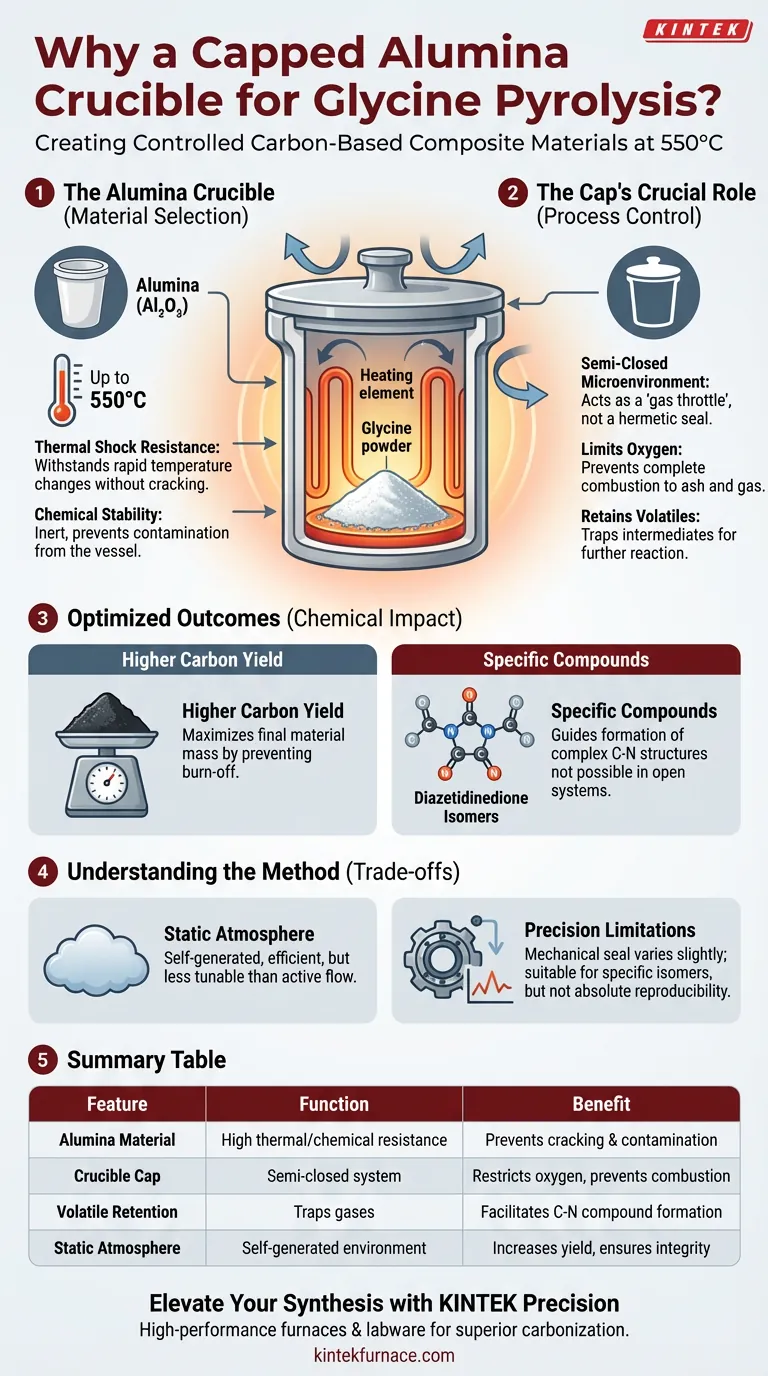
A capped alumina crucible is utilized primarily to create a controlled, semi-closed microenvironment that balances thermal stability with atmospheric regulation. The alumina material provides the necessary chemical inertness and resistance to thermal shock at temperatures reaching 550°C. Simultaneously, the cap restricts airflow, preventing rapid oxidation while retaining volatile intermediates essential for the reaction.
The use of a lid is the defining factor in this synthesis method; it transforms a standard heating process into a controlled carbonization event. By limiting external oxygen and trapping volatiles, the setup guides the chemical pathway toward forming specific carbon-nitrogen compounds rather than allowing complete combustion.

The Role of Material Selection
Thermal Shock Resistance
The pyrolysis of glycine involves ramping temperatures up to 550°C. Alumina is selected because it maintains structural integrity under these thermal stresses. It prevents the vessel from cracking during the heating or cooling phases.
