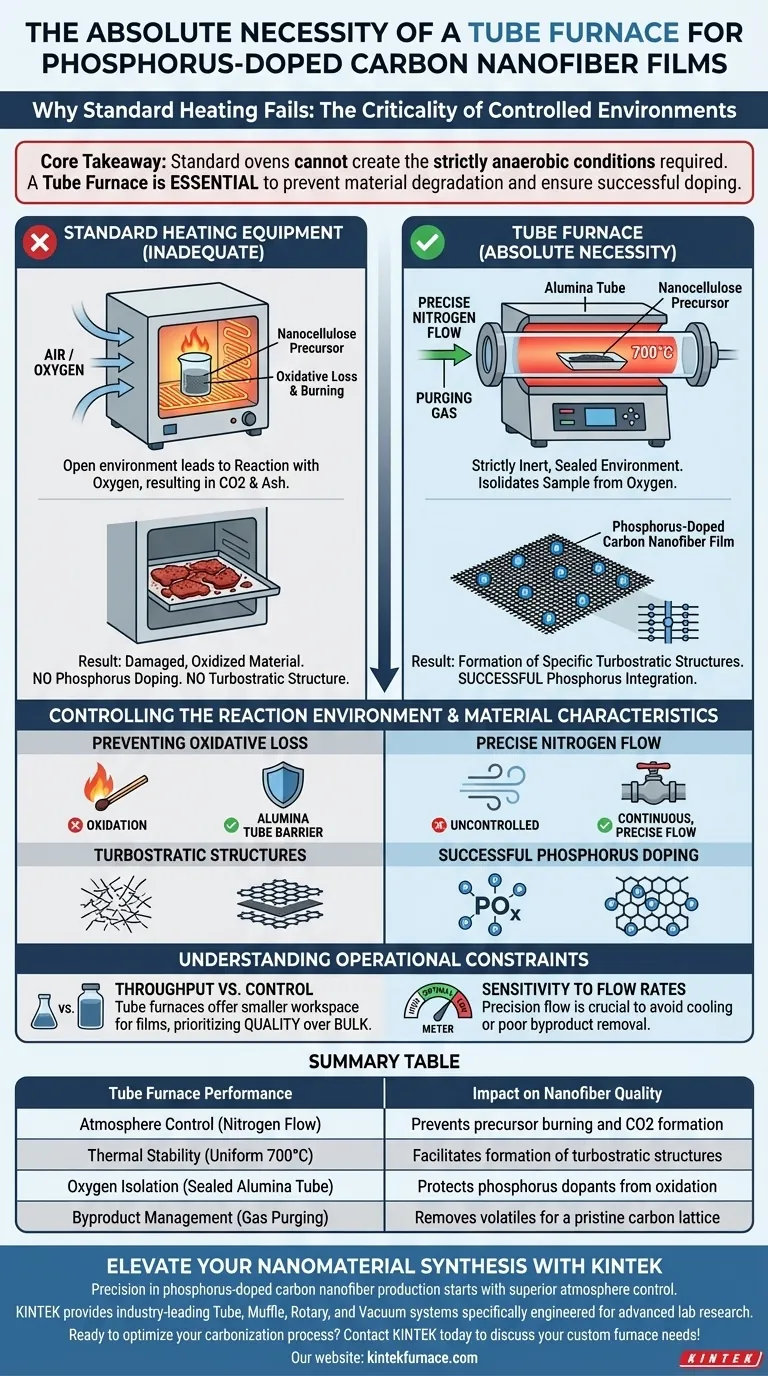
The absolute necessity of a Tube Furnace for this application lies in its ability to create a strictly controlled, high-purity inert environment. Unlike standard heating equipment, a Tube Furnace equipped with an alumina tube allows for precise nitrogen flow control, which completely isolates the sample from oxygen during the critical 700°C heating phase. This isolation is non-negotiable; without it, the nanocellulose precursor would suffer from oxidative loss (burning) rather than converting into the required phosphorus-doped carbon nanofiber films.
Core Takeaway: Standard ovens cannot create the strictly anaerobic conditions required for high-quality carbonization. A Tube Furnace is essential because it prevents material degradation through oxidation, ensuring the formation of specific turbostratic structures and the successful integration of phosphorus into the carbon lattice.

Controlling the Reaction Environment
The primary function of the Tube Furnace in this context is not just heating, but environmental isolation.
Preventing Oxidative Loss
At the target carbonization temperature of 700°C, carbon materials are highly reactive to oxygen. In a standard box furnace, complete air exclusion is difficult to guarantee.
The Tube Furnace utilizes a sealed alumina tube to create a physical barrier. This setup ensures that the nanocellulose remains intact and converts to carbon rather than reacting with oxygen to form CO2 and ash.
Precise Nitrogen Flow Control
Mere isolation is often insufficient; active atmosphere management is required.
The equipment allows for a continuous, precise flow of nitrogen gas. This purges any residual oxygen initially present and flushes away volatile byproducts generated during carbonization, maintaining a pristine environment for the film.
Achieving Specific Material Characteristics
The hardware you choose directly dictates the chemical structure of the final nanomaterial.
Formation of Turbostratic Structures
The primary reference notes that the goal is to convert nanocellulose into carbon nanofibers with specific turbostratic structures.
This structural rearrangement requires stable, high heat under anaerobic conditions. The uniform thermal profile of the tube furnace facilitates the alignment of carbon layers without the interference of oxidative defects.
Successful Phosphorus Doping
For phosphorus-doped films, the dopant atoms must integrate into the carbon lattice.
If oxygen were present, phosphorus would likely oxidize into phosphates or varying oxides rather than doping the carbon. The inert atmosphere provided by the Tube Furnace ensures the chemical conditions are right for phosphorus-doped characteristics to emerge stably.
Understanding Operational Constraints
While the Tube Furnace is necessary for quality, it introduces specific operational factors that must be managed.
Throughput vs. Control
Tube furnaces typically offer a smaller workspace compared to standard ovens.
While the supplementary data suggests rotary options can handle larger capacities, preparing "films" usually requires a static setup. This limits the size and quantity of films you can produce in a single batch compared to bulkier heating methods.
Sensitivity to Flow Rates
The supplementary context highlights the importance of atmosphere flow rate.
In a Tube Furnace, if the nitrogen flow is too high, it may cool the sample surface or mechanically disturb delicate films. If it is too low, volatile byproducts may not clear effectively. Precision here is just as critical as temperature control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
If your primary focus is chemical purity: Ensure the alumina tube is perfectly sealed and the nitrogen source is high-purity to prevent even trace oxidation at 700°C.
If your primary focus is structural uniformity: Monitor the temperature profile and dwell time carefully to ensure the entire film experiences the exact conditions needed for turbostratic formation.
The Tube Furnace is not merely a heater; it is a chemical reactor that dictates the success of your doping process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tube Furnace Performance | Impact on Nanofiber Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Strictly inert via nitrogen flow | Prevents precursor burning and CO2 formation |
| Thermal Stability | Uniform heating up to 700°C+ | Facilitates formation of turbostratic structures |
| Oxygen Isolation | Sealed alumina tube barrier | Protects phosphorus dopants from oxidation |
| Byproduct Management | Continuous gas purging | Removes volatiles for a pristine carbon lattice |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision in phosphorus-doped carbon nanofiber production starts with superior atmosphere control. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Muffle, Rotary, and Vacuum systems specifically engineered to meet the rigorous demands of advanced lab research.
Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, our high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to your unique chemical and structural requirements. Whether you need to maintain a strict anaerobic environment or require precise flow management for sensitive films, KINTEK has the solution.
Ready to optimize your carbonization process? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















