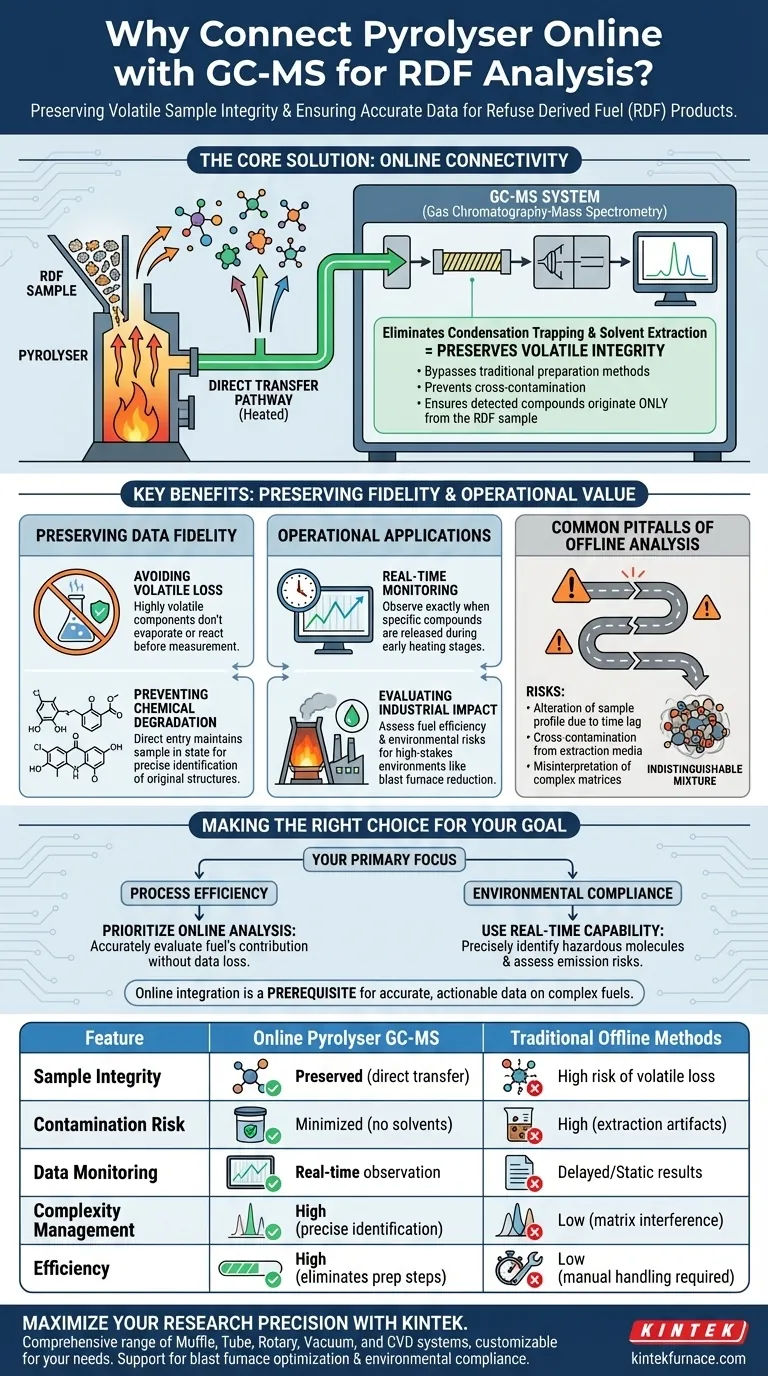
The primary necessity for connecting a pyrolyser online with a GC-MS system is the preservation of volatile sample integrity. By allowing pyrolysis products to flow directly into the chromatography column, this configuration eliminates the need for condensation trapping or solvent extraction, which are major sources of experimental error in Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF) analysis.
Online connectivity serves as a critical control measure, preventing the physical loss and chemical degradation of unstable volatiles. It ensures that the complex organic molecules identified are a true representation of the fuel's emissions, rather than artifacts of sample handling.

