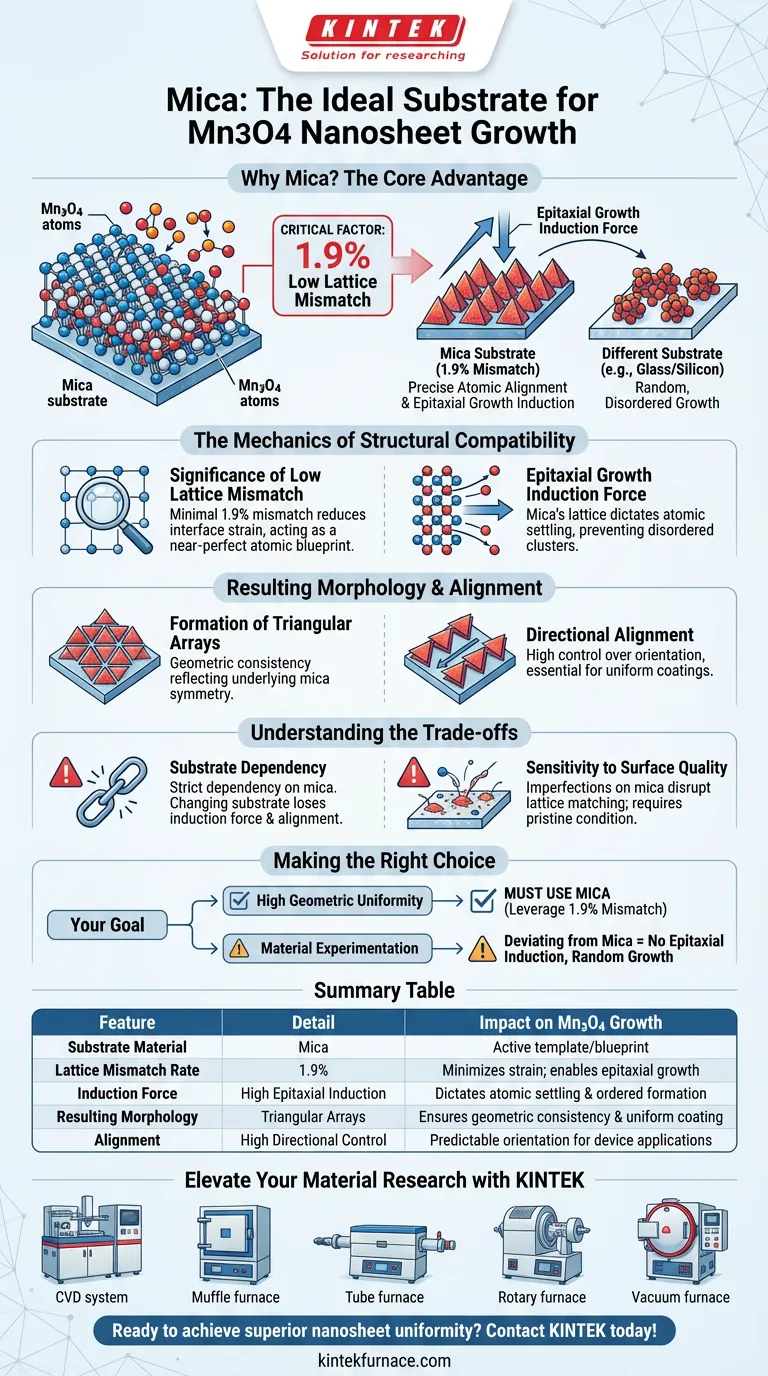
Mica is preferred as a substrate for the growth of Mn3O4 nanosheets primarily due to its exceptional structural compatibility with the material. The critical factor is the extremely low lattice mismatch rate of only 1.9% between the mica substrate and the Mn3O4 crystals. This precise atomic alignment provides a powerful "epitaxial growth induction force" that mechanically guides the formation of the nanosheets during Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
The core value of mica lies in its ability to act as a near-perfect atomic blueprint; the minimal 1.9% lattice mismatch ensures that Mn3O4 nanosheets do not grow randomly, but rather form highly ordered, consistent triangular arrays.

