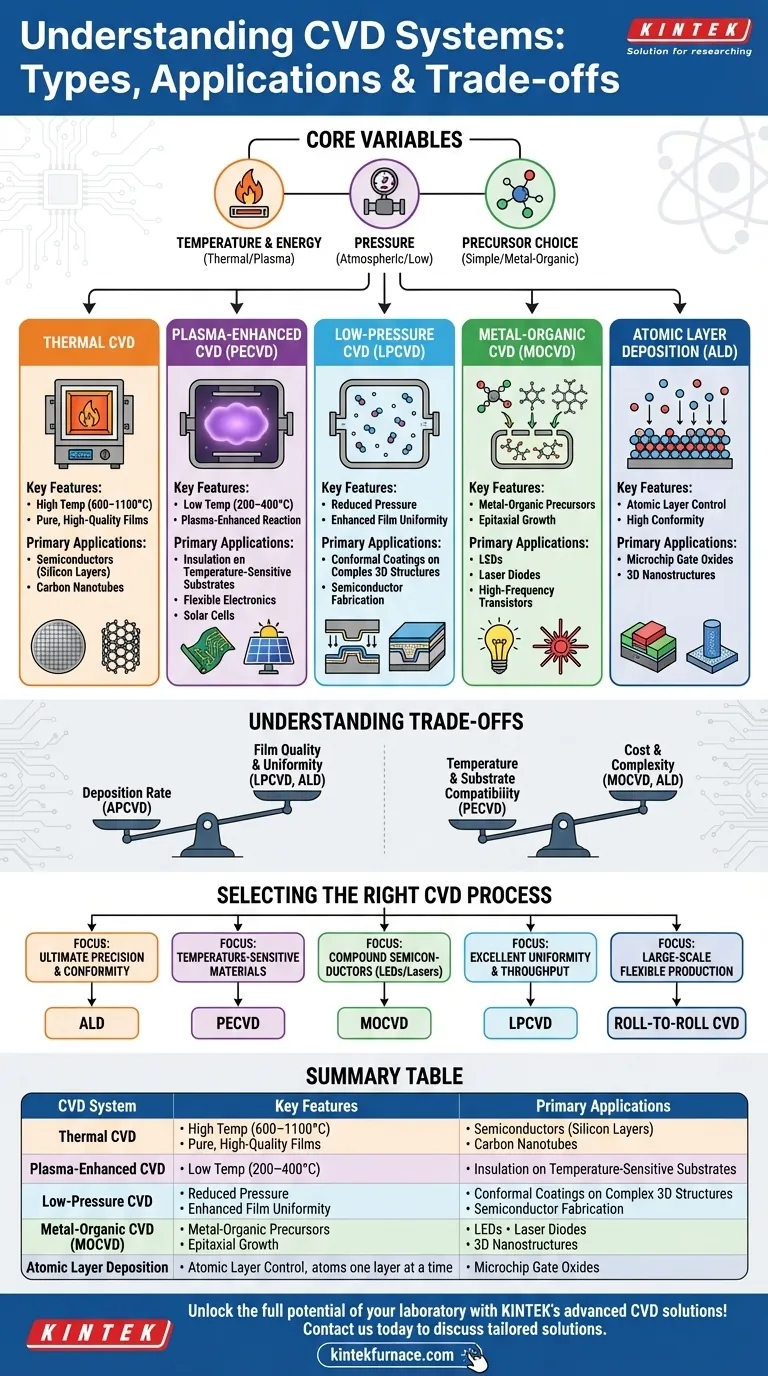
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is not a single technique but a family of processes used to deposit thin solid films from a gaseous state. The primary types include Thermal CVD, Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), Metal-Organic CVD (MOCVD), and Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD), each distinguished by its operating principles—such as temperature, pressure, and energy source—to suit specific applications from semiconductors to protective coatings.
The existence of different CVD systems is not about arbitrary choice; it's about solving specific engineering problems. Each variation is a strategic manipulation of temperature, pressure, and chemistry to achieve a desired balance between film quality, deposition speed, and compatibility with the underlying material.

The Core Variables Defining a CVD System
Understanding any CVD system begins with grasping the three fundamental variables that engineers manipulate to control the film deposition process.
The Role of Temperature and Energy
Temperature is the original driving force for CVD reactions. It provides the thermal energy needed to break down precursor gases and allow them to react on the substrate surface.
However, high temperatures can damage sensitive substrates like polymers or pre-existing electronic components. This limitation led to methods like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), which uses an energy-rich plasma to facilitate the reaction at much lower temperatures.
The Impact of Pressure
The pressure inside the reactor chamber directly influences the behavior of gas molecules. It is a critical lever for controlling film quality.
Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD) is fast and simple but can result in lower film uniformity. In contrast, Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) reduces gas-phase reactions, allowing precursors to cover the substrate more evenly and leading to highly uniform and conformal films.
The Significance of Precursor Choice
The "chemical" in Chemical Vapor Deposition refers to the precursor gases. The choice of precursor dictates the material being deposited.
For standard materials like silicon nitride, simple precursors are used. For more complex materials, such as the compound semiconductors used in LEDs, specialized Metal-Organic CVD (MOCVD) is required, which uses metal-organic compounds as its precursors.
A Breakdown of Key CVD Systems
Each type of CVD system is an optimized solution for a particular set of requirements.
Thermal CVD: The High-Temperature Foundation
This is the classic form of CVD, relying solely on high temperatures (typically 600–1100°C) to drive the chemical reaction.
It is highly effective for producing pure, high-quality films and is widely used for depositing silicon layers in semiconductor manufacturing and for growing carbon nanotubes. Its main drawback is the high thermal budget.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD): Lowering the Temperature Barrier
PECVD uses a plasma to energize the precursor gases, allowing deposition to occur at significantly lower temperatures (typically 200–400°C).
This makes it indispensable for depositing films, such as silicon nitride for insulation, onto temperature-sensitive substrates like finished semiconductor wafers or plastics for flexible electronics and solar cells.
Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD): Enhancing Film Uniformity
By operating at reduced pressure, LPCVD minimizes unwanted gas-phase reactions. This allows the reactive species to travel further and coat complex, three-dimensional structures with exceptional uniformity.
Its ability to produce highly conformal films makes it a workhorse in semiconductor fabrication for creating insulating and conductive layers over microscopic device topographies.
Metal-Organic CVD (MOCVD): For Advanced Compound Semiconductors
MOCVD is a specialized subtype of thermal CVD that uses metal-organic precursors to deposit high-quality, single-crystal films.
It is the dominant technology for manufacturing high-performance optoelectronics, including the gallium nitride (GaN) based materials used in modern LED lighting, laser diodes, and high-frequency transistors.
Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD): The Precision Standard
While sometimes considered a separate class, ALD is an advanced CVD technique that deposits material one atomic layer at a time in a sequential, self-limiting process.
This provides unparalleled control over film thickness and conformity, even on the most complex 3D structures. It is critical for producing the ultra-thin, high-k dielectric gate oxides required for modern, miniaturized microchips.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a CVD method involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" system; there is only the best system for a specific goal.
Deposition Rate vs. Film Quality
Generally, faster deposition methods like APCVD can sometimes compromise film quality and uniformity. Slower, more controlled processes like LPCVD and especially ALD offer superior quality and conformity but at the cost of throughput.
Temperature vs. Substrate Compatibility
The primary trade-off for Thermal CVD is its high temperature, which limits its use to robust substrates like silicon wafers. Processes like PECVD were invented specifically to overcome this limitation, enabling deposition on a much wider range of materials.
Cost and Complexity vs. Performance
Simpler systems like APCVD are less expensive to operate. In contrast, highly specialized systems like MOCVD and ALD require complex, expensive equipment and precursors but deliver performance and materials that are otherwise unattainable.
Selecting the Right CVD Process for Your Goal
Your choice of CVD technique should be driven directly by your primary application objective.
- If your primary focus is ultimate precision and conformity for nano-scale devices: ALD is the only choice for achieving angstrom-level control over film thickness.
- If your primary focus is depositing on temperature-sensitive materials: PECVD provides the necessary energy through plasma, protecting the underlying substrate.
- If your primary focus is creating high-quality compound semiconductors for LEDs or lasers: MOCVD is the industry standard for the required epitaxial growth.
- If your primary focus is excellent film uniformity over complex topographies: LPCVD offers a powerful balance of quality and reasonable throughput.
- If your primary focus is large-scale production of flexible electronics: Roll-to-Roll CVD is designed for high-volume manufacturing on flexible substrates like graphene.
Ultimately, the right CVD system is the one that delivers the required material properties and performance within the physical and economic constraints of your project.
Summary Table:
| CVD System Type | Key Features | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal CVD | High temperature (600–1100°C), pure films | Semiconductors, carbon nanotubes |
| PECVD | Low temperature (200–400°C), plasma-enhanced | Insulation on wafers, flexible electronics |
| LPCVD | Low pressure, high uniformity | Semiconductor fabrication, conformal coatings |
| MOCVD | Metal-organic precursors, epitaxial growth | LEDs, laser diodes, high-frequency transistors |
| ALD | Atomic layer control, high conformity | Microchip gate oxides, 3D nanostructures |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced CVD solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and specialized CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you're working on semiconductors, optoelectronics, or protective coatings. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your research and production efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition



















