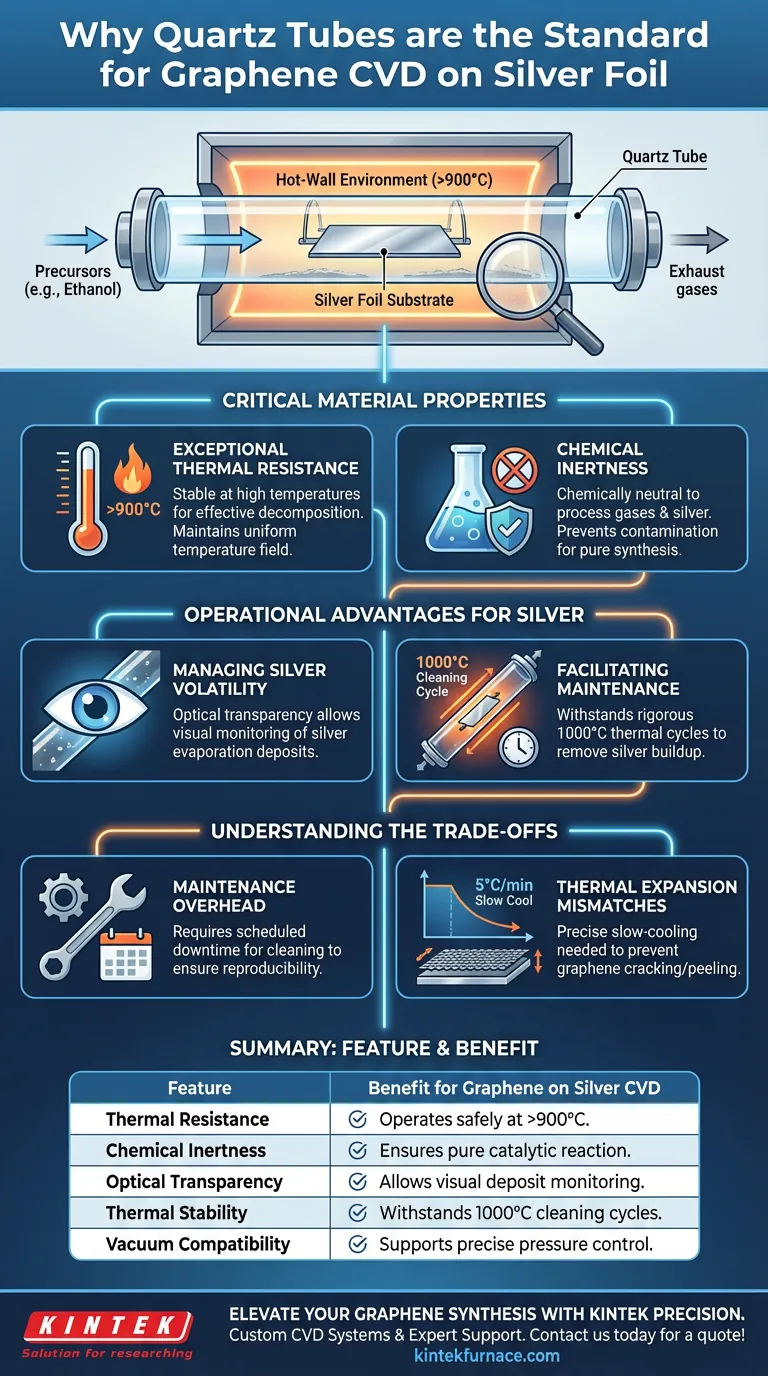
The selection of a quartz tube as the reaction chamber for graphene synthesis on silver is driven by the material's unique ability to maintain structural integrity and chemical neutrality in extreme environments. It supports the necessary growth temperatures exceeding 900°C while remaining chemically inert to both the hydrocarbon gases and the reactive silver foil.
Core Takeaway: Quartz is the standard for Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) because it creates a "hot-wall" environment that isolates the reaction thermally and chemically. It withstands high heat without contaminating the silver substrate and offers the optical transparency required to monitor and clean silver evaporation byproducts.

The Critical Material Properties
Exceptional Thermal Resistance
The growth of high-quality graphene on silver requires a precise high-temperature environment. Quartz tubes are chosen because they possess a very high melting point, allowing them to operate safely at temperatures exceeding 900°C.
