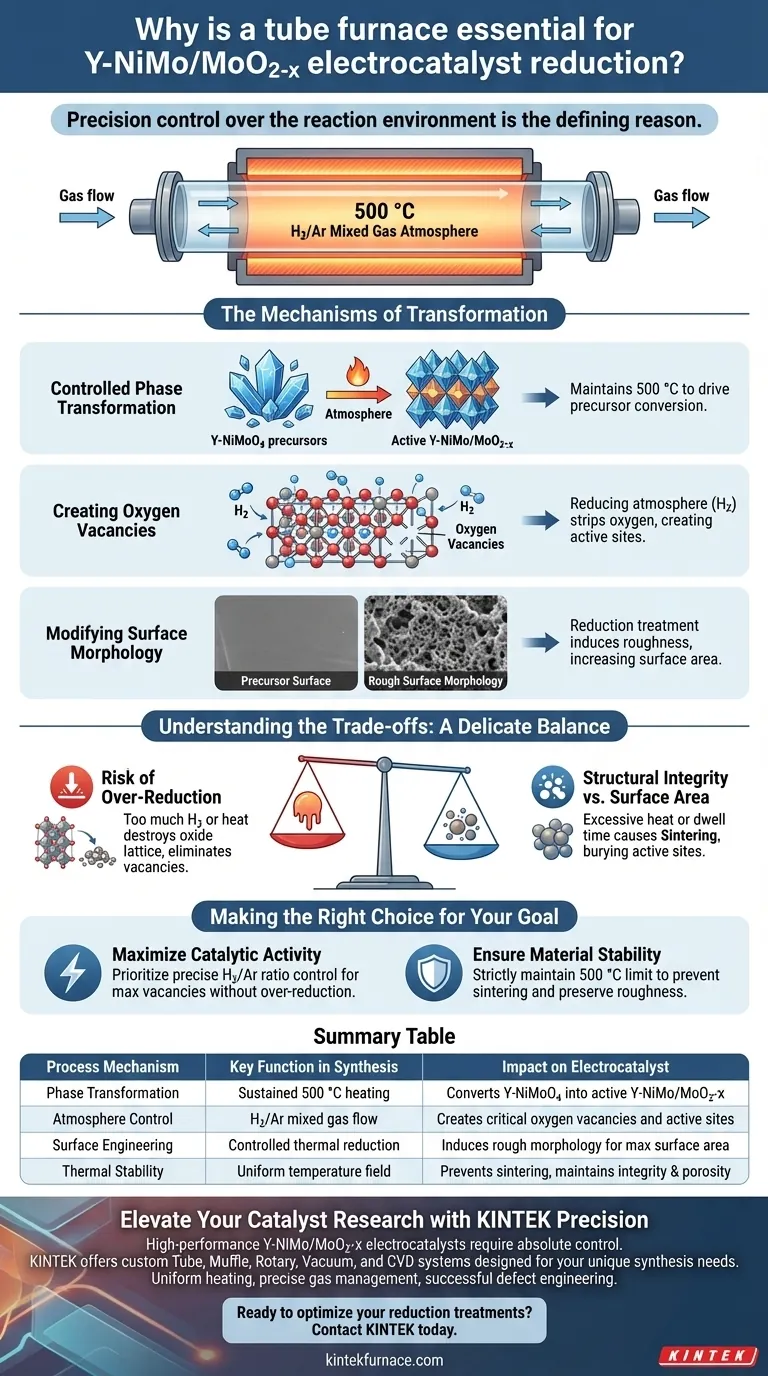
Precision control over the reaction environment is the defining reason for using a tube furnace in this synthesis.
For the reduction of Y-NiMo/MoO2-x electrocatalysts, a tube furnace is essential because it maintains a stable thermal environment at 500 °C while facilitating a specific hydrogen and argon (H2/Ar) mixed gas atmosphere. This precise combination is the only way to successfully convert Y-NiMoO4 precursors into the final active material, inducing the critical phase transformations and surface modifications required for high performance.
The tube furnace serves as the enabling vessel for defect engineering, allowing for the controlled creation of oxygen vacancies and surface roughness that directly dictate the electrocatalyst’s efficiency.

The Mechanisms of Transformation
The tube furnace is not merely a heater; it is a reactor that orchestrates three distinct physical and chemical changes in the material.
