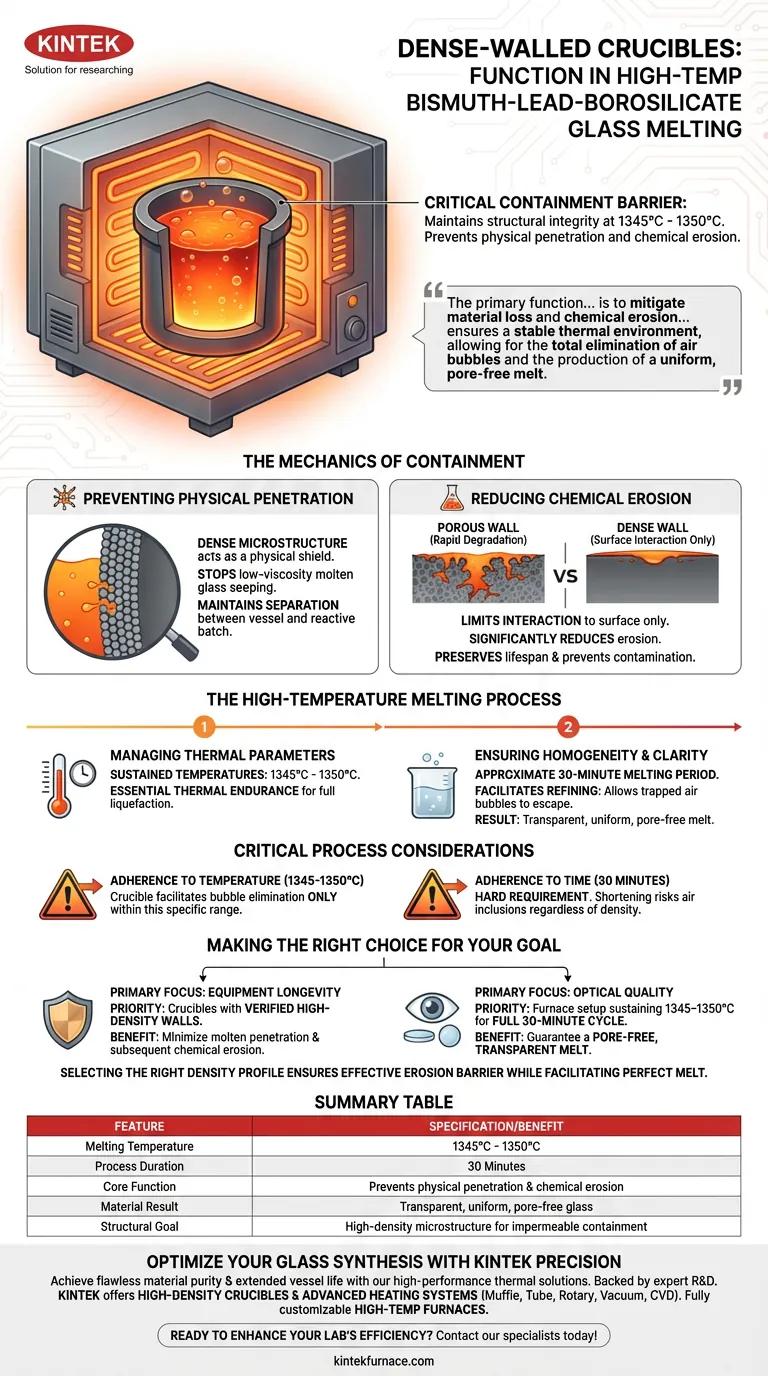
Dense-walled crucibles act as the critical containment barrier during the high-temperature synthesis of bismuth-lead-borosilicate glass. These vessels maintain their structural integrity inside automatic furnaces at temperatures between 1345°C and 1350°C, specifically functioning to prevent the molten glass from physically penetrating the vessel walls. By blocking this penetration, the crucible minimizes chemical erosion and allows the mixture to liquefy completely over a 30-minute period.
The primary function of a dense-walled crucible is to mitigate material loss and chemical erosion by creating an impermeable interface against molten glass. This containment ensures a stable thermal environment, allowing for the total elimination of air bubbles and the production of a uniform, pore-free melt.
