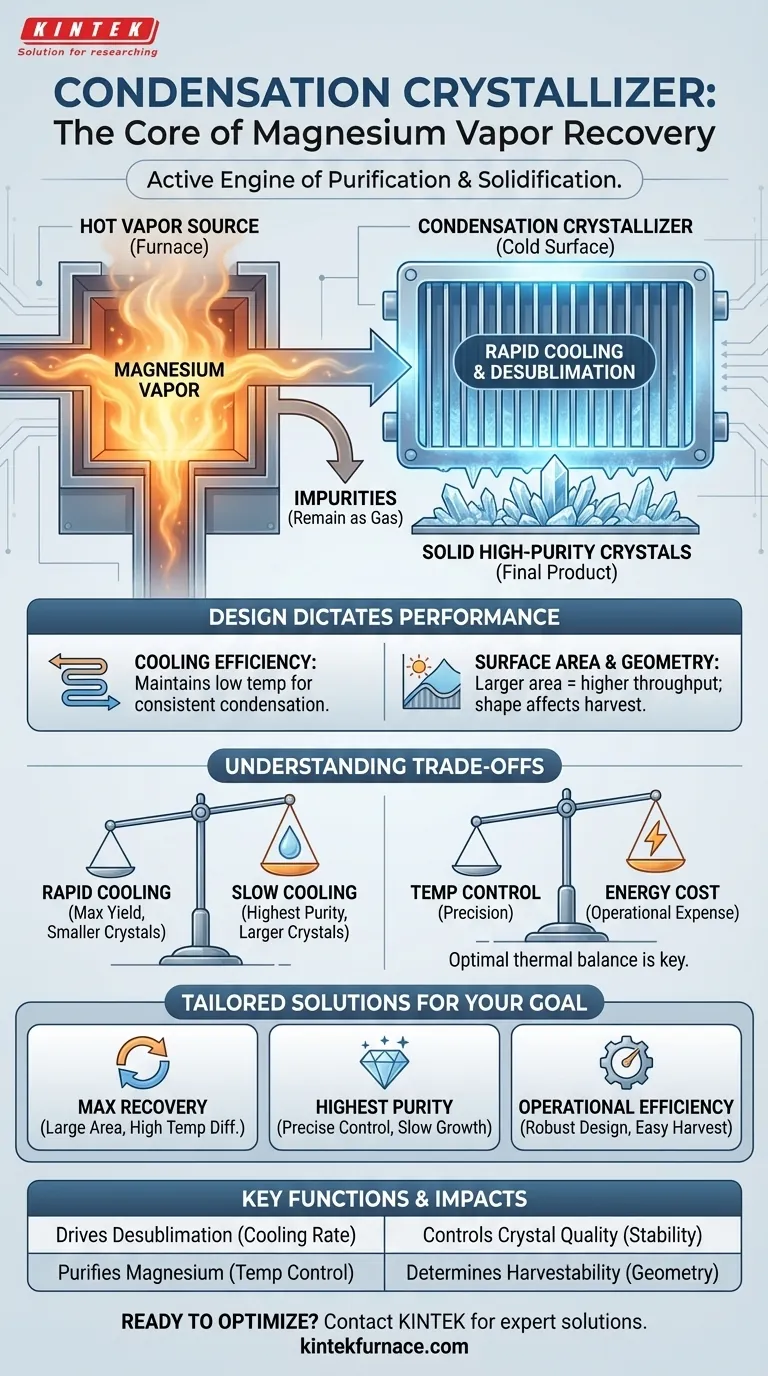
In any magnesium vapor recovery system, the condensation crystallizer serves one primary purpose. It provides a precisely controlled, low-temperature surface where hot, purified magnesium vapor rapidly cools and transforms from a gas directly into solid, high-purity crystals. This component acts as the designated collection point for the final metallic product.
The crystallizer is not merely a passive collection plate; it is the active engine of purification and solidification. By managing the temperature difference between the hot vapor and its cool surface, it dictates the efficiency of magnesium recovery and the quality of the final crystalline product.

