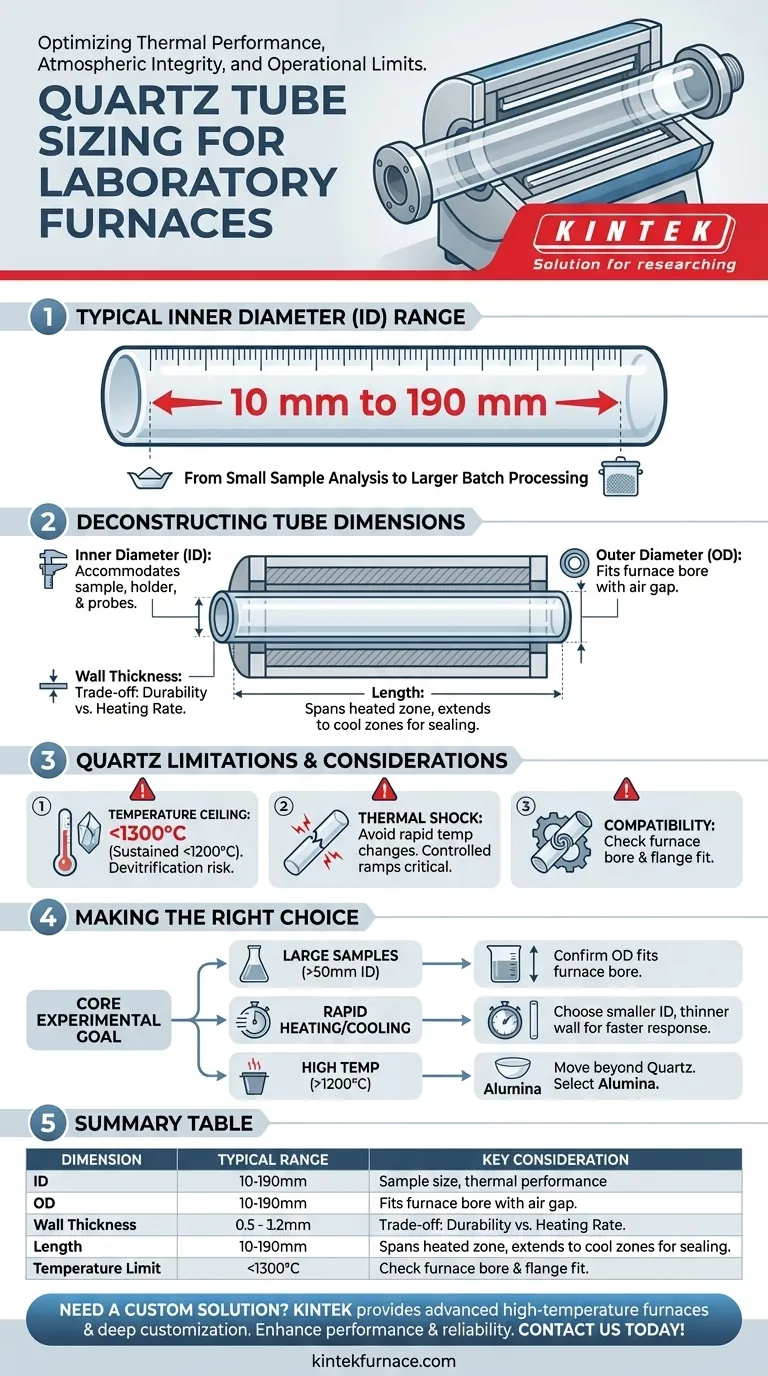
When specifying a quartz tube for a laboratory furnace, the most common dimension you will encounter is the inner diameter. For typical laboratory-scale tube furnaces, quartz work tubes are readily available with inner diameters ranging from 10 mm to 190 mm. This range accommodates everything from small-scale sample analysis to larger batch processing, but the diameter is only one part of the equation.
Selecting the right quartz tube is not merely about fitting your sample. It's a critical decision that directly impacts thermal performance, atmospheric integrity, and the operational limits of your entire experimental setup.

Deconstructing Quartz Tube Dimensions
While inner diameter is the primary metric, a complete specification involves several interconnected dimensions that determine the tube's suitability for a given furnace and application.
Inner Diameter (ID)
The inner diameter is the clear opening inside the tube. This dimension must be large enough to accommodate your sample, sample holder (or "boat"), and any necessary thermocouple probes.
Outer Diameter (OD)
The outer diameter dictates whether the tube will fit inside the bore of your furnace. It's crucial to ensure a small air gap exists between the tube's OD and the furnace insulation for proper placement and to prevent stress.
Wall Thickness
Wall thickness (the difference between OD and ID, halved) is a trade-off between durability and thermal performance. Thicker walls offer greater mechanical strength and are better for vacuum applications, but they also increase thermal mass, slowing down heating and cooling rates.
Length
The tube's length must be sufficient to span the entire heated zone of the furnace. It also needs to extend well into the cool zones on either end to allow for safe handling, gas fittings, and sealing flanges.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Limits of Quartz
Quartz is a popular choice for its high purity and excellent thermal properties, but it is not without limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for experimental success and safety.
The Temperature Ceiling
Quartz is only suitable for processing at temperatures below 1300°C. For sustained use, it's wise to stay below 1200°C to prevent devitrification—a process where the amorphous quartz crystallizes, becoming brittle and opaque.
Thermal Shock Sensitivity
Despite its good thermal properties, quartz can crack if subjected to extremely rapid or uneven temperature changes. Controlled heating and cooling ramps are critical, especially with larger or thicker-walled tubes.
Furnace and Flange Compatibility
A tube is only useful if it integrates with your system. You must confirm that the tube's outer diameter fits your furnace and that appropriate sealing flanges are available for that specific OD to create a controlled atmosphere or vacuum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your core experimental goal to guide your selection.
- If your primary focus is processing larger samples: Opt for a tube with a larger inner diameter (e.g., >50 mm), but first confirm its OD is compatible with your furnace bore.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and cooling: Choose a smaller diameter tube with a thinner wall to minimize thermal mass and achieve faster thermal response.
- If your primary focus is working above 1200°C: You must move beyond quartz and select a tube made from a different ceramic, such as high-purity alumina.
By considering these factors beyond simple diameter, you ensure your equipment is a perfect match for your scientific goals.
Summary Table:
| Dimension | Typical Range | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Inner Diameter (ID) | 10 mm to 190 mm | Accommodates sample size and accessories; affects thermal performance |
| Outer Diameter (OD) | Varies with ID | Must fit furnace bore with small air gap for proper placement |
| Wall Thickness | Depends on OD and ID | Trade-off between durability (thicker) and faster heating (thinner) |
| Length | Customizable | Must span heated zone and extend to cool zones for safety and fittings |
| Temperature Limit | Up to 1300°C (sustained use below 1200°C) | Avoids devitrification and brittleness; consider alumina for higher temps |
Need a custom quartz tube or furnace solution tailored to your lab's unique requirements? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your experimental needs, enhancing performance and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your setup!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















