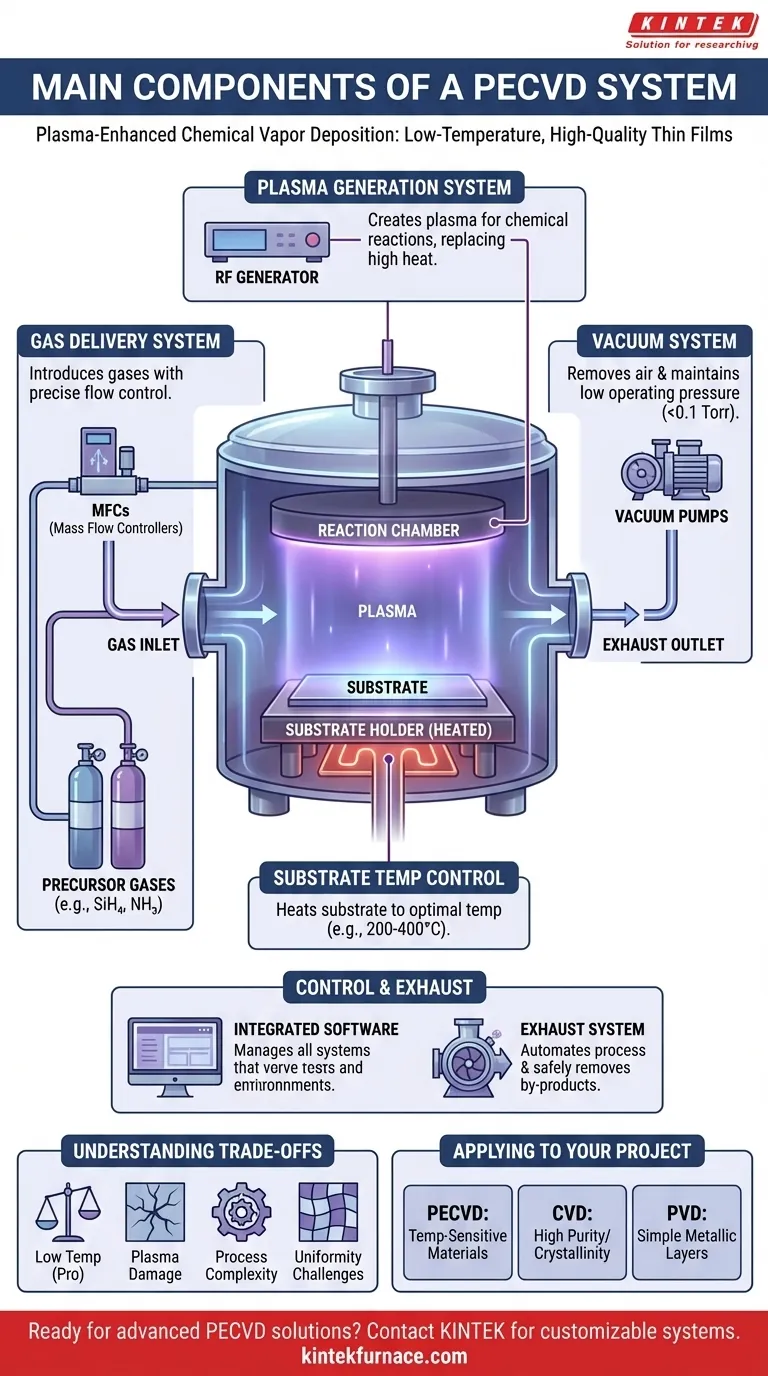
At its core, a Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) system is built around four primary functional units. These are a vacuum-sealed reaction chamber, a precise gas delivery system, a vacuum system to control pressure, and a power source to generate the plasma that defines the process. These components work in concert to deposit high-quality thin films at significantly lower temperatures than traditional CVD methods.
The crucial insight is that PECVD augments a standard deposition system with a plasma generator. This use of plasma, rather than high heat, to drive chemical reactions is what allows for the processing of temperature-sensitive materials.

How Each Component Contributes to Deposition
To understand a PECVD system is to understand the specific role each part plays in creating a controlled, plasma-driven chemical reaction.
The Reaction Chamber
The reaction chamber is the sealed environment where the entire deposition process occurs. It is designed to hold a vacuum and contain the plasma.
