At their core, CVD tube furnace systems are the enabling technology for synthesizing high-quality, single-layer 2D materials. They are not merely ovens; they are highly controlled micro-environments that provide the four critical conditions—precise temperature, a pure atmosphere, uniform heating, and a stable process for chemical deposition—necessary to grow materials one atomic layer at a time.
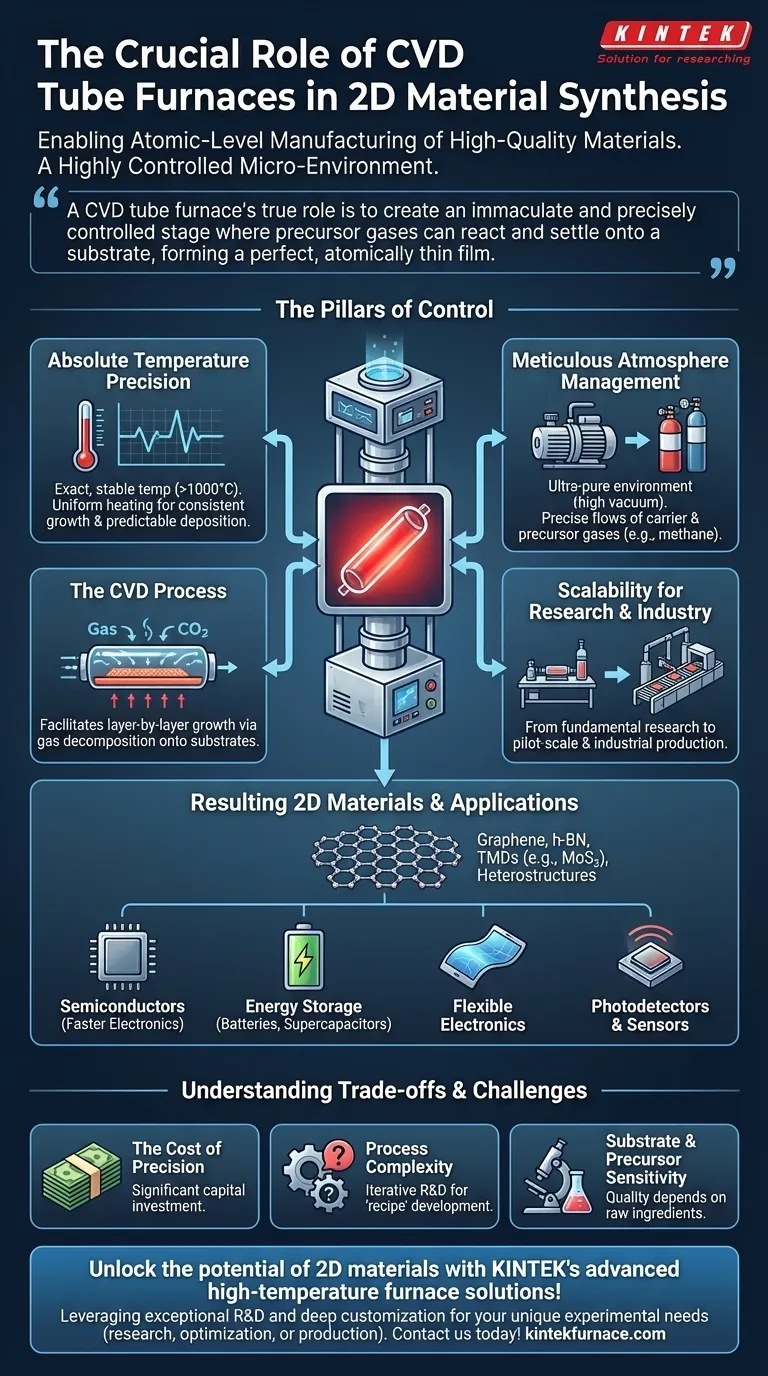
A CVD tube furnace's true role is to create an immaculate and precisely controlled stage where precursor gases can react and settle onto a substrate, forming a perfect, atomically thin film. Without this level of environmental control, creating high-purity 2D materials like graphene would be impossible.

The Pillars of Control in 2D Material Synthesis
A CVD tube furnace provides an integrated solution to the fundamental challenges of atomic-level manufacturing. Its role is defined by its ability to master four key variables.
