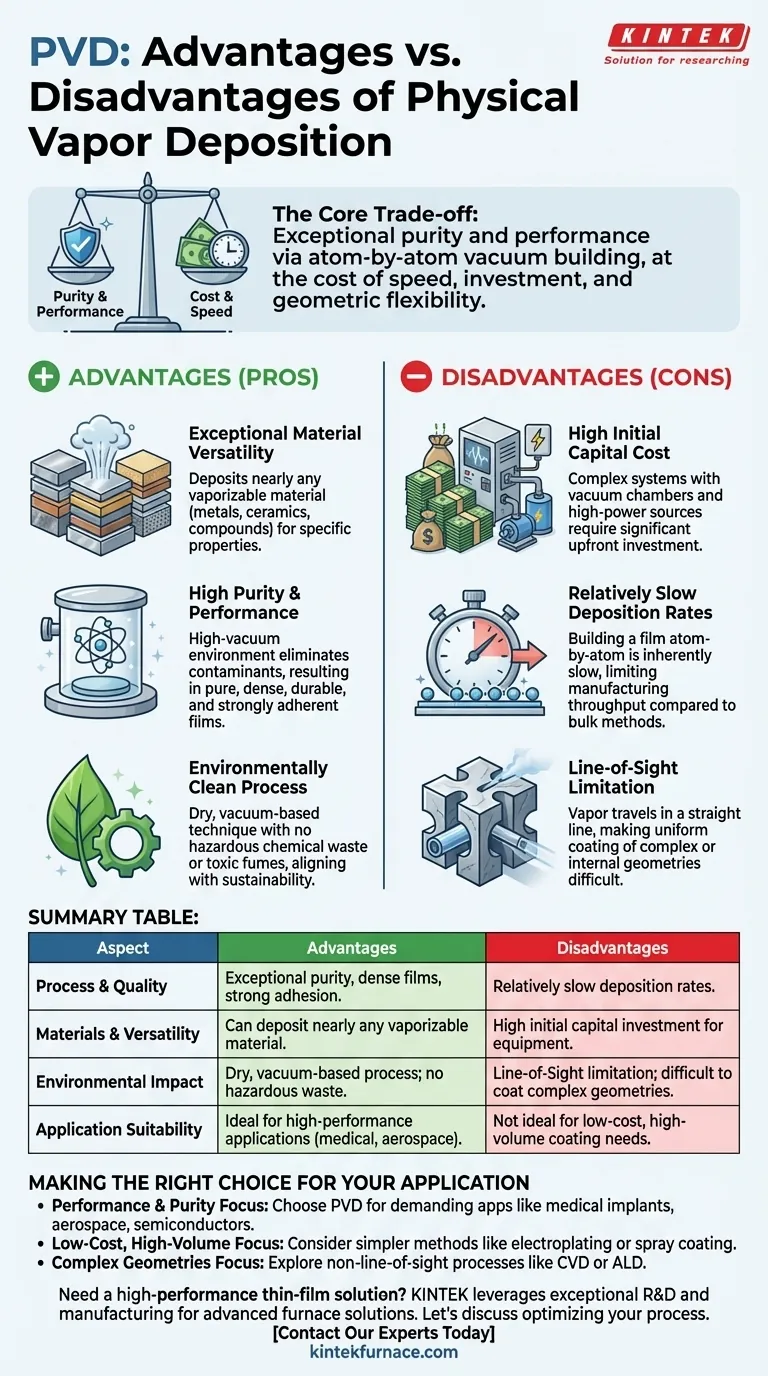
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a cornerstone of modern thin-film coating, known for its ability to produce high-performance, durable surfaces. Its primary advantages are its environmental friendliness and its versatility across an enormous range of materials. However, these benefits are balanced by significant disadvantages, including high capital investment, slow deposition rates, and inherent difficulties in coating complex shapes.
The core trade-off of PVD is clear: it delivers exceptional purity and performance by building films atom-by-atom in a vacuum. This precision comes at the cost of speed, initial investment, and geometric flexibility.

The Core Advantages of PVD Explained
Physical Vapor Deposition operates by vaporizing a solid material in a vacuum and depositing it onto a substrate. This fundamental mechanism is the source of its key strengths.
Exceptional Material Versatility
PVD is a physical, not chemical, process. This means it can be used to deposit nearly any material that can be vaporized, including metals, alloys, ceramics, and various compounds.
This makes it invaluable for applications requiring specific material properties, from the wear-resistant titanium nitride on cutting tools to the reflective aluminum on mirrors.
High Purity and Performance
The entire process takes place in a high-vacuum chamber. This environment is crucial because it eliminates atmospheric gases and contaminants that could otherwise be incorporated into the film.
The result is an extremely pure, dense, and defect-free coating. These films exhibit strong adhesion and superior properties like hardness, corrosion resistance, and specific optical or electrical characteristics.
Environmentally Clean Process
Unlike wet-chemical processes like electroplating, PVD is a dry, vacuum-based technique. It produces no hazardous chemical waste or toxic fumes that require special disposal.
This makes PVD a significantly more environmentally friendly technology, aligning with modern manufacturing's push for sustainable and safe processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Disadvantages
The precision and quality of PVD come with practical and economic limitations that must be carefully considered.
High Initial Capital Cost
PVD systems are complex machines. The necessary components—including the vacuum chamber, high-power energy sources (for evaporation or sputtering), pumping systems, and process controls—represent a significant capital investment.
This high upfront cost can be a barrier to entry, particularly for smaller-scale operations or for products with very low margins.
Relatively Slow Deposition Rates
Building a film layer by layer, essentially atom by atom, is an inherently slow process. While excellent for controlling thickness and structure, it limits manufacturing throughput.
Compared to bulk coating methods like painting or electroplating, PVD is far slower. This makes it less suitable for applications where rapid, high-volume coating is the primary goal.
The Line-of-Sight Limitation
This is the most critical technical drawback. In PVD, the vaporized coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate.
This means it is very difficult to uniformly coat non-visible surfaces, such as the inside of a narrow tube, deep crevices, or the backside of a complex part. Achieving uniform coverage on 3D objects often requires complex and costly substrate rotation and fixturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision to use PVD should be driven by a clear understanding of your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is performance and purity: PVD is the ideal choice for creating dense, durable thin films for demanding applications like medical implants, aerospace components, or semiconductor devices.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, high-volume coating: Simpler, faster methods like electroplating or spray coating are likely more cost-effective, provided you can manage their environmental impact.
- If your primary focus is coating complex internal geometries: A non-line-of-sight process like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) or Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) may be a more suitable technology to explore.
Ultimately, selecting PVD is a strategic decision where the demand for superior coating quality and environmental responsibility must justify the investment in equipment and process time.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Process & Quality | Exceptional purity, dense films, strong adhesion | Relatively slow deposition rates |
| Materials & Versatility | Can deposit nearly any vaporizable material (metals, ceramics) | High initial capital investment for equipment |
| Environmental Impact | Dry, vacuum-based process; no hazardous waste | Line-of-sight limitation; difficult to coat complex geometries |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for high-performance applications (medical, aerospace) | Not ideal for low-cost, high-volume coating needs |
Need a high-performance thin-film solution tailored to your specific requirements?
The advantages and limitations of PVD highlight that the right furnace system is critical for success. At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions for diverse laboratory needs.
Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and specialized CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities. We can precisely engineer a system to overcome common PVD challenges, optimize your process for specific materials, and help you achieve the superior coating quality your research or production demands.
Let's discuss how we can optimize your thin-film deposition process. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















