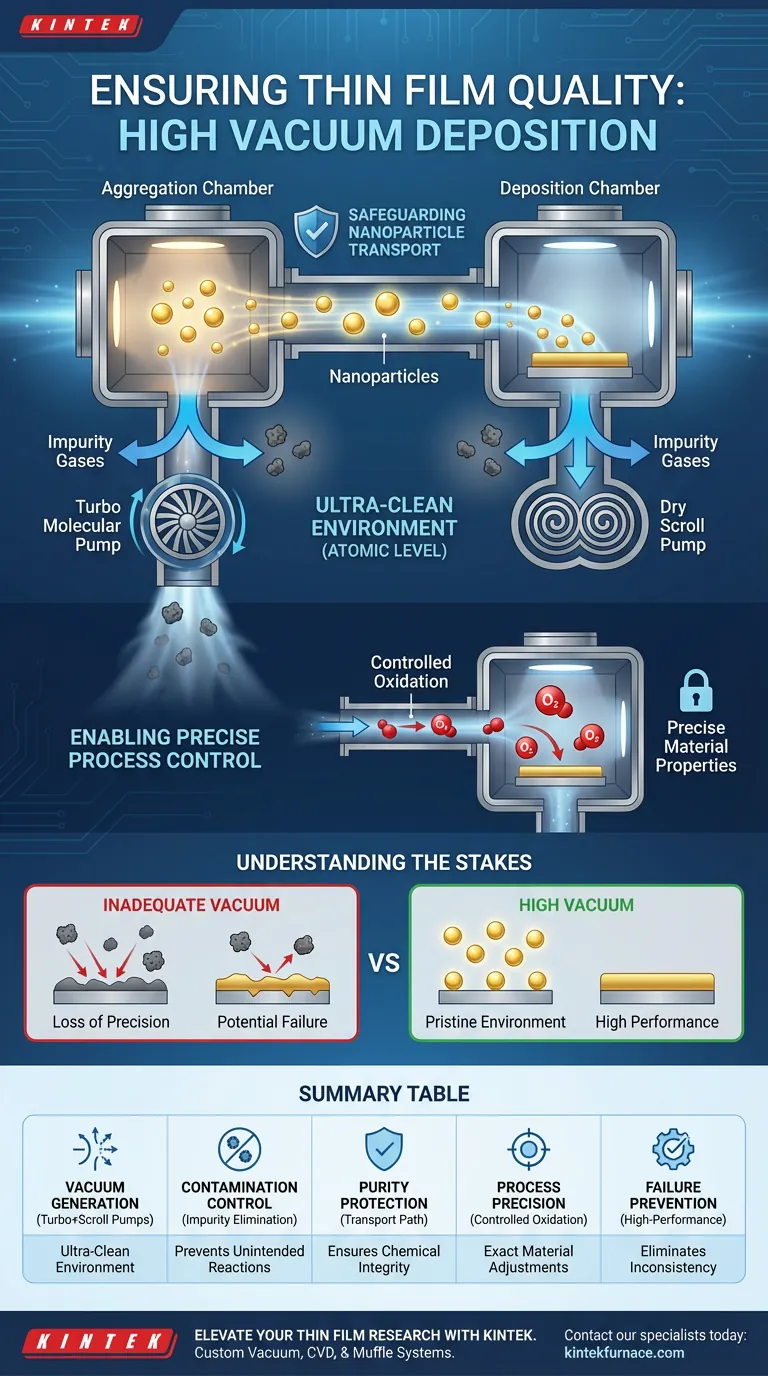
A high vacuum deposition system ensures the quality of thin films by employing a synchronized combination of turbo molecular and dry scroll pumps to generate an ultra-clean environment. This specific pumping configuration eliminates impurity gases that would otherwise contaminate nanoparticles as they travel from the aggregation chamber to the deposition chamber.
By establishing a pristine vacuum environment, this system safeguards material purity during transport and enables precise control over post-deposition processes like oxidation.

Creating an Ultra-Clean Environment
The Role of Specialized Pumping
The core of the system’s reliability lies in the pairing of turbo molecular pumps and dry scroll pumps. This combination is engineered to evacuate the chamber to a high vacuum level.
