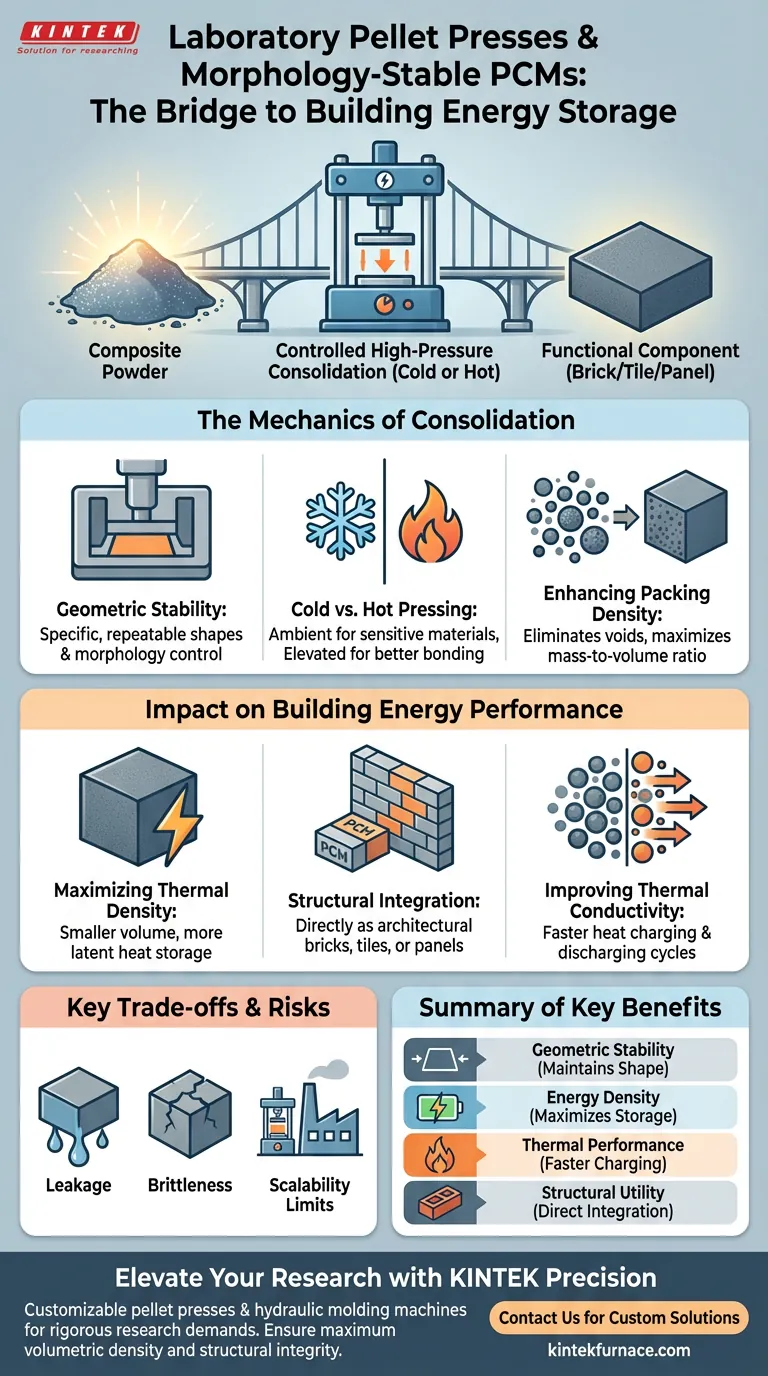
A laboratory pellet press serves as the critical bridge between loose composite powders and functional, structural components for building energy storage. By applying controlled high pressure through cold or hot pressing, these machines consolidate phase change material (PCM) powders into high-density bulk solids with fixed geometries and enhanced mechanical strength.
The core function of a hydraulic molding machine is to maximize the volumetric energy storage density of PCM composites by eliminating voids and ensuring the material can be directly integrated into architectural structures without losing its shape.
The Mechanics of Material Consolidation
Achieving Geometric Stability
The press utilizes specialized molds to force composite powders into specific, repeatable shapes. This process ensures the PCM remains "morphology-stable," meaning it maintains its external dimensions even as the internal components undergo phase transitions from solid to liquid.
Cold vs. Hot Pressing Techniques
Depending on the binder and PCM type, researchers use either ambient temperature (cold) or elevated temperature (hot) pressing. Hot pressing can facilitate better bonding between particles, while cold pressing is often preferred for materials sensitive to thermal degradation during the manufacturing stage.
