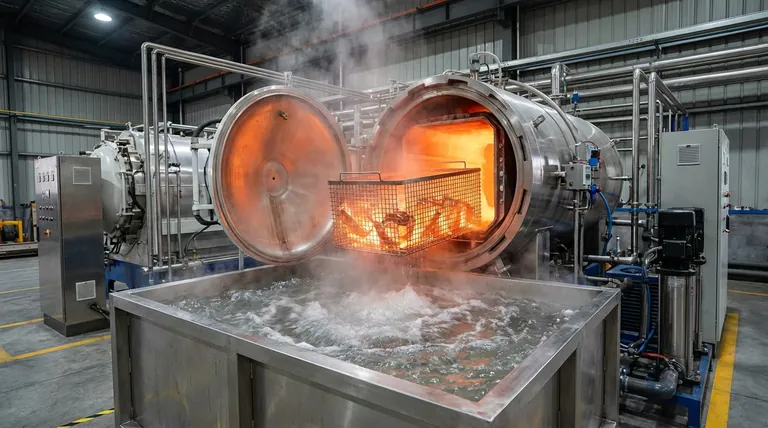
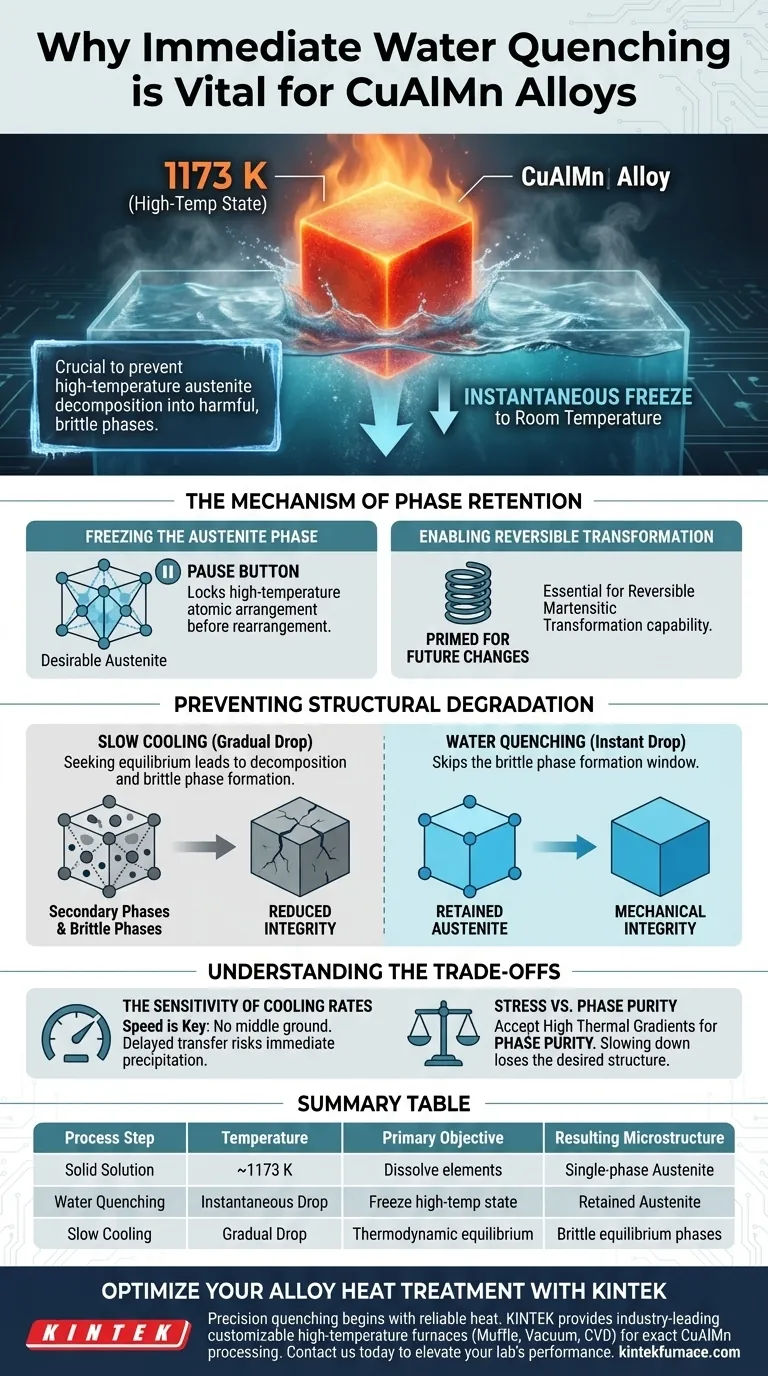
Immediate water quenching is required to instantaneously "freeze" the CuAlMn alloy’s microstructure from a high-temperature state of 1173 K down to room temperature. This rapid cooling rate is the only way to prevent the high-temperature austenite phase from decomposing into harmful, brittle equilibrium phases.