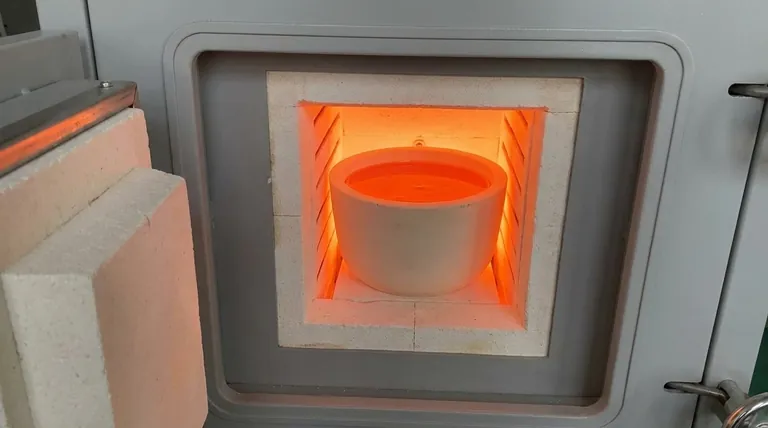

The Mechanics of Containment
Preventing Physical Penetration
The defining characteristic of these crucibles is their dense microstructural composition.
This high density acts as a physical shield, stopping the low-viscosity molten glass from seeping into the crucible's pores.
By preventing this infiltration, the crucible maintains a distinct separation between the vessel material and the reactive glass batch.
Reducing Chemical Erosion
When molten glass penetrates a crucible's wall, it increases the surface area available for chemical attack, leading to rapid degradation.
The dense walls of these crucibles effectively limit this interaction to the surface only.
This significantly reduces chemical erosion, preserving the crucible's lifespan and preventing the contamination of the glass batch with crucible material.
The High-Temperature Melting Process
Managing Thermal Parameters
The crucible must withstand a precise and aggressive temperature window.
The process requires the vessel to hold raw materials at sustained temperatures ranging from 1345°C to 1350°C.
This thermal endurance is necessary to transition the raw batch into a fully liquid state.
Ensuring Homogeneity and Clarity
The function of the crucible extends beyond simple holding; it facilitates the refining of the glass.
During an approximate 30-minute melting period, the stable environment provided by the crucible allows trapped air bubbles to escape.
The result is a transparent, uniform, and pore-free glass melt, essential for high-quality bismuth-lead-borosilicate applications.
Critical Process Considerations
Adherence to Time and Temperature
While the dense walls provide protection, the quality of the final glass is strictly dependent on process parameters.
The crucible can only facilitate bubble elimination if the specific temperature range (1345–1350°C) is maintained.
Furthermore, the 30-minute duration is a hard requirement; shortening this window risks leaving air inclusions in the melt, regardless of the crucible's density.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your glass melting process, consider your primary objective when evaluating crucible performance:
- If your primary focus is Equipment Longevity: Prioritize crucibles with verified high-density walls to minimize molten penetration and subsequent chemical erosion.
- If your primary focus is Optical Quality: Ensure your furnace setup can sustain the vessel at 1345–1350°C for the full 30-minute cycle to guarantee a pore-free, transparent melt.
Selecting the right density profile ensures your crucible serves as an effective barrier against erosion while facilitating the perfect melt.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Specification/Benefit |
|---|---|
| Melting Temperature | 1345°C - 1350°C |
| Process Duration | 30 Minutes |
| Core Function | Prevents physical penetration & chemical erosion |
| Material Result | Transparent, uniform, pore-free glass |
| Structural Goal | High-density microstructure for impermeable containment |
Optimize Your Glass Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Achieve flawless material purity and extended vessel life with our high-performance thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-density crucibles and advanced heating systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you need standard lab equipment or a fully customizable high-temp furnace tailored to your unique bismuth-lead-borosilicate glass applications, we provide the technical edge you need.
Ready to enhance your lab’s efficiency? Contact our specialists today to discuss your custom project requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- M. Gopi Krishna, N V Prasad. Characterization of a Novel System of Bismuth Lead Borosilicate Glass Containing Copper. DOI: 10.17485/ijst/v17i9.81
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What information does laboratory XRD provide for Gallium Sulfide? Master GaS Single Crystal Characterization
- What key functions do high-strength graphite molds perform? Optimize Al2O3/TiC Hot Press Sintering Success
- How does a laboratory drying oven contribute to maintaining material activity? Preserve Catalyst Performance Easily
- Why is a U-shaped quartz reactor required for H2-TPR? Ensure Precision for Cu–Ce/HZSM-5 Analysis
- Why is a high vacuum pumping system necessary for carbon nanotube peapods? Achieve Precise Molecular Encapsulation
- What is the primary function of high-purity quartz sealed tubes? Master Sb-Te Alloy Synthesis with Precision Isolation
- What are quartz tubes used for? Essential for High-Temperature, High-Purity Applications
- Why are sealed Niobium (Nb) tubes utilized as reaction vessels during the high-temperature solid-state synthesis of Ba1-xEuxZn2Sb2?


















