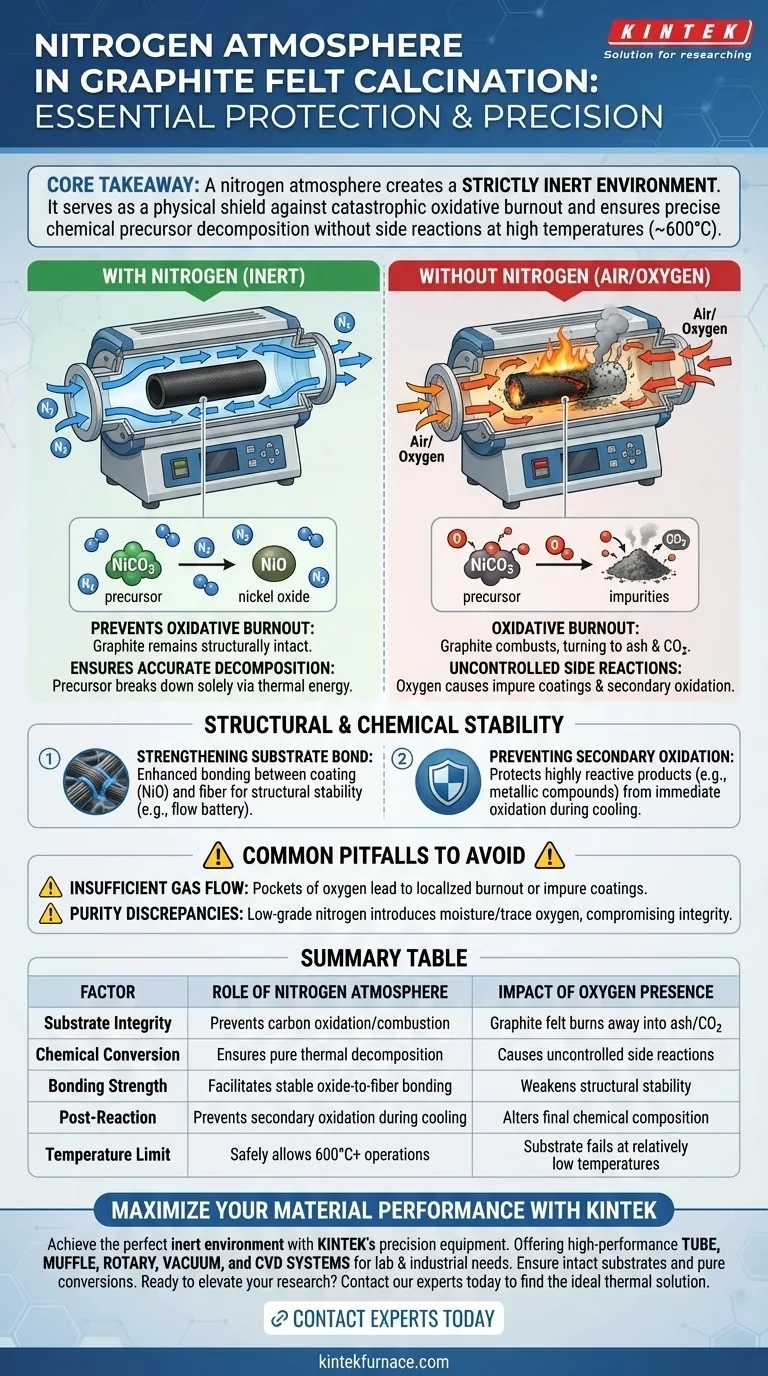
A nitrogen atmosphere is strictly required to create an inert environment during the calcination of modified graphite felt. Without this protective barrier, the high operating temperatures (typically around 600 °C) would cause the graphite substrate to react with atmospheric oxygen and burn away, while also compromising the precise chemical conversion of the coating materials.
Core Takeaway The nitrogen atmosphere serves a dual purpose: it acts as a physical shield to prevent the catastrophic combustion (oxidative burnout) of the carbon-based graphite felt, and it ensures the chemical precursor decomposes exclusively into the target oxide without uncontrolled side reactions.

The Mechanics of Inert Atmosphere Protection
Preventing Oxidative Burnout
Graphite felt is composed of carbon fibers. In the presence of oxygen, carbon begins to oxidize and burn at relatively low temperatures.