Enhancing Packing Density
Loose powders contain significant air gaps that reduce the overall thermal efficiency of a storage system. The hydraulic press eliminates these interstitial spaces, significantly increasing the mass-to-volume ratio of the finished pellet or brick.
Impact on Building Energy Performance
Maximizing Volumetric Thermal Density
In building applications, space is a premium commodity. By increasing packing density, the pellet press allows a smaller volume of material to store a larger amount of latent heat, making energy storage systems more compact and efficient.
Integration into Architectural Components
The mechanical strength provided by high-pressure molding allows these composites to function as "structured" components. This means the PCMs can be used directly as bricks, tiles, or panels within a building's envelope rather than requiring secondary encapsulation.
Improving Thermal Conductivity
High-pressure consolidation brings the conductive particles within a composite (such as graphite or metal foams) into closer contact. This reduction in contact resistance allows for faster heat charging and discharging cycles within the building environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Pressure-Induced Leakage
Applying excessive pressure during the molding process can sometimes damage the supporting matrix of the composite. If the matrix is compromised, the PCM may leak out during subsequent melting cycles, leading to structural failure and loss of thermal capacity.
Mechanical Brittleness
While pressing increases density, it can also make the resulting pellets brittle. If the compaction force is not optimized, the material may develop micro-cracks that expand during the thermal expansion and contraction cycles typical of building environments.
Scalability Limits
Laboratory pellet presses are designed for precision and small-batch testing. Translating the exact pressure profiles and material densities achieved in a lab setting to industrial-scale manufacturing requires careful calibration to maintain the same morphology-stable characteristics.
Applying This Process to Your Research
When utilizing a hydraulic molding machine for PCM preparation, your technical approach should vary based on your specific performance targets.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy capacity: Focus on optimizing the compaction pressure to achieve the highest possible packing density without compromising the structural integrity of the supporting matrix.
- If your primary focus is structural integration: Prioritize the hot pressing method and specific mold geometries to ensure the resulting blocks meet the mechanical load-bearing requirements of architectural standards.
- If your primary focus is rapid thermal response: Use the press to consolidate composites with high concentrations of thermal conductivity enhancers, ensuring the pressure is sufficient to create a continuous conductive network.
Mastering the consolidation of PCM powders is the definitive step in transforming raw chemical potential into a durable, high-performance building material.
Summary Table:
| Function Category | Key Benefit | Technical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric Stability | Morphology Control | Maintains shape during phase transitions and solid-liquid cycles. |
| Energy Density | Packing Optimization | Eliminates air gaps to maximize volumetric latent heat storage. |
| Thermal Performance | Enhanced Conductivity | Reduces contact resistance between particles for faster charging. |
| Structural Utility | Mechanical Strength | Enables direct integration into architectural tiles, panels, or bricks. |
Elevate Your PCM Research with KINTEK Precision
Transform your composite powders into high-performance, morphology-stable materials with KINTEK’s industry-leading laboratory solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers customizable pellet presses, hydraulic molding machines, and high-temp vacuum systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of building energy storage research.
Whether you require precise pressure control for cold pressing or integrated heating for advanced consolidation, our equipment ensures maximum volumetric density and structural integrity for your unique materials. Unlock the full potential of your lab's thermal storage innovations—contact us today to find your custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Yuan Jia, Yushi Liu. Recent advances in energy storage and applications of form‐stable phase change materials with recyclable skeleton. DOI: 10.1002/cnl2.117
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do the quartz crucible and descending device function in Bridgman method? Precision Growth for CsPbBr3 Crystals
- What is the role of an optical pyrometer in diffusion bonding? Ensure Precision in High-Temperature Simulations
- Why is a high-purity graphite box required for CZTS sulfurization? Protect Thin Film Integrity and Crystallinity
- What are the limitations of ultra-pure alumina porcelain tubes? Manage Brittleness for Reliable High-Temp Use
- Why are laboratory heating and stirring devices necessary for Pechini and sol-gel synthesis? Ensure Precise Homogeneity
- What role does a high-purity Graphite Crucible play in super-gravity zinc recovery? Key Benefits & Functions
- What role does a Molybdenum Boat play in ZTO thin film deposition? Master Thermal Evaporation Success
- What are the primary functions of the vacuum pump system and inert gases? Achieve High-Purity Atomization