Controlled Phase Transformation
The primary function of the furnace is to drive the conversion of the precursor material.
By holding the temperature at exactly 500 °C, the furnace provides the thermal energy necessary to transform Y-NiMoO4 precursors into the desired Y-NiMo/MoO2-x phase.
Without this sustained and uniform heat application, the material would fail to crystallize into the correct structure, rendering it chemically inert for the intended application.
Creating Oxygen Vacancies
Catalytic activity often relies on "imperfections" in the material structure known as oxygen vacancies.
The tube furnace allows for the introduction of a reducing atmosphere (H2/Ar). As the hydrogen interacts with the material, it strips away specific oxygen atoms from the lattice.
This process creates a high concentration of oxygen vacancies, which serve as active sites where electrochemical reactions can occur more rapidly.
Modifying Surface Morphology
The physical texture of a catalyst is just as important as its chemical makeup.
The reduction treatment within the furnace induces a rough surface morphology on the material.
A rougher surface creates a larger surface area, exposing more active sites to the electrolyte and significantly enhancing the overall catalytic activity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the tube furnace is essential, the parameters used within it involve a delicate balance.
The Risk of Over-Reduction
Precision is critical because the reducing atmosphere is potent.
If the hydrogen concentration is too high or the temperature exceeds the optimal 500 °C window, you risk reducing the metal oxides entirely to metallic states.
This would destroy the oxide lattice structure and eliminate the beneficial oxygen vacancies, leading to a collapse in catalytic performance.
Structural Integrity vs. Surface Area
Thermal treatment inevitably impacts the material's pore structure.
While the goal is to create roughness and vacancies, excessive heat or prolonged dwell times can cause sintering (the fusing of particles).
Sintering reduces the overall surface area and closes off pores, effectively burying the active sites you worked to create.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When designing your synthesis protocol using a tube furnace, align your parameters with your specific material objectives.
- If your primary focus is maximizing catalytic activity: Prioritize the precise control of the H2/Ar ratio to maximize the concentration of oxygen vacancies without fully reducing the oxide.
- If your primary focus is material stability: Focus on strictly maintaining the 500 °C temperature limit to prevent sintering and ensure the preservation of the rough surface morphology.
Success depends not just on heating the material, but on regulating the atmosphere that defines its final chemical identity.
Summary Table:
| Process Mechanism | Key Function in Synthesis | Impact on Electrocatalyst |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Transformation | Sustained 500 °C heating | Converts Y-NiMoO4 precursors into active Y-NiMo/MoO2-x |
| Atmosphere Control | H2/Ar mixed gas flow | Creates critical oxygen vacancies and catalytic active sites |
| Surface Engineering | Controlled thermal reduction | Induces rough morphology to maximize electrochemical surface area |
| Thermal Stability | Uniform temperature field | Prevents sintering to maintain structural integrity and porosity |
Elevate Your Catalyst Research with KINTEK Precision
High-performance electrocatalysts like Y-NiMo/MoO2-x require absolute control over thermal and atmospheric variables. At KINTEK, we understand that even a minor deviation in hydrogen concentration or temperature can compromise your research outcomes.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers advanced Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the rigorous demands of material science. Our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique synthesis needs, ensuring uniform heating and precise gas management for successful defect engineering.
Ready to optimize your reduction treatments? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace solution
Visual Guide
References
- Shujie Liu, Mingkui Wang. Yttrium-doped NiMo-MoO2 heterostructure electrocatalysts for hydrogen production from alkaline seawater. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-55856-4
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes a vertical tube furnace efficient and energy-saving? Unlock Superior Thermal Control & Cost Savings
- What is sintering, and how is it performed in horizontal furnaces? Unlock Precision in Powder Processing
- How is a three-zone furnace structured? Unlock Precision Heating for Your Lab
- What is the function of a vacuum tube furnace in the regeneration of expanded graphite? Deep Pore Restoration Expert
- What is the function of a tube furnace in catalyst annealing? Unlock L10 Ordered Structures for Peak Performance
- What is the uniform length of a tube furnace and what factors affect it? Maximize Your Lab's Thermal Precision
- What is the necessity of using a Tube Furnace for phosphorus-doped carbon nanofiber films? Ensure Anaerobic Precision
- How do furnace chamber working conditions influence the choice of a tube furnace? Optimize Performance and Cost



















