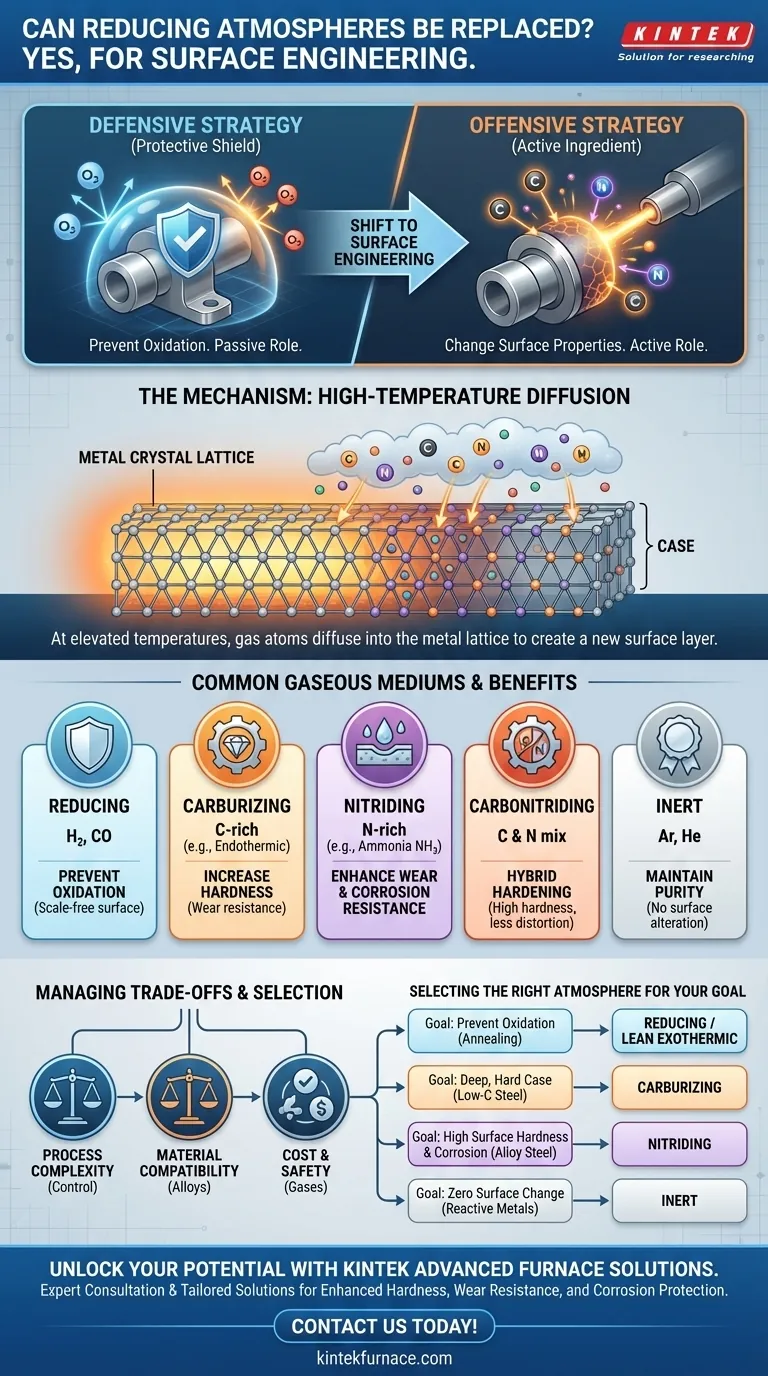
Yes, absolutely. A reducing atmosphere is just one type of controlled gaseous environment used in thermal processing. It can be—and frequently is—replaced with other specific gaseous mediums to deliberately engineer the surface of a workpiece, a process far more advanced than simply preventing oxidation. These alternative atmospheres are chosen to induce specific chemical reactions that impart desired properties like extreme hardness, wear resistance, or corrosion protection.
The core principle is shifting from a defensive to an offensive strategy. Instead of merely using a gas to protect a material's surface from the environment, you use a specific gas as an active ingredient to change the surface and create properties the base material does not possess.

From Protective to Active: The Role of a Gaseous Atmosphere
Understanding the function of a furnace atmosphere is key. Its role can be passive (protective) or active (reactive), depending on the engineering goal.
The Baseline: Reducing Atmospheres
A reducing atmosphere is the standard for preventing oxidation. Composed of gases like hydrogen (H₂) and carbon monoxide (CO), its primary job is to react with and remove any oxygen present, protecting the metal surface from scaling and discoloration during heating.
