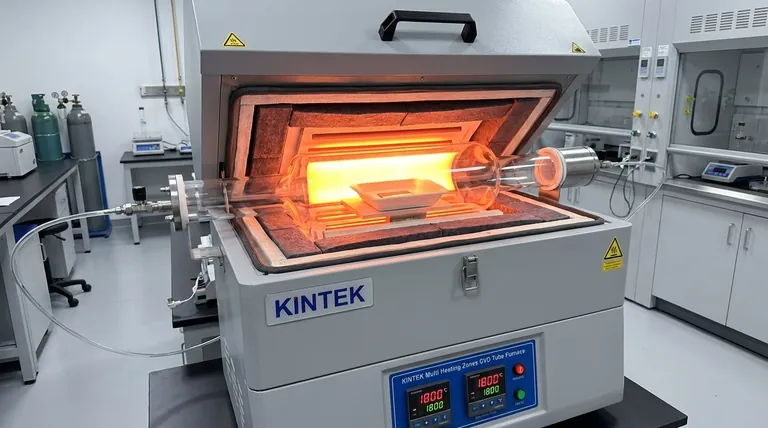
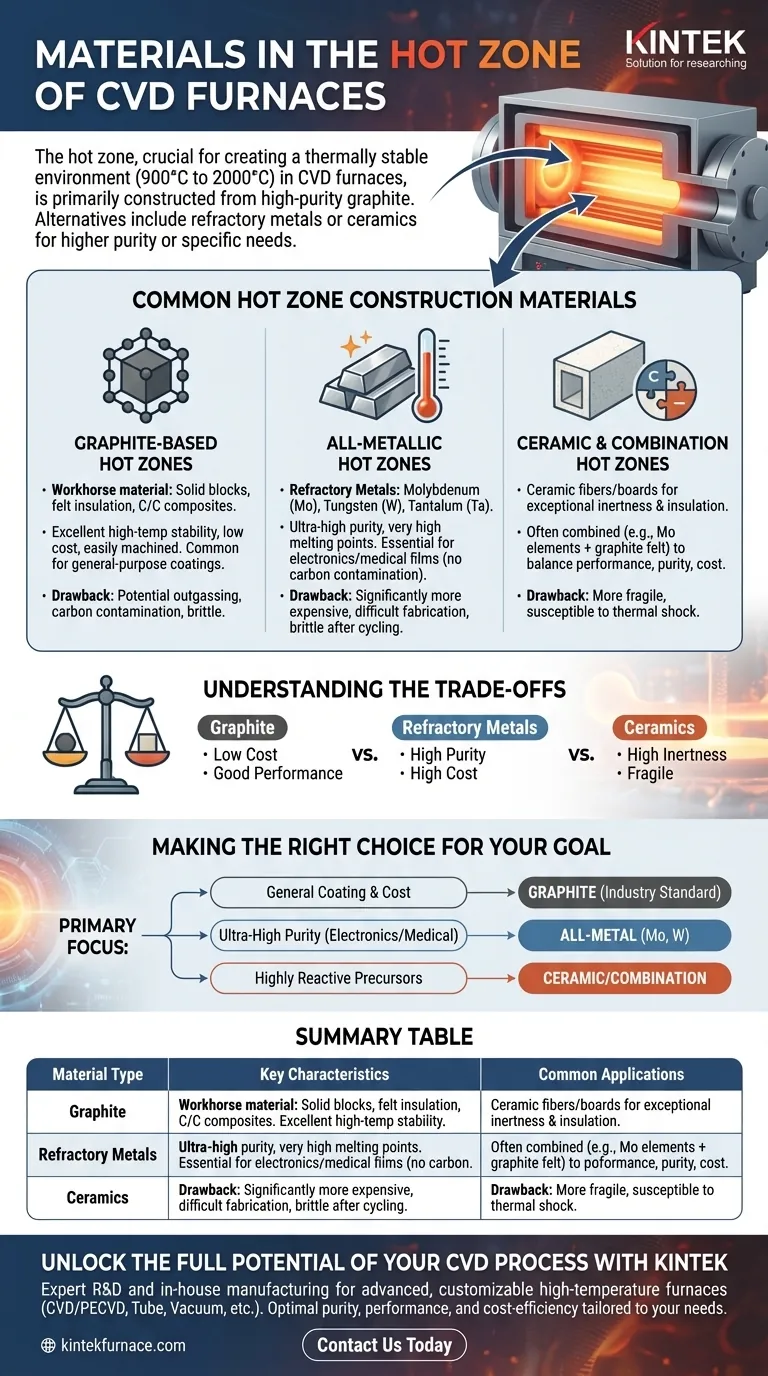
In a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) furnace, the hot zone is most commonly constructed from high-purity graphite, with carbon or graphite felt used for thermal insulation. However, the choice of material is a critical engineering decision, and alternatives like refractory metals (molybdenum, tungsten) or ceramics are used for applications requiring higher purity or specific chemical compatibility.