Absolute Temperature Precision
The synthesis of 2D materials is a thermally-driven process. The furnace must maintain an exact, stable temperature, often exceeding 1000°C, to achieve the desired outcome.
Even slight deviations can ruin a sample. This precision ensures that precursor gases decompose predictably and that the atoms have the right energy to arrange themselves into the desired crystalline structure on the substrate.
Furthermore, uniform heating across the entire tube ensures that the 2D material grows consistently over the whole substrate, which is critical for producing large, usable films.
Meticulous Atmosphere Management
The furnace's tube is evacuated to a high vacuum to remove all atmospheric contaminants like oxygen and water vapor.
This step is non-negotiable. An ultra-pure environment prevents unwanted chemical reactions that would introduce defects and impurities into the material's atomic lattice.
Once evacuated, precisely controlled flows of specific carrier and precursor gases are introduced. This management of the atmosphere dictates the final chemical composition of the material being grown.
The Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Process
The furnace's primary function is to facilitate the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process.
Volatile precursor gases (e.g., methane for graphene) are introduced into the hot furnace. When they flow over a heated substrate (e.g., a copper foil), they decompose and "deposit" a thin film of the desired material onto its surface.
This process allows for the controlled, layer-by-layer growth that defines 2D materials.
Scalability for Research and Industry
CVD tube furnaces are designed with scalability in mind. A process developed in a small-diameter tube for fundamental research can be transferred to a larger furnace for pilot-scale or industrial production.
This scalability is a key reason why CVD remains central to both academic research and the commercialization of 2D materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While indispensable, these systems are not without their complexities. Acknowledging the trade-offs is crucial for any serious practitioner.
The Cost of Precision
High-quality furnace systems capable of the temperature stability and vacuum purity required for 2D material synthesis represent a significant capital investment.
Process Complexity and Development Time
A CVD furnace is a tool, not a "one-click" solution. Developing a successful "recipe"—the specific combination of temperature, pressure, gas flow rates, and timing—for a new material is a complex and iterative R&D process.
Substrate and Precursor Sensitivity
The final quality of the 2D material is not solely dependent on the furnace. It is equally sensitive to the quality of the substrate it is grown on and the purity of the precursor gases used. The furnace can only provide the right environment; the raw ingredients must also be perfect.
The Materials and Their Applications
The control offered by CVD tube furnaces has unlocked a new class of materials that are powering next-generation technology.
From Graphene to Heterostructures
These systems are the workhorses for producing the most well-known 2D materials, including graphene, hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), and transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) like MoS₂.
They are also used to create "heterostructures," which are complex stacks of different 2D materials, opening up entirely new possibilities in materials engineering.
Powering Next-Generation Technology
The high-quality films produced in these furnaces are essential for a wide range of industries.
Applications include advanced semiconductors for faster electronics, materials for energy storage in batteries and supercapacitors, flexible electronics, and highly sensitive photodetectors and sensors.
Applying This to Your Goal
Your specific objective will determine which system capabilities you should prioritize.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: Prioritize a system with maximum flexibility in temperature ranges, gas handling options, and vacuum levels to explore novel materials and growth parameters.
- If your primary focus is process optimization: Emphasize a system with excellent automation, data logging, and run-to-run reproducibility to standardize a reliable growth recipe.
- If your primary focus is industrial production: Focus on system throughput, reliability, and scalability to ensure you can manufacture consistent, high-quality material in large volumes.
Ultimately, the CVD tube furnace is the foundational instrument that allows scientists and engineers to practice the atomic-scale architecture required to build the future of materials science.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Role in 2D Material Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Ensures stable, uniform heating for predictable atomic layer deposition and crystal formation. |
| Atmosphere Management | Maintains ultra-pure environments to prevent defects and control chemical composition. |
| CVD Process | Facilitates layer-by-layer growth via gas decomposition on substrates. |
| Scalability | Supports transition from research to industrial production of high-quality films. |
| Applications | Powers semiconductors, energy storage, flexible electronics, and sensors. |
Unlock the potential of 2D materials with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored CVD tube furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, whether for fundamental research, process optimization, or industrial production. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your material synthesis and drive innovation in your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics



















