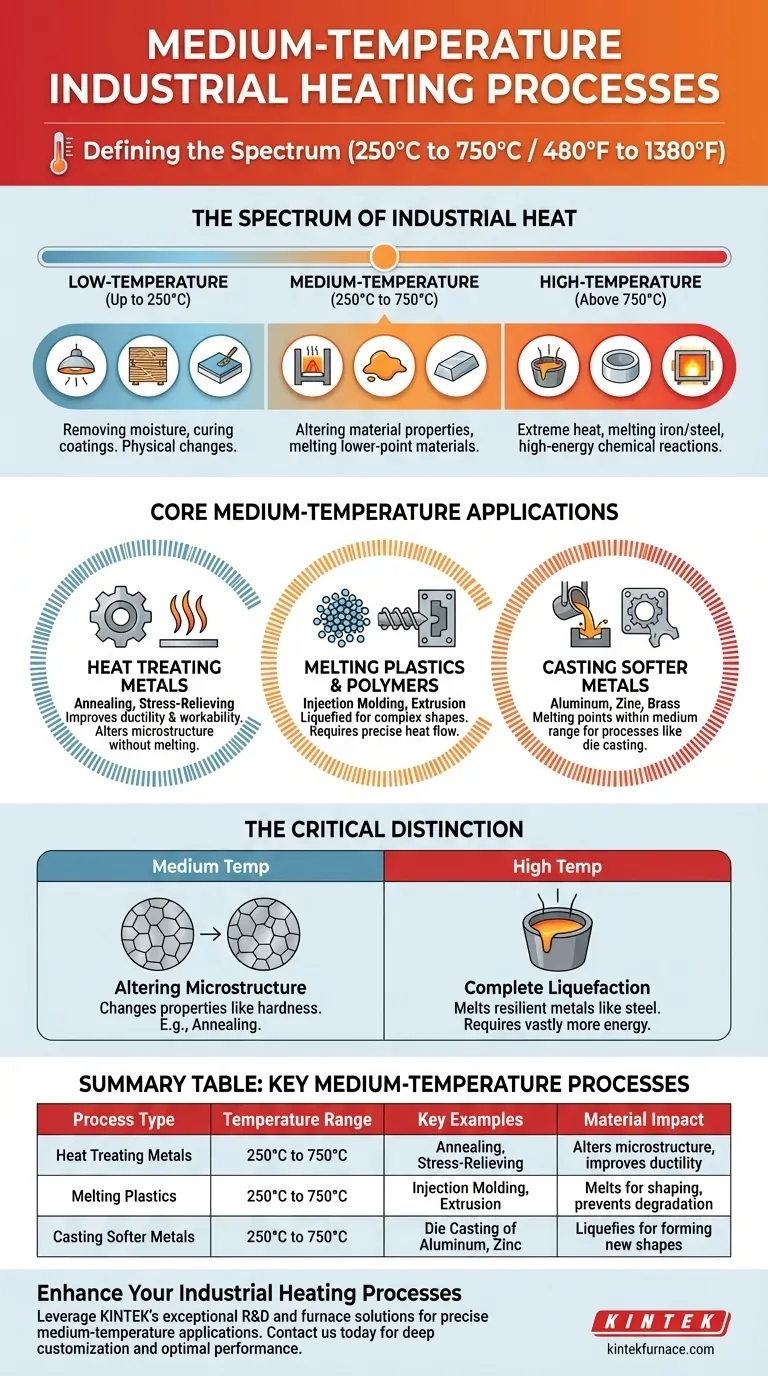
Medium-temperature industrial heating refers to processes that operate roughly between 250°C and 750°C (480°F to 1380°F). Key examples include the heat treatment of metals through annealing and stress-relieving, as well as the melting and reshaping of plastics and certain non-ferrous metals for casting.
The critical distinction of medium-temperature processes is their ability to fundamentally alter a material's internal structure or physical state—like softening a metal or melting a plastic—without reaching the extreme heats required to liquefy industrial steel or drive high-energy chemical reactions.