By bypassing the natural cooling process, water quenching forces the alloy to retain a specific high-temperature structure. This inhibition of decomposition is what enables the reversible martensitic transformation necessary for the alloy's functional properties.

The Mechanism of Phase Retention
Freezing the Austenite Phase
At high temperatures (approximately 1173 K), CuAlMn alloys exist in a desirable austenite phase. To utilize the alloy's unique properties, this specific atomic arrangement must be maintained at room temperature.
Water quenching provides an extremely high cooling rate that acts as a "pause button" on the alloy's thermodynamics. It creates a state where the high-temperature structure is locked in place before the atoms have time to rearrange.
Enabling Reversible Transformation
The primary goal of solid solution treatment is not just to heat the metal, but to prepare it for future phase changes. By successfully retaining the high-temperature austenite phase, the alloy is primed for subsequent low-temperature environments.
This preparation allows the alloy to undergo reversible martensitic transformation. Without the initial rapid quench, this functional transformation capability would be lost due to microstructural changes during cooling.
Preventing Structural Degradation
Inhibiting Equilibrium Decomposition
If a CuAlMn alloy is allowed to cool slowly—or even gradually—it will naturally seek a state of thermodynamic equilibrium. During this process, the single-phase structure begins to decompose.
This decomposition results in the precipitation of secondary phases. Once these phases form, they disrupt the uniformity of the microstructure required for the alloy's performance.
Avoiding Brittle Phases
The most critical risk of insufficient cooling speeds is the formation of brittle phases. The primary reference indicates that slow cooling allows these harmful phases to precipitate out of the solid solution.
The presence of these brittle phases drastically reduces the mechanical integrity of the alloy. Water quenching effectively skips the temperature window where these brittle phases are able to form.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Sensitivity of Cooling Rates
The process relies entirely on the speed of the temperature drop. There is no middle ground; a "moderate" cooling rate is often as detrimental as slow cooling.
If the transfer from the furnace to the water bath is delayed, the temperature may drop into a range where precipitation begins immediately.
Stress vs. Phase Purity
While water quenching is aggressive and induces thermal stress, it is a necessary trade-off to ensure phase purity.
You are effectively choosing to accept high thermal gradients to avoid the chemical decomposition of the alloy. Any attempt to reduce thermal shock by slowing the cooling rate will result in the loss of the desired austenite structure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the success of your heat treatment, align your process with your specific requirements:
- If your primary focus is Functional Performance: Ensure the transfer to the quench bath is instantaneous to maximize the volume of retained austenite for martensitic transformation.
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Ductility: Prioritize the cooling rate to strictly avoid the precipitation of brittle phases that act as crack initiation sites.
Mastering the quench rate is the single most important factor in transitioning CuAlMn from a raw material into a functional, high-performance alloy.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Temperature | Primary Objective | Resulting Microstructure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid Solution | ~1173 K | Dissolve elements | Single-phase Austenite |
| Water Quenching | Instantaneous Drop | 'Freeze' high-temp state | Retained Austenite |
| Slow Cooling | Gradual Drop | Thermodynamic equilibrium | Brittle equilibrium phases |
Optimize Your Alloy Heat Treatment with KINTEK
Precision quenching begins with reliable heat. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature systems including Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD furnaces—all customizable to meet the exacting thermal requirements of CuAlMn alloy processing. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our equipment ensures your materials reach precise solid solution temperatures before the critical quench.
Ready to elevate your lab's performance? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Adelaide Nespoli, Carlo Fanciulli. A Study of a Cryogenic CuAlMn Shape Memory Alloy. DOI: 10.3390/met14030323
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- How does a high vacuum deposition system ensure thin film quality? Purity Through Advanced Pumping
- How does a rotating substrate holder contribute to the quality of CuGaO2 thin films? Achieve Uniformity in Sputtering
- What is the function of a solvothermal reactor? Optimize Carbon Polymer Dots (CPDs) Synthesis with Precision Pressure
- Why is a vacuum drying oven required for precursor mixtures? Achieve Stable, High-Quality Powder Processing
- What is a batch furnace and how does it operate? Master Precision Heat Treatment for Diverse Applications
- What are some examples of medium-temperature industrial heating processes? Optimize Material Properties Efficiently
- What are the advantages of SLRP compared to traditional high-temperature furnaces? Revolutionizing UHTC Coatings
- What is the function of a high-precision electric oven in ZnO-CuO synthesis? Expert Thermal Control for Nanosheets



