By removing the vast majority of air and gas molecules, the system creates a controlled "clean room" at the atomic level.
Preventing Gas Contamination
The primary threat to thin film quality is the presence of impurity gases.
If these gases remain in the system, they can interact with the deposition material. The high vacuum setup ensures these impurities are removed before they can degrade the film quality.
Safeguarding Nanoparticle Transport
Protecting the Material Path
The system is designed to facilitate the movement of nanoparticles between two distinct zones: the aggregation chamber and the deposition chamber.
This transit phase is critical. The high vacuum environment protects the particles as they move, ensuring they arrive at the substrate without picking up contaminants from the atmosphere.
Ensuring Material Purity
Because the vacuum prevents interaction with background gases, the nanoparticles maintain their chemical integrity.
This guarantees that the deposited thin film possesses the exact purity levels required for high-performance applications.
Enabling Precise Process Control
Managing Chemical Interactions
High vacuum does more than just keep the chamber clean; it creates a baseline for intentional chemical modification.
The reference specifically notes that this environment allows for precise control over subsequent processing steps.
Controlled Oxidation
One specific benefit of this setup is the ability to manage oxidation.
Because the background environment is free of random impurities, operators can introduce oxygen in a highly controlled manner to achieve specific material properties, rather than suffering from accidental, uncontrolled oxidation.
Understanding the Stakes
The Consequence of Inadequate Vacuum
While the system is designed for high performance, it is vital to understand what happens if the vacuum level is compromised.
Without the ultra-clean environment provided by the turbo and dry scroll pumps, impurity gases become active variables in the deposition process.
Loss of Process Precision
If the vacuum is insufficient, the ability to control subsequent steps—like oxidation—is lost.
The "clean canvas" required for precise chemical adjustments disappears, leading to inconsistent film properties and potential device failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your thin film deposition, align your operational focus with the capabilities of your vacuum system:
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Ensure the turbo molecular and dry scroll pumps are fully operational to eliminate impurity gases during the transport of nanoparticles.
- If your primary focus is Process Tuning: Leverage the high vacuum environment to execute precise post-deposition steps, such as controlled oxidation, without interference from background gases.
The integration of high-performance pumping is not just about pressure; it is the fundamental enabler of purity and precision in thin film fabrication.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Component/Method | Impact on Thin Film Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Generation | Turbo Molecular + Dry Scroll Pumps | Creates an ultra-clean, high-vacuum environment free of contaminants. |
| Contamination Control | Elimination of Impurity Gases | Prevents unintended chemical reactions with nanoparticles during transport. |
| Purity Protection | Aggregation to Deposition Path | Ensures chemical integrity of particles from source to substrate. |
| Process Precision | Controlled Oxidation | Enables exact material property adjustments without background interference. |
| Failure Prevention | High-Performance Evacuation | Eliminates inconsistent film properties and potential device failure. |
Elevate Your Thin Film Research with KINTEK
Precision in thin film deposition starts with a pristine vacuum environment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Vacuum, CVD, and Muffle systems—all customizable to meet your unique laboratory requirements. Whether you are focusing on nanoparticle research or complex material synthesis, our systems equipped with advanced pumping technologies ensure the purity and control your projects demand.
Ready to optimize your deposition process? Contact our specialists today to find your custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Ján Prokeš, Ondřej Kylián. Novel technique to produce porous thermochromic VO2 nanoparticle films using gas aggregation source. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-86272-9
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is it necessary to dry Industrial EAF slag before hydrogen reduction? Crucial Safety and Accuracy Prep
- What is the significance of using a high-precision gas mass flow controller for hydrogen flow? | Master Uniform Thermal Reduction
- How does a multi speed furnace work? Achieve Ultimate Comfort & Efficiency
- What morphological changes occur in POMOF after treatment? Unlock High Catalytic Performance via Thermal Evolution
- Why is a constant temperature drying oven set to 60°C for 24 hours? Optimizing Sr4Al6O12SO4 Powder Quality
- What is Joule Heating and how does it relate to induction heating? Master the Physics of Contactless Heating
- What are the process advantages of using template synthesis for the preparation of zinc selenide (ZnSe)?
- How does a continuous furnace differ from a batch furnace? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process



















