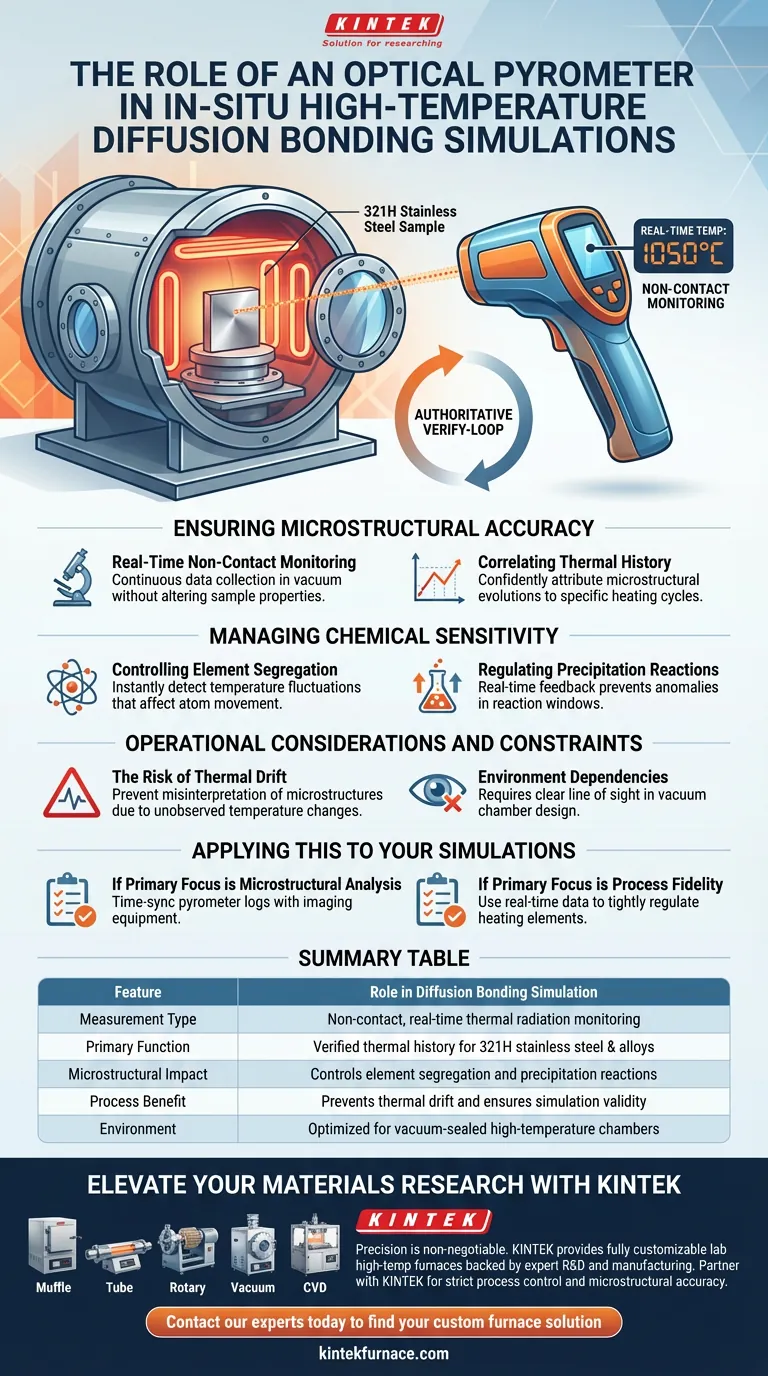
The primary function of an optical pyrometer in this context is to provide precise, non-contact, real-time temperature monitoring of samples, such as 321H stainless steel, situated within vacuum equipment. By constantly measuring the surface temperature without physical contact, it acts as the authoritative verify-loop for the thermal conditions during the simulation.
Because diffusion bonding involves highly sensitive element segregation and precipitation reactions, the optical pyrometer is critical for ensuring that any observed microstructural changes are the direct result of a specifically verified thermal history.
