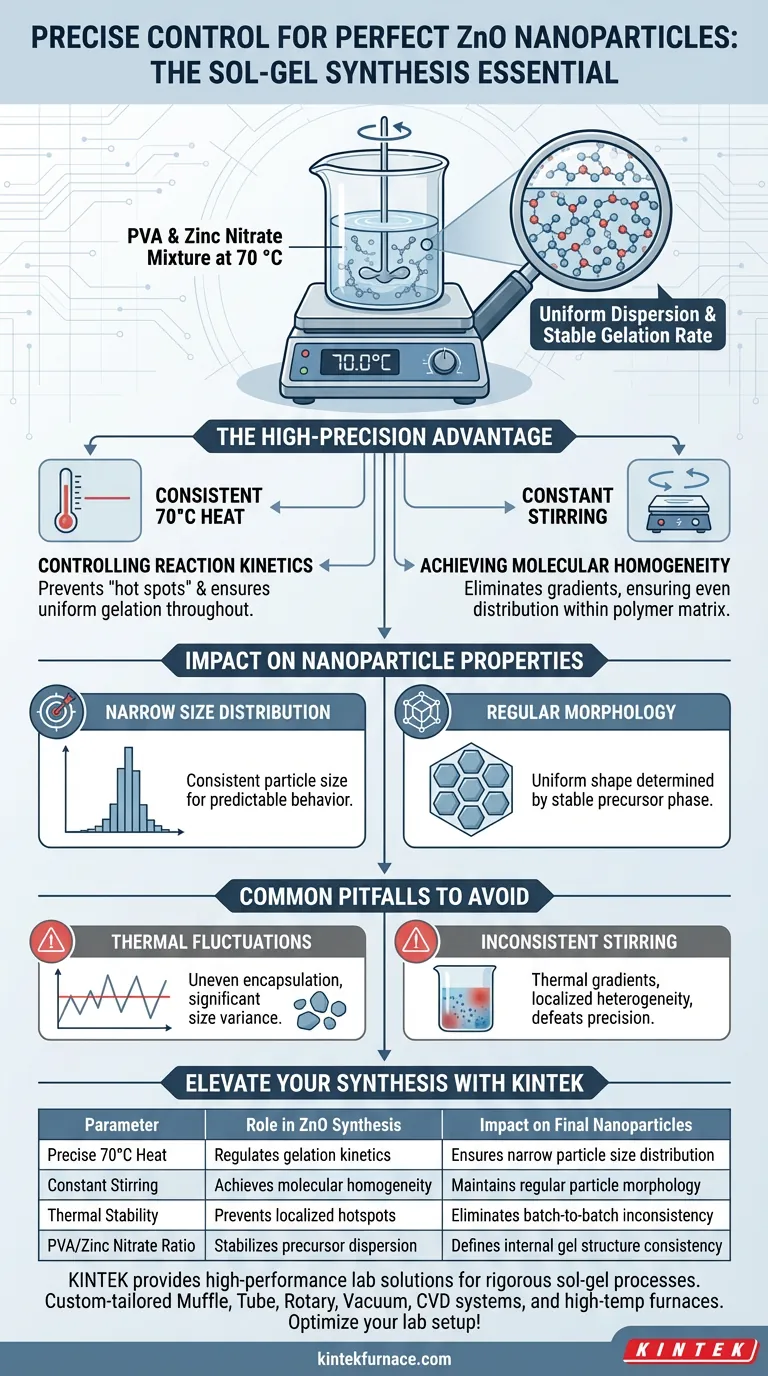
Precise temperature control and stirring are critical to stabilize the reaction mixture of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and zinc nitrate specifically at 70 °C. This specific thermal environment is necessary to strictly regulate the gelation reaction rate, ensuring that zinc ions achieve a uniform, molecular-level dispersion throughout the polymer matrix.
The success of the sol-gel process hinges on thermal stability; without a constant temperature, you cannot achieve the homogeneous dispersion required to produce nanoparticles with a narrow size distribution and regular morphology.

The Mechanics of Gelation and Dispersion
Stabilizing the Precursor Mixture
For the successful synthesis of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles, the precursor mixture—typically PVA and zinc nitrate—must be maintained at a steady 70 °C.
A standard hotplate often fluctuates, but a high-precision platform eliminates these thermal gradients. This stability is the first step in preventing premature or uneven reactions within the solution.
