In short, an improperly controlled furnace atmosphere has severe consequences. It leads to chemical reactions that ruin part quality, causing direct financial losses from rejected products and wasted time. More critically, it can damage expensive furnace equipment and create significant safety risks for personnel from both hazardous gases and potentially defective final parts.
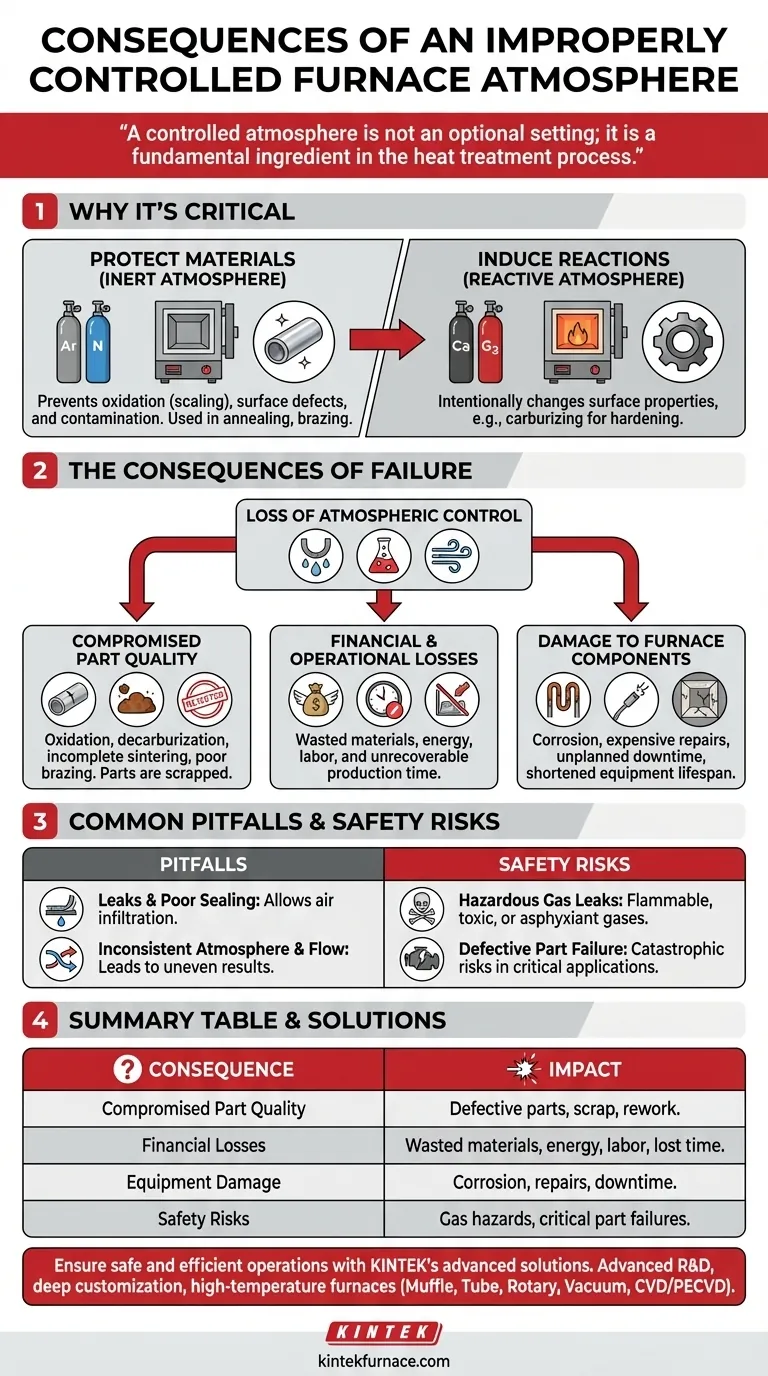
A controlled atmosphere is not an optional setting; it is a fundamental ingredient in the heat treatment process. Failure to control it means you are not merely producing a subpar part—you are actively creating a defective material, risking your equipment, and compromising the safety of your operation.