Inside the chamber, a substrate holder, often referred to as a platen or chuck, positions the material to be coated. In many designs, this holder also functions as one of the system's electrodes.
The Gas Delivery System
This system introduces reactive precursor gases into the chamber with extreme precision. The goal is to create a specific, repeatable chemical environment.
Gases like silane (SiH₄) or ammonia (NH₃) are managed by mass flow controllers (MFCs). These devices ensure the exact volume of each gas enters the chamber, which is critical for controlling the final film's chemical composition.
The Vacuum System
The vacuum system, composed of one or more vacuum pumps, serves two functions. First, it removes ambient air to create a highly pure, low-pressure environment before deposition begins.
Second, it maintains a specific, low operating pressure (often below 0.1 Torr) during the process. This low pressure is essential for sustaining a stable plasma and ensuring a long mean free path for gas molecules.
The Plasma Generation System
This is the defining component of PECVD. It consists of electrodes inside the chamber and an external power source, which is typically a Radio Frequency (RF) generator.
When the RF power is applied to the electrodes, it creates a powerful electric field. This field excites the precursor gas molecules, stripping electrons and creating a highly reactive mixture of ions, electrons, and neutral species known as a plasma. This plasma provides the energy for the chemical reactions, replacing the need for very high temperatures.
Substrate Temperature Control
While PECVD is a low-temperature process, precise temperature control is still vital. The substrate holder is almost always equipped with a heating mechanism.
This allows the substrate to be held at an optimal, moderately elevated temperature (e.g., 200-400°C). This thermal energy influences film density, adhesion, and stress without damaging sensitive substrates.
Control and Exhaust
Modern PECVD systems are managed by integrated software that controls gas flow, pressure, RF power, and temperature. This allows for complex, multi-step recipes and process ramping. An exhaust system then safely removes unreacted precursor gases and reaction by-products from the chamber.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the PECVD process involves inherent compromises that are important to recognize for any application.
Temperature vs. Film Quality
The primary benefit of PECVD is its low deposition temperature. However, films deposited at lower temperatures can sometimes have lower density or incorporate more hydrogen compared to films from high-temperature conventional CVD. The energy from the plasma compensates for the lack of thermal energy, but the resulting film microstructure may differ.
Plasma-Induced Damage
The high-energy ions within the plasma can bombard the substrate surface. While this bombardment can be beneficial for film densification, it also has the potential to create defects or damage in the underlying substrate, particularly with sensitive electronic materials.
Process Complexity
The addition of plasma introduces more process variables than in standard CVD or PVD. Parameters like RF power, frequency, pressure, and gas chemistry must be carefully optimized and controlled, adding a layer of complexity to process development.
Uniformity Challenges
Achieving a perfectly uniform film thickness and composition across a large substrate can be difficult. It is highly dependent on the design of the chamber, the electrode configuration, and the gas flow dynamics.
Applying This to Your Project
Your choice of deposition technology should always be driven by the specific requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive materials (like polymers or pre-processed electronics): PECVD is the superior choice because its plasma-driven chemistry avoids the high heat that would cause damage.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity and crystallinity for bulk materials: Conventional high-temperature CVD may be a better option, as the thermal energy can produce highly ordered crystal structures.
- If your primary focus is depositing a simple metallic layer with line-of-sight coverage: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) methods like sputtering or evaporation are often more direct and cost-effective.
By understanding how these components interact, you can effectively diagnose issues and manipulate the process to achieve your desired thin-film properties.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Reaction Chamber | Sealed environment for deposition | Holds vacuum, contains plasma, includes substrate holder |
| Gas Delivery System | Introduces precursor gases | Uses mass flow controllers for precise gas control |
| Vacuum System | Maintains low-pressure environment | Comprises vacuum pumps for purity and plasma stability |
| Plasma Generation System | Generates plasma for reactions | Includes electrodes and RF power source |
| Substrate Temperature Control | Manages substrate temperature | Heating mechanisms for optimal film properties |
| Control and Exhaust | Oversees process and removes by-products | Integrated software and exhaust systems |
Ready to elevate your thin film deposition with advanced PECVD solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions like CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for temperature-sensitive materials. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored PECVD systems can enhance your research and production efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection



