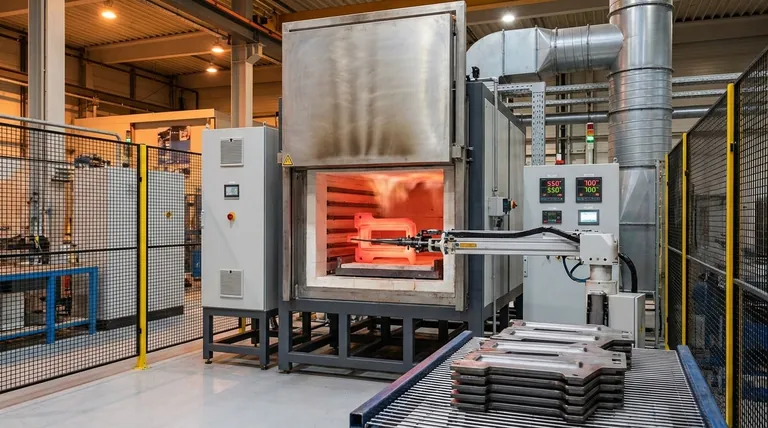

The Spectrum of Industrial Heat
Industrial heating is not a single concept but a spectrum. Processes are categorized by the temperature required to achieve a desired transformation in a material.
Low-Temperature Processes (Up to 250°C)
These processes typically involve removing moisture or curing coatings. Common examples include drying lumber, curing paint, and preparing food products. The goal is a physical change, not a structural one.
Medium-Temperature Processes (250°C to 750°C)
This is the range where a material's fundamental properties can be changed. The heat is intense enough to alter the crystalline structure of metals or melt polymers and soft metals, forming the focus of this discussion.
High-Temperature Processes (Above 750°C)
Reserved for the most energy-intensive tasks, this range includes melting and casting iron and steel, creating advanced materials like ceramics, and facilitating specific chemical reactions that only occur at extreme heat.
Core Medium-Temperature Applications Explained
The examples provided for medium-temperature work fall into two primary categories: modifying existing solids or creating new shapes from materials with lower melting points.
Heat Treating Metals
Annealing and stress-relieving are crucial processes that improve a metal's workability and durability. Instead of melting the metal, they heat it to a precise temperature to relieve internal stresses created during manufacturing, making the material softer and less brittle. This is a classic medium-temperature application.
Melting Plastics and Polymers
Most industrial plastics melt well within the 250°C to 750°C range. This allows them to be liquefied for injection molding, extrusion, or casting into complex shapes. The process requires enough heat to ensure the material flows properly but not so much that the polymer degrades.
Casting Softer Metals
While steel requires high temperatures to melt, many other common metals do not. Aluminum, zinc, and certain brass alloys have melting points that fall directly within the medium-temperature range, making them ideal for casting processes like die casting without requiring high-temperature furnaces.
The Critical Distinction: Medium vs. High Temperature
The line between medium and high-temperature work can seem blurry, as terms like "heat treating" and "casting" are used in both. The key difference lies in the material and the intended outcome.
Altering a Microstructure vs. Complete Liquefaction
Medium-temperature heat treating, like annealing, alters the internal grain structure of a metal to change its properties. High-temperature heat treating may do the same but at more extreme levels, while high-temperature casting involves the complete liquefaction of resilient metals like iron and steel.
The Role of the Material
The classification depends entirely on the material's properties. For example, casting zinc (melting point 420°C) is a medium-temperature process. In contrast, casting steel (melting point ~1370°C) is unequivocally a high-temperature process. The action is the same, but the energy required is vastly different.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use these guidelines to correctly classify your industrial heating needs.
- If your primary focus is improving metal ductility without melting it: You are working in the medium-temperature range with processes like annealing or stress-relieving.
- If your primary focus is shaping parts from plastics or aluminum: Your molding or casting operations fall squarely within the medium-temperature domain.
- If your primary focus is melting steel or creating ceramics: You have moved into the high-temperature category, which demands different equipment and safety protocols.
Understanding where your process fits on the thermal spectrum is the foundational step toward achieving precise material control and operational efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Temperature Range | Key Examples | Material Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heat Treating Metals | 250°C to 750°C | Annealing, Stress-Relieving | Alters microstructure, improves ductility |
| Melting Plastics | 250°C to 750°C | Injection Molding, Extrusion | Melts for shaping, prevents degradation |
| Casting Softer Metals | 250°C to 750°C | Die Casting of Aluminum, Zinc | Liquefies for forming new shapes |
Ready to enhance your industrial heating processes? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're heat treating metals, melting plastics, or casting softer metals, our expertise ensures optimal performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications and drive success in your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