This thermal stability is essential for "hot-wall" CVD systems. The quartz allows the system to maintain a stable, uniform temperature field, which is critical for decomposing precursors like ethanol vapor effectively.
Chemical Inertness
Purity is paramount in graphene synthesis. Quartz is chemically inert, meaning it does not react with the process gases or the metal foil, regardless of the temperature or pressure conditions.
This ensures that the catalytic reaction between the carbon source and the silver substrate occurs without interference. The tube acts solely as a vessel, preventing impurities from leaching into the reaction zone and compromising the graphene quality.
Operational Advantages for Silver Substrates
Managing Silver Volatility
Silver presents a specific challenge in CVD processes due to its high vapor pressure. At growth temperatures, silver tends to evaporate and deposit onto the cooler parts of the reaction chamber.
The transparency of the quartz tube is a significant functional advantage here. It allows operators to visually identify these silver deposits on the tube walls, ensuring that the buildup does not go unnoticed.
Facilitating Equipment Maintenance
Because silver deposits are inevitable, the reaction chamber must be cleaned regularly to ensure experiment reproducibility. Quartz is robust enough to undergo rigorous thermal cleaning cycles.
To remove silver buildup, the tube can be heated to 1000°C for approximately 30 minutes under air or a hydrogen-argon flow. Only a material with the thermal shock resistance of quartz could endure these repeated heating and cooling cycles without failing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Maintenance Overhead
While quartz handles the process well, the high vapor pressure of silver creates a recurring maintenance burden. The inner walls will accumulate silver deposits over time.
This requires scheduled downtime for the thermal cleaning steps mentioned above. If this maintenance is skipped, the reproducibility of the reaction environment degrades, potentially altering the thermal profile or introducing contaminants into subsequent runs.
Thermal Expansion Mismatches
While the quartz tube itself is stable, the silver substrate inside expands and contracts at a different rate than the graphene coating.
This is not a fault of the quartz, but a challenge of the system. Precise programmable control of the tube furnace—such as slow-cooling at 5°C per minute—is required to mitigate thermal stress and prevent the graphene from cracking or peeling during the cool-down phase.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your CVD process, consider the following based on your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Experiment Reproducibility: rigorous adherence to the 1000°C thermal cleaning cycle is mandatory to remove silver deposits between runs.
- If your primary focus is Film Continuity: Utilize the programmable nature of the tube furnace to implement slow-cooling strategies that prevent thermal shock between the silver and the graphene.
Success in graphene CVD on silver relies on leveraging the stability of quartz to strictly control the thermal environment while actively managing the volatility of the substrate.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for Graphene on Silver CVD |
|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Operates safely at >900°C for precursor decomposition. |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents contamination; ensures pure catalytic reaction on silver. |
| Optical Transparency | Allows visual monitoring of silver vapor deposits on tube walls. |
| Thermal Stability | Withstands 1000°C cleaning cycles to remove silver buildup. |
| Vacuum Compatibility | Supports precise pressure control for high-quality film growth. |
Elevate Your Graphene Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Are you looking to optimize your CVD processes? Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for advanced material research. Whether you need a standard quartz tube furnace or a fully customizable system for unique high-temperature applications, our engineering team is here to support your laboratory's success.
Maximize your research potential—contact us today for a custom quote!
Visual Guide
References
- Hikaru Iwatani, Fumihiko Maeda. Graphene Synthesis on Silver Foil by Chemical Vapor Deposition Using Ethanol. DOI: 10.1380/ejssnt.2025-026
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What materials are used in the hot zone of CVD furnaces? Optimize for Purity, Cost, and Performance
- What are the key differences between PVD and CVD in terms of deposition mechanism? Choose the Right Coating Method for Your Lab
- How durable are CVD coatings? Unlock Extreme Durability for Your Components
- What are the primary functions of a high vacuum pump system within a CVD graphene process? Ensure High-Purity Synthesis
- How does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) work? Master Thin Film Fabrication for Superior Materials
- What advantages do CVD coatings provide for sub-micron filters? Enhance Purity and Durability in Filtration
- Why is mica preferred as a substrate for CVD growth of Mn3O4 nanosheets? Key Structural Advantages
- How can integrating CVD tube furnaces with other technologies benefit device fabrication? Unlock Advanced Hybrid Processes



