Ensuring Microstructural Accuracy
Real-Time Non-Contact Monitoring
In-situ simulations often take place in vacuum environments where physical thermocouples may be impractical or intrusive. An optical pyrometer solves this by measuring thermal radiation from a distance.
This allows for continuous data collection on the 321H stainless steel samples without altering their physical position or surface properties.
Correlating Thermal History
The validity of a simulation depends on knowing exactly what temperature the sample experienced and for how long. The pyrometer creates a precise record of the thermal history.
This ensures that the microstructural evolutions observed by researchers can be confidently attributed to the specific heating cycle applied.
Managing Chemical Sensitivity
Controlling Element Segregation
Diffusion bonding is a process driven by the movement of atoms. The segregation of specific elements within the steel is highly sensitive to thermal changes.
If the temperature deviates even slightly, the rate and nature of segregation change. The pyrometer detects these fluctuations instantly, allowing for strict process control.
Regulating Precipitation Reactions
Similar to segregation, precipitation reactions are dictated by precise temperature windows.
The real-time feedback from the pyrometer ensures these reactions occur exactly as intended, preventing anomalies that could skew the simulation results.
Operational Considerations and Constraints
The Risk of Thermal Drift
Because the chemical reactions involved are so sensitive, any failure in monitoring can render a simulation invalid.
Without the real-time feedback loop provided by the pyrometer, unobserved thermal drift could lead researchers to misinterpret why specific microstructures formed.
Environment Dependencies
While powerful, the optical pyrometer relies on a clear line of sight within the vacuum equipment.
It is strictly an observational tool; it ensures accuracy but requires the vacuum chamber design to accommodate non-contact optical paths.
Applying This to Your Simulations
To ensure your high-temperature simulations yield valid scientific data, focus on how you utilize thermal telemetry.
- If your primary focus is microstructural analysis: Ensure your pyrometer logs are time-synced with your imaging equipment to correlate specific structural changes to exact temperatures.
- If your primary focus is process fidelity: Use the real-time data to tightly regulate the heating elements, minimizing thermal fluctuations that trigger unwanted element segregation.
Precise thermal monitoring is the only way to guarantee that your simulation results truly reflect the physics of the diffusion bonding process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Diffusion Bonding Simulation |
|---|---|
| Measurement Type | Non-contact, real-time thermal radiation monitoring |
| Primary Function | Verified thermal history for 321H stainless steel & alloys |
| Microstructural Impact | Controls element segregation and precipitation reactions |
| Process Benefit | Prevents thermal drift and ensures simulation validity |
| Environment | Optimized for vacuum-sealed high-temperature chambers |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable in diffusion bonding and high-temperature simulations. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions backed by expert R&D and manufacturing. Whether you require Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research needs.
Don't let thermal drift compromise your results. Partner with KINTEK to achieve the strict process control and microstructural accuracy your project demands. Contact our experts today to find your custom furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Isac Lazar, Filip Lenrick. Diffusion Bonding 321-Grade Stainless Steel: Failure and Multimodal Characterization. DOI: 10.1093/mam/ozae019
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory drying oven contribute to the preparation of C@TiC/SiO2 xerogels? Ensure Structural Integrity
- Why is a cylindrical mold made of SS400 steel utilized for slag casting experiments? Explained
- What role does a heated substrate platform play in the spray pyrolysis deposition? Optimize Your Thin Film Quality
- Why is molybdenum (Mo) selected as the crucible material for the evaporation of NiO-doped Ga2O3? Expert Insights
- What are the specific functions of a magnetic stirrer and a condenser reflux apparatus in the synthesis of KCC-1? Expert Insights
- What is the function of a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave in the hydrothermal synthesis of Bi2O3 precursors?
- What are the primary functions of the vacuum pump system and inert gases? Achieve High-Purity Atomization
- What are the typical size ranges available for quartz tubes used in laboratory furnaces? Find Your Perfect Fit for High-Temp Applications