The Goal: Surface Engineering
The more advanced application is surface engineering. Here, the atmosphere is no longer just a shield. It becomes a delivery mechanism for specific elements that are intended to chemically alter the workpiece's surface layer.
The Mechanism: High-Temperature Diffusion
This process works because at elevated temperatures, the atoms in a solid metal are more mobile. When a hot metal surface is exposed to a gas containing elements like carbon or nitrogen, those elements can diffuse into the metal's crystal lattice, creating a new, distinct surface layer or "case."
Common Gaseous Mediums and Their Purpose
Replacing a simple reducing gas with a chemically active one allows for a range of surface-hardening treatments. Each process uses a unique gas composition to achieve a different outcome.
Carburizing Atmospheres (for Hardness)
To create a hard, wear-resistant surface on steel, a carburizing atmosphere is used. These are rich in carbon, typically derived from endothermic gas or the direct addition of natural gas. Carbon diffuses into the surface of the steel, which can then be quenched to form an extremely hard martensitic case over a tough, ductile core.
Nitriding Atmospheres (for Wear and Corrosion Resistance)
Nitriding uses an atmosphere rich in nitrogen, most commonly by dissociating ammonia (NH₃) at the metal's surface. Nitrogen diffuses into the steel, forming extremely hard iron nitride compounds. This process occurs at lower temperatures than carburizing and provides excellent wear resistance, anti-galling properties, and a notable improvement in corrosion resistance.
Carbonitriding Atmospheres (A Hybrid Approach)
As the name implies, carbonitriding involves diffusing both carbon and nitrogen into the surface. This is done by adding ammonia to a carburizing atmosphere. The resulting case is harder than a carburized case and can be achieved at lower temperatures, reducing part distortion.
Inert Atmospheres (for Purity)
In some cases, the goal is zero chemical reaction. For sensitive or reactive metals like titanium, or for processes like brazing where you cannot tolerate any surface change, a truly inert atmosphere of argon or helium is used. While expensive, these gases ensure the surface remains completely unaltered.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an active atmosphere is a significant engineering decision with clear trade-offs that must be managed.
Process Complexity and Control
Active atmospheres require precise control. Gas composition, temperature, and time must be meticulously managed. Improper control can lead to undesirable outcomes like sooting (excess carbon), embrittlement, or inconsistent case depths, potentially ruining an entire batch of parts.
Material Compatibility
Not all materials are suitable for every treatment. For instance, nitriding is most effective on steels containing alloying elements like aluminum, chromium, or molybdenum, which form stable, hard nitrides. Plain carbon steel does not respond as well to nitriding.
Cost and Safety
The gases involved carry different costs and safety concerns. Hydrogen, a powerful reducing agent, is highly flammable. Ammonia, the source for nitriding, is toxic. Inert gases like argon are very safe but significantly more expensive than nitrogen or endothermic gas.
Selecting the Right Atmosphere for Your Goal
The choice of atmosphere should be driven entirely by the desired final properties of the component.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation during simple annealing: A basic reducing atmosphere (hydrogen/nitrogen) or even a lean exothermic gas is sufficient and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is creating a deep, hard, wear-resistant case on low-carbon steel: A carburizing atmosphere is the standard engineering choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving high surface hardness and corrosion resistance with minimal distortion: A nitriding atmosphere is the ideal solution, especially for alloy steels.
- If your primary focus is treating highly reactive metals or ensuring zero surface contamination: A pure inert atmosphere like argon is necessary, despite the higher cost.
Ultimately, treating the furnace atmosphere as an active ingredient, not just a protective shield, unlocks a new level of material performance.
Summary Table:
| Gaseous Medium | Primary Purpose | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Reducing Atmosphere | Prevent oxidation | Protects metals from scaling and discoloration |
| Carburizing Atmosphere | Increase hardness | Creates wear-resistant surface on steel |
| Nitriding Atmosphere | Enhance wear and corrosion resistance | Improves hardness and anti-galling properties |
| Carbonitriding Atmosphere | Hybrid hardening | Achieves high hardness with reduced distortion |
| Inert Atmosphere | Maintain purity | Ensures no surface alteration for sensitive materials |
Unlock the full potential of your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering enhanced hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion protection. Ready to optimize your surface engineering? Contact us today for expert consultation and tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition (MPCVD)? Unlock Ultra-Pure Diamond Synthesis
- What are the differences in film quality between PVD and CVD? Discover the Best Method for Your Application
- How is MPCVD used in manufacturing polycrystalline diamond optical components? Achieve Superior Optical Performance
- What does CVD stand for and what is its primary function? Discover High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- How does the ionization degree in MPCVD compare to other methods? Uncover Superior Film Quality and Speed



