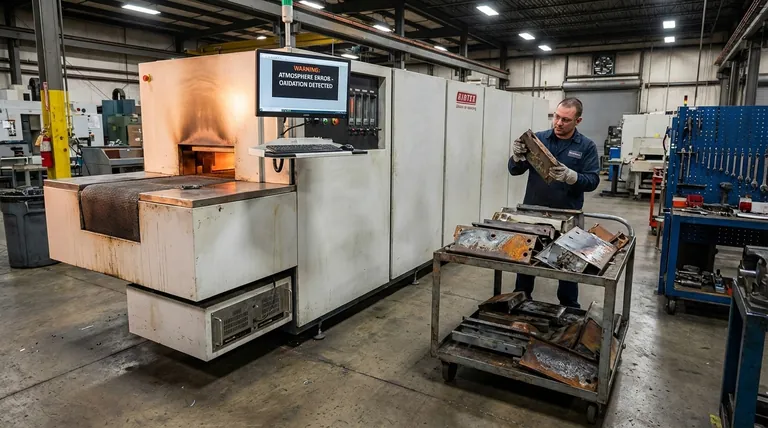

Why a Controlled Atmosphere is Critical
To understand the consequences of failure, we must first understand the purpose of atmospheric control. A controlled atmosphere furnace creates a tightly sealed environment to achieve one of two primary goals.
To Protect Materials from Contamination
Many heat treatment processes, such as annealing or brazing, require an inert atmosphere. Gases like nitrogen or argon are used to displace oxygen and moisture from the air.
Without this protective layer, high temperatures would cause the metal to react with oxygen, leading to oxidation (scaling) and other surface defects that compromise its integrity and finish.
To Induce Desired Chemical Reactions
Conversely, some processes use a reactive atmosphere to intentionally change a material's surface properties.
For example, carburizing introduces a carbon-rich gas to harden the surface of steel. If this atmosphere is not precisely controlled, the part will not achieve the required hardness and performance specifications.
The Consequences of an Uncontrolled Atmosphere
When atmospheric control is lost due to leaks, incorrect gas mixtures, or poor flow, the results are predictable and costly.
Compromised Part Quality
This is the most immediate outcome. An incorrect atmosphere causes unwanted chemical reactions.
This can manifest as oxidation, decarburization (loss of surface carbon and hardness), incomplete sintering in powdered metals, or poor braze joints. The parts are fundamentally defective and must be scrapped.
Financial and Operational Losses
Rejected parts translate directly to financial loss. This includes the cost of the raw materials, the energy consumed by the furnace, the labor involved, and the lost production time that can never be recovered.
Damage to Furnace Components
The wrong atmosphere can actively harm the furnace itself. Certain gases at high temperatures can corrode heating elements, thermocouples, and the furnace's internal lining.
This leads to expensive repairs, unplanned downtime, and a shortened lifespan for a critical piece of capital equipment.
Common Pitfalls and Safety Risks
Failures in atmospheric control are rarely abstract; they are tied to specific operational oversights and carry very real human risks.
The Danger of Leaks and Poor Sealing
A controlled atmosphere is useless if the furnace chamber is not hermetically sealed. Even a small leak can allow external air to infiltrate, contaminating the environment and rendering the entire process void. This is a common point of failure in older or poorly maintained equipment.
Inconsistent Atmosphere and Flow
Proper control requires a uniform flow of gas throughout the chamber to ensure every part is exposed to the same conditions. Poor distribution leads to inconsistent results across a single batch, making quality control a nightmare.
The Risk to Personnel
Handling industrial gases carries inherent dangers. An improperly managed system can lead to leaks of flammable, toxic, or asphyxiant gases, posing a direct threat to employees.
Furthermore, shipping a defective part that later fails in a critical application—such as in an automotive or aerospace component—can have catastrophic safety consequences for the end-user.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Achieving proper control is about aligning your procedures and equipment with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is consistent part quality: Ensure your furnace has a verified tight seal and that your gas selection, purity, and flow rates are precisely managed for every cycle.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Invest in modern control systems and preventative maintenance to eliminate the rework, scrap, and downtime caused by atmospheric failures.
- If your primary focus is safety: Enforce rigorous protocols for gas handling, regularly inspect all seals and safety devices, and never compromise on part validation before shipment.
Ultimately, precise control over your furnace atmosphere is the defining factor that separates a reliable, high-quality manufacturing process from one that produces waste and risk.
Summary Table:
| Consequence | Impact |
|---|---|
| Compromised Part Quality | Defective parts due to oxidation, decarburization, or poor sintering, leading to scrap and rework. |
| Financial Losses | Costs from wasted materials, energy, labor, and lost production time. |
| Equipment Damage | Corrosion of heating elements and furnace linings, causing expensive repairs and downtime. |
| Safety Risks | Hazards from gas leaks, toxic fumes, and potential part failures in critical applications. |
Ensure your furnace operations are safe and efficient with KINTEK's advanced solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability precisely meets your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your process and protect your investments!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance
- What is the significance of nitrogen in atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Enhanced Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity



