Chemical Stability
Alumina is chemically inert in this context. It does not react with the glycine or the developing carbonaceous material. This ensures that the final composite remains free of contaminants derived from the crucible itself.
The Function of the Cap
Creating a Semi-Closed Microenvironment
The lid does not create a hermetic seal; instead, it establishes a semi-closed system within the static air furnace. This restricts the free flow of air found in an open furnace environment. It effectively acts as a throttle for gas exchange.
Limiting Oxygen Exposure
By physically blocking the free entry of external air, the cap controls the amount of oxygen reaching the sample. Unchecked oxygen access at high temperatures would lead to the complete combustion of glycine into ash and gas. The cap ensures the process remains a carbonization reaction rather than an incineration.
Retaining Volatile Intermediates
Glycine decomposes into various volatile gases before solidifying into carbon. The cap traps these intermediates within the crucible for a longer duration. This retention allows these gases to participate further in the reaction rather than escaping immediately into the furnace exhaust.
Impact on Chemical Composition
Optimizing Carbonization Yield
The combination of oxygen restriction and volatile retention directly impacts the efficiency of the process. By keeping the reactants contained and preventing burn-off, the capped system significantly increases the final mass yield of the carbon-based material.
Guiding Compound Formation
The specific atmospheric conditions created by the cap influence the molecular structure of the product. The environment promotes the formation of specific carbon-nitrogen compounds. Notably, it facilitates the synthesis of diazetidinedione isomers, which might not form in an open or fully inert environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Static vs. Dynamic Atmosphere
While the capped crucible offers control, it relies on a "static air" furnace setup. This is distinct from systems that use active gas flow (like Nitrogen or Argon). The "semi-closed" nature means the atmosphere is self-generated by the decomposing sample, which is efficient but less tunable than active gas flow systems.
Precision Limitations
The seal of a crucible lid is mechanical and can vary slightly between runs. This means the "leak rate" of volatiles can fluctuate. While sufficient for producing diazetidinedione isomers, it may lack the absolute reproducibility of a sealed reactor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Synthesis
To apply this to your own material production, consider your specific chemical targets:
- If your primary focus is maximizing yield: Ensure the lid fits securely to minimize the loss of carbon through oxidation and volatile escape.
- If your primary focus is chemical specificity: Use the capped method to promote the formation of complex C-N structures like diazetidinedione isomers, which require a rich, semi-contained atmosphere.
The capped alumina crucible is not just a container; it is an active component in shaping the thermodynamic environment of your reaction.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Glycine Pyrolysis | Benefit to Carbon Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Alumina Material | High thermal shock resistance & chemical inertness | Prevents contamination and vessel cracking at 550°C |
| Crucible Cap | Creates a semi-closed microenvironment | Restricts oxygen to prevent combustion/incineration |
| Volatile Retention | Traps decomposition gases within the crucible | Facilitates formation of specific carbon-nitrogen compounds |
| Atmosphere Control | Self-generated static atmosphere | Increases carbonization yield and ensures structural integrity |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Ready to achieve superior carbonization yields and precise chemical compositions? Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with premium alumina labware. Whether you need standard equipment or a fully customizable furnace for unique high-temperature pyrolysis needs, our experts are here to support your laboratory's success.
Contact KINTEK Today to Find Your Perfect Lab Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Pedro Chamorro‐Posada, Pablo Martín‐Ramos. On a Composite Obtained by Thermolysis of Cu-Doped Glycine. DOI: 10.3390/c10020049
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a condensation crystallizer in a magnesium vapor recovery system? Master Purification & Yield
- What role does specialized graphite adhesive play? Expert Bonding Solutions for High-Temp Systems
- Where are water circulating vacuum pumps commonly used? Essential for Lab and Industrial Vapor Handling
- Why is the precision of a Mass Flow Controller (MFC) critical for ethanol vapor detection? Master Accurate Gas Mixing
- What is the function of a laboratory pellet press in PCM preparation? Optimize Building Energy Storage Materials
- How does a heating stage contribute to the quality of multi-material 3D printing? Optimize Precision and Stability
- How do dense-walled crucibles function during the high-temperature melting of bismuth-lead-borosilicate glass?
- Why is an alumina crucible necessary for g-C3N4 synthesis? Ensure High Purity & Stability in Polycondensation


