The Core Principle: Driving a Phase Change
The entire process hinges on controlling the physical state of the magnesium. The crystallizer's function is to force a specific, highly desirable phase change from gas to solid.
From Hot Vapor to Solid Metal
Inside the furnace, raw magnesium-containing material is heated under vacuum, causing the pure magnesium to turn into a high-temperature vapor. This vapor is less dense than the surrounding atmosphere, so it rises.
The Role of a Cold Surface
The condensation crystallizer is strategically placed in the path of this rising vapor. It is actively cooled to maintain a temperature significantly lower than that of the magnesium gas.
Condensation and Desublimation
When the hot vapor molecules make contact with this cold surface, they lose thermal energy almost instantly. This rapid cooling forces them to condense from a gaseous state directly into a solid state, a process known as desublimation. This bypass of the liquid phase is critical for forming a crystalline structure.
Crystal Growth and Purification
As the pure magnesium deposits onto the crystallizer, it begins to grow into a solid mass of crystals. Impurities with different boiling points or vapor pressures tend to remain in the gaseous phase and are not collected, making this a crucial step in the purification process.
How Design Dictates Performance
The physical design and operational parameters of the crystallizer directly impact the success of the entire recovery operation. Its efficiency is not an accident; it is an engineered outcome.
Cooling Efficiency
The ability to consistently remove heat and maintain a low surface temperature is the most critical factor. This is often achieved with internal water or external air-cooling systems. Inefficient cooling leads to lower recovery rates because some magnesium vapor will fail to condense.
Surface Area and Geometry
A larger surface area provides more space for condensation to occur, directly influencing the throughput of the system. The geometry of the crystallizer also affects how the magnesium crystals grow and how easily they can be harvested after the process is complete.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing a crystallizer involves balancing competing priorities. The ideal setup depends entirely on the desired outcome for the final product.
Cooling Rate vs. Crystal Quality
A very rapid cooling rate (a large temperature difference) will maximize the amount of magnesium recovered. However, this can result in smaller, less dense crystals. A slower, more controlled cooling process often yields larger, higher-purity crystals but may slightly reduce the overall recovery rate.
Temperature Control vs. Energy Cost
Maintaining a significant temperature difference is an energy-intensive process. Over-cooling the crystallizer is wasteful and increases operational costs, while under-cooling directly harms the recovery efficiency. Finding the optimal thermal balance is key to economic viability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The operation of the crystallizer should be tailored to your specific production objectives.
- If your primary focus is maximum recovery rate: Prioritize a large surface area and a significant temperature differential to capture as much vapor as possible, even if it sacrifices crystal size.
- If your primary focus is highest product purity: Emphasize precise and stable temperature control to promote slower, more selective crystal growth that leaves impurities behind.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Choose a simple, robust crystallizer design that balances a high recovery rate with ease of harvesting and minimal maintenance downtime.
Ultimately, mastering the function of the condensation crystallizer is the key to controlling both the quantity and quality of your recovered magnesium.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Factor | Impact on Recovery |
|---|---|---|
| Drives Desublimation | Cooling Rate & Surface Temperature | Dictates the rate of vapor-to-solid transformation. |
| Purifies Magnesium | Temperature Control | Selectively condenses pure Mg, leaving impurities in vapor phase. |
| Controls Crystal Quality | Cooling Rate & Stability | Influences crystal size, density, and purity. |
| Determines Harvestability | Crystallizer Geometry & Surface Area | Affects how easily the final solid product is collected. |
Ready to optimize your magnesium vapor recovery system? The condensation crystallizer is the heart of your process, dictating purity, yield, and efficiency. At KINTEK, our expertise in high-temperature vacuum systems translates directly into designing and manufacturing crystallizers and furnaces tailored to your specific goals—whether maximum recovery, highest purity, or operational efficiency. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable for unique needs.
Let's engineer your solution. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection



