The Mechanics of Structural Compatibility
The Significance of Low Lattice Mismatch
In CVD processes, the substrate acts as the foundation for crystal growth. For high-quality nanosheets, the atomic spacing of the substrate must match the spacing of the material being grown.
Mica offers a mismatch rate of only 1.9% relative to Mn3O4. In materials science, a mismatch this low is statistically significant, reducing the strain at the interface between the two materials.
Epitaxial Growth Induction Force
Because the lattice structures match so closely, the mica exerts a physical influence known as an epitaxial growth induction force.
This force dictates how the initial atoms of Mn3O4 settle onto the surface. Instead of accumulating in disordered clusters, the atoms are compelled to follow the existing crystalline pattern of the mica.
Resulting Morphology and Alignment
Formation of Triangular Arrays
The macroscopic result of this atomic compatibility is a specific geometric consistency. The Mn3O4 nanosheets naturally organize into triangular arrays.
This shape is not accidental; it is a direct reflection of the underlying symmetry provided by the mica lattice.
Directional Alignment
Beyond just shape, the orientation of these nanosheets is highly controlled.
The strong induction force ensures the sheets align in specific, predictable directions. This results in a uniform coating or pattern, which is often essential for the performance of the final device or material application.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Substrate Dependency
While mica ensures high-quality growth, relying on epitaxial induction creates a strict dependency on the substrate material.
You cannot simply swap mica for a different substrate (like glass or silicon) and expect the same results. Without the specific 1.9% mismatch conditions, the induction force vanishes, and the alignment will likely be lost.
Sensitivity to Surface Quality
The process relies on the interface between the mica and the vapor. Any imperfections or contaminants on the mica surface can disrupt the lattice matching.
Therefore, the quality of the resulting Mn3O4 is inextricably linked to the pristine condition of the mica substrate prior to the CVD process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
If you are designing a CVD experiment or manufacturing process for Mn3O4, your substrate choice dictates your outcome.
- If your primary focus is high geometric uniformity: You must use mica to leverage the 1.9% lattice mismatch for precise triangular alignment.
- If your primary focus is material experimentation: Understand that deviating from mica will remove the epitaxial induction force, likely resulting in random or disordered growth patterns.
Ultimately, mica is not just a passive holder for the material; it is an active template that defines the structural integrity of the Mn3O4 nanosheets.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Detail | Impact on Mn3O4 Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate Material | Mica | Acts as an active template/blueprint |
| Lattice Mismatch Rate | 1.9% | Minimizes interface strain; enables epitaxial growth |
| Induction Force | High Epitaxial Induction | Dictates atomic settling and ordered formation |
| Resulting Morphology | Triangular Arrays | Ensures geometric consistency and uniform coating |
| Alignment | High Directional Control | Predictable orientation for device applications |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision in CVD growth begins with the right equipment and expertise. KINTEK provides industry-leading CVD systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum furnaces designed to meet the rigorous demands of epitaxial growth and nanotechnology research. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to ensure your substrates—like mica—reach the exact thermal and chemical conditions required for perfect crystal alignment.
Ready to achieve superior nanosheet uniformity? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique laboratory needs with our high-temperature furnace specialists.
Visual Guide
References
- Jiashuai Yuan, Wei Liu. Controllable synthesis of nonlayered high-κ Mn3O4 single-crystal thin films for 2D electronics. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56386-9
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What factors are important for maximizing CVD coating performance? Achieve Superior Coating Quality and Durability
- What challenges are associated with CVD? Overcome Cost, Control, and Safety Hurdles
- Why is NaCl used in WTe2 CVD synthesis? Enhance Crystal Growth with Salt-Assisted Flux
- What role does an industrial-grade CVD system play in Ni-Based Superalloys? Enhancing Durability via Precise Coating
- What advanced materials and applications utilize CVD in electronics? Unlock Next-Gen Electronics with Precision CVD
- What advantages does a CVD Tube Furnace offer for material research? Unlock Precision and Versatility for Advanced Synthesis
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth
- What are the different types of CVD systems and their applications? Choose the Right CVD for Your Lab Needs