The selection of a hot zone material is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It is a deliberate trade-off between thermal performance, chemical compatibility with the deposition process, purity requirements, and overall cost.

The Core Challenge: Containing Extreme Temperatures
A CVD furnace's primary function is to create a thermally stable environment, often at extremely high temperatures. This environment is what drives the chemical reactions necessary for depositing thin films onto a substrate.
The Demands of the CVD Process
Deposition temperatures in CVD frequently range from 900 °C to 2000 °C. These conditions place immense stress on the structural components of the furnace interior.
The hot zone materials must maintain their structural integrity and not deform, melt, or degrade at these temperatures. They must also be chemically compatible with the precursor gases used in the deposition process.
Common Hot Zone Construction Materials
While graphite is the most prevalent choice, several materials are used based on the specific requirements of the CVD application.
Graphite-Based Hot Zones
Graphite is the workhorse material for many CVD hot zones. This includes components machined from solid graphite blocks, flexible graphite felt for insulation, and rigid Carbon-Carbon (C/C) composites for enhanced strength.
Its popularity stems from its excellent high-temperature stability and relatively low cost. It can be easily machined into complex shapes for heating elements, support structures, and furnace linings.
All-Metallic Hot Zones
For processes that demand ultra-high purity or cannot tolerate the presence of carbon, all-metal hot zones are employed. These are constructed from refractory metals with extremely high melting points.
Common metals include molybdenum (Mo), tungsten (W), and tantalum (Ta). These materials are essential for depositing certain electronic or medical-grade films where carbon contamination from a graphite furnace would be unacceptable.
Ceramic and Combination Hot Zones
In some cases, ceramic fibers or boards are used for their exceptional chemical inertness and thermal insulation properties.
More commonly, furnaces use a combination of materials. A design might feature molybdenum heating elements within a graphite-felt-insulated chamber to balance performance, purity, and cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of material directly impacts the furnace's capabilities, operational lifetime, and cost.
Graphite: The Versatile Standard
Graphite offers the best balance of cost and performance for a wide range of applications. Its primary drawback is the potential to outgas or react with certain precursors, which can introduce carbon impurities into the deposition film. It can also be brittle.
Refractory Metals: The High-Purity Choice
Molybdenum and tungsten provide a superior level of purity and are ideal for high-vacuum environments. However, they are significantly more expensive than graphite and can be more difficult to fabricate. They can also become brittle after repeated high-temperature thermal cycles.
Ceramics: The Inert Specialist
Ceramics offer the highest chemical resistance but are often more fragile and susceptible to thermal shock than metals or graphite. They are typically used in specialized applications where reactivity is the primary concern.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct hot zone material is critical for achieving the desired outcome in your CVD process.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose coating and cost-effectiveness: A graphite-based hot zone is the industry standard and the most practical choice.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high purity for electronics or medical devices: An all-metal hot zone using molybdenum or tungsten is necessary to avoid carbon contamination.
- If your primary focus is depositing materials using highly reactive precursors: A specialized ceramic-lined or combination hot zone may be required to ensure chemical inertness.
Ultimately, understanding these material properties empowers you to select a furnace design that aligns perfectly with your technical and economic goals.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite | Cost-effective, easily machined, good thermal stability | General-purpose coatings, cost-sensitive processes |
| Refractory Metals (e.g., Mo, W) | Ultra-high purity, high melting point, expensive | Electronics, medical devices, high-vacuum environments |
| Ceramics | Chemically inert, fragile, thermal shock resistant | Highly reactive precursor processes, specialized applications |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your CVD Process with KINTEK
Struggling to choose the right hot zone material for your specific CVD application? Our expert team at KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Whether you require Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, or CVD/PECVD Systems, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements—ensuring optimal purity, performance, and cost-efficiency.
Don't let material limitations hold back your research or production. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities and drive success in your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of CVD tube furnace sintering systems? Achieve Superior Material Control and Purity
- What are the key design features of a CVD Tube Furnace? Optimize Your Material Synthesis with Precision
- What are 2D heterostructures and how are they created using CVD tube furnaces? Unlock Atomic-Scale Material Engineering
- What are the practical applications of gate media prepared by CVD tube furnaces? Unlock Advanced Electronics and More
- What are the operational benefits of using a CVD Tube Furnace? Enhance Precision and Efficiency in Your Lab



