Controlling Reaction Kinetics
The rate at which the solution transforms into a gel is directly dependent on temperature.
By using a high-precision platform, you ensure the gelation rate remains constant throughout the entire volume of the liquid. This prevents "hot spots" where the reaction might accelerate unpredictably.
Achieving Molecular Homogeneity
The ultimate goal of the stirring and heating process is molecular-level dispersion.
Constant stirring combined with precise heat ensures that zinc ions are distributed evenly within the polymer matrix. This homogeneity is impossible to achieve if the temperature drifts, as viscosity and solubility would change across the mixture.
Impact on Nanoparticle Properties
Narrowing Particle Size Distribution
The uniformity achieved during the sol-gel phase directly dictates the consistency of the final product.
When zinc ions are evenly dispersed, the resulting ZnO nanoparticles exhibit a narrow particle size distribution. This consistency is vital for applications requiring predictable physical and chemical behaviors.
Ensuring Regular Morphology
Beyond size, the shape (morphology) of the nanoparticles is determined by the stability of the precursor phase.
A high-precision platform ensures that the internal structure of the gel is uniform. This leads to regular, predictable particle shapes during the subsequent thermal treatments that convert the gel into the final oxide.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The Risk of Thermal Fluctuations
If the temperature deviates even slightly from the 70 °C target, the viscosity of the PVA mixture can change rapidly.
This leads to uneven encapsulation of the zinc ions. The result is often a batch of nanoparticles with significant variance in size, rendering them less effective for high-performance applications.
Inconsistent Stirring Speeds
While temperature is the primary variable, inconsistent stirring can undermine thermal precision.
If the mixture is not agitated uniformly, thermal gradients will form despite the heating element's accuracy. This results in localized heterogeneity, defeating the purpose of the high-precision equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your ZnO synthesis yields the highest quality results, consider your specific experimental objectives:
- If your primary focus is uniform particle size: Prioritize a platform with a PID controller to lock the temperature at exactly 70 °C, preventing reaction rate variance.
- If your primary focus is reproducible morphology: Ensure your platform offers robust magnetic stirring to maintain molecular-level homogeneity throughout the gelation process.
Mastering the thermal environment is the single most effective way to transition from random chemical precipitation to engineered nanomaterial synthesis.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Role in ZnO Synthesis | Impact on Final Nanoparticles |
|---|---|---|
| Precise 70°C Heat | Regulates gelation kinetics | Ensures narrow particle size distribution |
| Constant Stirring | Achieves molecular homogeneity | Maintains regular particle morphology |
| Thermal Stability | Prevents localized hotspots | Eliminates batch-to-batch inconsistency |
| PVA/Zinc Nitrate Ratio | Stabilizes precursor dispersion | Defines internal gel structure consistency |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between random precipitation and engineered excellence. KINTEK provides the high-performance laboratory solutions necessary for rigorous sol-gel processes. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique research needs.
Ensure your ZnO nanoparticles meet the highest standards of morphology and size distribution. Contact us today to optimize your lab setup!
Visual Guide
References
- Farzaneh Edrisi, Nasrin Shadjou. Preparation of an innovative series of respiratory nano-filters using polystyrene fibrous films containing KCC-1 dendrimer and ZnO nanostructures for environmental assessment of SO<sub>2</sub>, NO<sub>2</sub> and CO<sub>2</sub>. DOI: 10.1039/d4ra00176a
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- Why use a fusion furnace and platinum crucibles for XRF analysis of magnesium slag? Ensure Accurate Results
- Are customization options available for alumina ceramic furnace tubes? Tailor Them for Your Lab's Needs
- What are the primary functions of high-purity graphite molds in the SPS of TiB2 ceramics? Enhance Sintering Precision
- What maintenance is required for a water circulating vacuum pump? Ensure Peak Performance and Longevity
- What is the purpose of a water-cooled condenser in a thermal vacuum mercury removal apparatus? Key for Safe Recovery
- What role do graphite molds play in graphite flake alignment? Engineered Precision for High Thermal Conductivity
- What role does the planetary ball mill play in LLZO mixing? Unlock High-Performance Solid-State Electrolyte Synthesis
- What is the primary purpose of a benchtop blast drying oven? Optimize Barium Titanate Ceramic Preparation



