Because the calcination process requires heating the material to approximately 600 °C, the presence of air would cause the felt to combust, turning your substrate into ash and carbon dioxide.
A continuous flow of high-purity nitrogen displaces oxygen in the tube furnace, ensuring the graphite remains structurally intact throughout the thermal treatment.
Ensuring Accurate Chemical Decomposition
The goal of this process is often to convert a precursor, such as nickel carbonate, into a specific target material like nickel oxide.
Nitrogen ensures this decomposition happens solely through thermal energy, rather than through chemical interaction with atmospheric gases.
This isolation allows the precursor to break down accurately into stable nickel oxide crystals without interference from oxygen-fueled side reactions.
Structural and Chemical Stability
Strengthening the Substrate Bond
Beyond simple protection, the controlled atmosphere facilitates a specific interaction between the coating and the fiber.
The high-temperature treatment under nitrogen strengthens the bond between the newly formed nickel oxide and the graphite felt fibers.
This enhanced bonding is critical for ensuring the material possesses the necessary structural stability to survive the rigors of applications like flow battery cycling.
Preventing Secondary Oxidation
When modifying materials, the reaction products (such as metallic compounds or carbides) can be highly reactive immediately after formation.
If exposed to oxygen while still hot, these newly formed materials can undergo "secondary oxidation," altering their chemical composition instantly.
The nitrogen barrier protects these reduction products until they have cooled or stabilized, ensuring the final chemical properties match your analytical targets.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Insufficient Gas Flow
Simply filling the tube with nitrogen is often not enough; a continuous flow is required to flush out any oxygen released during the heating process.
If the flow rate is too low, pockets of oxygen may remain or seep in, leading to localized burnout or impure coatings.
Purity Discrepancies
Using low-grade nitrogen can introduce moisture or trace oxygen into the furnace.
Even small impurities can compromise the integrity of the graphite felt at 600 °C. Always ensure the nitrogen grade matches the sensitivity of your specific modification process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the success of your calcination process, align your setup with your specific research objectives:
- If your primary focus is Substrate Integrity: Ensure your nitrogen purge begins before the heating ramp starts to completely eliminate oxygen before the critical combustion temperature is reached.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Verify that your nitrogen flow rate allows for the complete removal of off-gases generated during the decomposition of the nickel carbonate precursor.
Success in modifying graphite felt lies in managing the invisible competition between thermal treatment and oxidative destruction.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Role of Nitrogen Atmosphere | Impact of Oxygen Presence |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate Integrity | Prevents carbon oxidation/combustion | Graphite felt burns away into ash/CO2 |
| Chemical Conversion | Ensures pure thermal decomposition | Causes uncontrolled side reactions |
| Bonding Strength | Facilitates stable oxide-to-fiber bonding | Weakens structural stability of the coating |
| Post-Reaction | Prevents secondary oxidation during cooling | Alters final chemical composition immediately |
| Temperature Limit | Safely allows 600°C+ operations | Substrate fails at relatively low temperatures |
Maximize Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Achieving the perfect inert environment for graphite felt calcination requires precision equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for lab-scale and industrial high-temperature needs. Whether you require customizable gas flow controls or ultra-pure nitrogen seals, our systems ensure your substrates remain intact and your chemical conversions remain pure.
Ready to elevate your research or production? Contact our experts today to find the ideal thermal solution for your unique requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Jingping Xie, Xiao‐min Wang. Performance Study of Nickel Oxide Graphite Felts as Electrode Materials for Ferrochromium Flow Batteries. DOI: 10.1002/open.202500405
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a carbothermic reduction step necessary for copper slag glass-ceramics? Optimize Your Material Purification
- What is a retort furnace and what is its primary purpose? Master Controlled Heat Treatment for Your Materials
- How does an inert atmosphere furnace work? Master Controlled Heating for Oxidation-Free Results
- Can the reducing atmosphere be replaced with other gaseous mediums? Explore Advanced Surface Engineering Solutions
- What are the consequences of an improperly controlled furnace atmosphere? Avoid Costly Defects and Safety Hazards
- How does the atmosphere differ between tube furnaces and box furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- How does a thermal oxidation furnace facilitate the phase transformation of metallic vanadium? Learn V2O5 Optimization
- How does a high-temperature electric furnace facilitate the sintering process of 3Y-TZP ceramics? Master Densification



