The Mechanics of Direct Transfer
Eliminating Intermediate Steps
In an online setup, the volatiles generated during pyrolysis enter the analysis stream immediately. This bypasses traditional preparation methods such as condensation trapping or solvent extraction.
Preventing Sample Contamination
By removing the need for external solvents and manual handling, the system effectively neutralizes the risk of cross-contamination. This ensures that the detected compounds originate strictly from the RDF sample and not from the extraction medium or prior experiments.
Preserving Data Fidelity
Avoiding Volatile Loss
Many components released during RDF pyrolysis are highly volatile or chemically unstable. An online connection prevents these components from evaporating or reacting before they can be measured, preventing the loss of critical data points.
Preventing Chemical Degradation
Complex organic molecules can degrade rapidly when exposed to changes in temperature or atmosphere during offline transfer. Direct entry into the GC-MS column maintains the sample in a state that allows for precise identification of the original molecular structures.
Operational Applications
Real-Time Monitoring
The online configuration enables real-time monitoring of the pyrolysis process. This allows researchers to observe exactly when specific compounds are released during the early stages of heating.
Evaluating Industrial Impact
Accurate identification of these volatiles is essential for determining how RDF will behave in high-stakes environments, such as blast furnace reduction processes. It provides the necessary data to evaluate both the fuel's efficiency and its potential environmental risks.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The Risks of Offline Analysis
It is crucial to understand that attempting this analysis "offline" (without a direct connection) introduces significant variables. The primary pitfall is the alteration of the sample profile due to the time lag between pyrolysis and injection.
Misinterpretation of Complex Matrices
Without the direct separation provided by the online GC-MS link, the complex mixture of organics in composite fuels can become indistinguishable. This leads to an inability to accurately assess the contribution of specific components to the overall fuel performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the value of your RDF analysis, align your approach with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Process Efficiency: Prioritize online analysis to accurately evaluate the fuel's contribution to blast furnace reduction without data loss from handling.
- If your primary focus is Environmental Compliance: Use the real-time capability to precisely identify hazardous organic molecules and assess potential emission risks.
The online integration of a pyrolyser with GC-MS is not just a convenience; it is a prerequisite for accurate, actionable data regarding complex composite fuels.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Online Pyrolyser GC-MS | Traditional Offline Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Integrity | Preserved (direct transfer) | High risk of volatile loss |
| Contamination Risk | Minimized (no solvents) | High (extraction artifacts) |
| Data Monitoring | Real-time observation | Delayed/Static results |
| Complexity Management | High (precise identification) | Low (matrix interference) |
| Efficiency | High (eliminates prep steps) | Low (manual handling required) |
Maximize Your Research Precision with KINTEK
Ensure the integrity of your RDF pyrolysis data with high-performance laboratory solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as other lab high-temperature furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique experimental needs.
Don't let sample degradation compromise your results. Whether you are optimizing blast furnace reduction or ensuring environmental compliance, our team is ready to support your mission with precision-engineered equipment.
Contact KINTEK Today to Customize Your Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Eurig W. Jones, Peter J. Holliman. Pyrolysis-GCMS of Plastic and Paper Waste as Alternative Blast Furnace Reductants. DOI: 10.3390/chemengineering9010015
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is precise nitrogen flow critical for AlN nanofibers? Mastering High-Performance Nitridation Results
- Why is a 1200°C hold required for Ti(C,N)-FeCr sintering? Unlock Superior Material Density
- Why is determining the hypercooling limit necessary when measuring the heat of fusion? Optimize Your Material Research
- What is the role of mortar grinding combined with heat gun processing in catalyst synthesis? Achieving PtCln Dispersion
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- Why is a high-purity argon flow control system essential? Ensure Precision in Metallurgy Simulations
- What function does a fluidized bed reactor perform in oil sludge pyrolysis? Enhance Thermal Efficiency
- What is the role of calcination using high-temperature furnaces in the top-down synthesis of ZnO-NPs?



















